Abstract
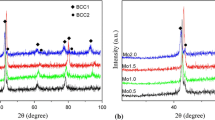
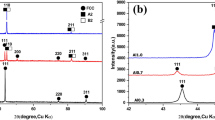
A high-entropy alloy coating of AlCoCrFeNi was prepared by plasma spraying and then remelted via laser remelting. The effect of laser remelting on the microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance of the AlCoCrFeNi coating was investigated. Particularly, the effect of surface free energy on the wear resistance of the coatings before and after remelting was explored. The results showed that the remelted AlCoCrFeNi coating retained the same single BCC solid solution structure as the as-sprayed AlCoCrFeNi coating. Besides, the defects in the coating were basically eliminated by laser remelting, leading to the porosity of the coating decreased from 4.8 to only 0.3%. Consequently, the hardness, elastic modulus and fracture toughness of the coating were enhanced by 38%, and the wear loss of the remelted AlCoCrFeNi coating was only 22% of that of the as-sprayed one. Therefore, laser remelting is a feasible method to improve the microstructure and enhance the wear resistance of the AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.G. Ma and Y. Zhang, Effect of Nb Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 532, p 480–486.
Y. Geng, J. Chen, H. Tan, J. Cheng, and W. Liu, Vacuum Tribological Behaviors of CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy at Elevated Temperatures, Wear, 2020, 456–457, p 203368.
Y. Yu, J. Wang, J. Yang, Z.H. Qiao, H.T. Duan, J.S. Li, J. Li, and W.M. Liu, Corrosive and Tribological Behaviors of AlCoCrFeNi-M High Entropy Alloys Under 90 wt.% H2O2 Solution, Tribol. Int., 2019, 131, p 24–32.
J. Dabrowa, G. Cieslak, M. Stygar, K. Mroczka, K. Berent, T. Kulik, and M. Danielewski, Influence of Cu Content on High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of AlCoCrCuxFeNi High Entropy Alloys (x=0; 0.5; 1), Intermetallics, 2017, 84, p 52–61.
Y.Y. Chen, T. Duval, U.D. Hung, J.W. Yeh, and H.C. Shih, Microstructure and Electrochemical Properties of High Entropy Alloys—A Comparison with type-304 Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2005, 47(9), p 2257–2279.
Z.Z. Niu, Y.Z. Wang, C. Geng, J. Xu, and Y. Wang, Microstructural Evolution, Mechanical and Corrosion Behaviors of as-Annealed CoCrFeNiMox (x=0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1) High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2020, 820, p 153273.
W. Zhang, R. Tang, Z.B. Yang, C.H. Liu, H. Chang, J.J. Yang, J.L. Liao, Y.Y. Yang, and N. Liu, Preparation, Structure, and Properties of an AlCrMoNbZr High-Entropy Alloy Coating for Accident-Tolerant Fuel Cladding, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2018, 347, p 13–19.
S. Zhao, L.X. He, X.X. Fan, C.H. Liu, J.P. Long, L. Wang, H. Chang, J. Wang, and W. Zhang, Microstructure and Chloride Corrosion Property of Nanocrystalline AlTiCrNiTa High Entropy Alloy Coating on X80 Pipeline Steel, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2019, 375, p 215–220.
P. Shi, Y. Yu, N. Xiong, M. Liu, and Q. Wang, Microstructure and Tribological Behavior of a Novel Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy Matrix Self-Lubricating Composite Coatings, Tribol. Int., 2020, 151, p 106470.
L.H. Tian, W. Xiong, C. Liu, S. Lu, and M. Fu, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Atmospheric Plasma-Sprayed AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25(12), p 5513–5521.
H.L. Wang, Q.B. Liu, Y.X. Guo, and H.W. Lan, MoFe1.5CrTiWAlNbx Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding, Intermetallics, 2019, 115, p 106613.
Y. Tian, C.Y. Lu, Y.F. Shen, and X.M. Feng, Microstructure and Corrosion Property of CrMnFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy Coating on Q235 Substrate via Mechanical Alloying Method, Surf. Interfaces, 2019, 15, p 135–140.
X.R. Wang, Z.Q. Wang, T.S. Lin, and P. He, Mass Transfer Trends of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings on TC11 Substrate via Electrospark Computer Numerical Control Deposition, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, 241, p 93–102.
A. Anupam, R.S. Kottada, S. Kashyap, A. Meghwal, B.S. Murty, C.C. Berndt, and A.S.M. Ang, Understanding the Microstructural Evolution of High Entropy Alloy Coatings Manufactured by Atmospheric Plasma Spray Processing, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 505, p 144117.
Y.K. Mu, L.B. Zhang, L. Xu, K. Prashanth, N.Z. Zhang, X.D. Ma, Y.F. Jia, Y.L. Xu, Y.D. Jia, and G. Wang, Frictional Wear and Corrosion Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Synthesized by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying, Entropy, 2020, 22(7), p 740.
A.S.M. Ang, C.C. Berndt, M.L. Sesso, A. Anupam, S. Praveen, R.S. Kottada, and B.S. Murty, Plasma-Sprayed High Entropy Alloys: Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi and MnCoCrFeNi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46(2), p 791–800.
C.M. Wang, J.X. Yu, Y. Zhang, and Y. Yu, Phase Evolution and Solidification Cracking Sensibility in Laser Remelting Treatment of the Plasma-Sprayed CrMnFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy Coating, Mater Design., 2019, 182, p 108040.
Z.B. Cai, X.F. Cui, Z. Liu, Y. Li, M.L. Dong, and G. Jin, Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladded Ni-Cr-Co-Ti-V High-Entropy Alloy Coating After Laser Remelting Processing, Opt. Laser Technol., 2018, 99, p 276–281.
N.N. Li, G.L. Li, H.D. Wang, J.J. Kang, T.S. Dong, and H.J. Wang, Influence of TiO2 Content on the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cr2O3-Based Coating, Mater. Design., 2015, 88, p 906–914.
D.Y. Kwok, and A.W. Neumann, Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation Advances in Colloid and Interface Science., 1999, 81(3), p 167.
D. Li, and A.W. Neumann, Contact Angles on Hydrophobic Solid Surfaces and Their Interpretation, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1992, 148(1), p 190.
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, 61, p 15–22.
Y. Jien-Wei, Alloy Design Strategies and Future Trends in High-Entropy Alloys, Jom-Us, 2013, 65(12), p 1759.
G. Jin, Z.B. Cai, Y.J. Guan, X.F. Cui, Z. Liu, Y. Li, M.L. Dong, and D. Zhang, High Temperature Wear Performance of Laser-Cladded FeNiCoAlCu High-Entropy Alloy Coating, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 445, p 113.
W. Ji, Z.Y. Fu, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, J.Y. Zhang, Y.C. Wang, and F. Zhang, Mechanical Alloying Synthesis and Spark Plasma Sintering Consolidation of CoCrFeNiAl High-Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy Compd., 2014, 589, p 61–66.
Y.P. Wang, B.S. Li, M.X. Ren, C. Yang, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Compressive Properties of AlCrFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 491(1–2), p 154–158.
M. Vaidya, A. Prasad, A. Parakh, and B.S. Murty, Influence of Sequence of Elemental Addition on Phase Evolution in Nanocrystalline AlCoCrFeNi: Novel Approach to Alloy Synthesis Using Mechanical Alloying, Mater. Design., 2017, 126, p 37–46.
C.Y. Sun, L. Li, M.W. Fu, and Q.J. Zhou, Element Diffusion Model of Bimetallic hot Deformation in Metallurgical Bonding Process, Mater Design., 2016, 94, p 433.
S. Mohanty, T.N. Maity, S. Mukhopadhyay, S. Sarkar, N.P. Gurao, S. Bhowmick, and K. Biswas, Powder Metallurgical Processing of Equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 679, p 299–313.
M. Barlet, J.M. Delaye, T. Charpentier, M. Gennisson, D. Bonamy, T. Rouxel, and C.L. Rountree, Hardness and Toughness of Sodium Borosilicate Glasses via Vickers’s Indentations, J. Non-Crystall. Solids, 2015, 417–418, p 66.
R.D. Dukino, and M.V. Swain, Comparative Measurement of Indentation Fracture Toughness with Berkovich and Vickers Indenters, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 75, p 3299–3304.
Y.M. Liu, J.Y. Shi, Q.Q. Lu, Y.Z. Guo, R.Q. Chen, and D.C. Yin, Research Progress of Solid Surface Energy Calculation Based on Young’s Equation, Mater. Guide, 2013, 027(011), p 123–129. (in Chinese)
Z.Q. Zhang, H.D. Wang, B.S. Xu, and G.S. Zhang, Characterization of Microstructure and Rolling Contact Fatigue Performance of NiCrBSi/WC–Ni Composite Coatings Prepared by Plasma Spraying, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2015, 261, p 60.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51675158). The authors also wish to thank Professor Lijun Yang for his help in laser remelting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Dong, Ts., Fu, Bg. et al. Effect of Laser Remelting on Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 5728–5735 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05806-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05806-0