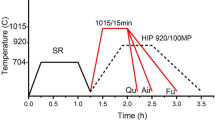
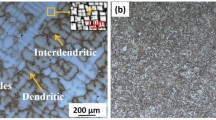
Abstract
In the present study, 5052 Al alloy was processed through different rolling methods to obtain ultrafine grains and its high-cycle fatigue behavior were investigated. The solution-treated Al-Mg alloys (AA 5052) were deformed through different methods such as cryorolling (CR), cryo groove rolling (CGR) and cryo groove rolling followed by warm rolling (CGW), up to 75% thickness reduction. The deformed samples were subjected to mechanical testing such as hardness, tensile and high-cycle fatigue (HCF) test at stress control mode. The CGW samples exhibit better HCF strength when compared to other conditions. The microstructure of the tested samples was characterized by optical microscopy, SEM fractography and TEM to understand the deformation behavior of deformed Al alloy. The improvement in fatigue life of CR and CGR samples is due to effective grain refinement, subgrain formations, and high dislocation density observed in the heavily deformed samples at cryogenic condition as observed from SEM and TEM analysis. However, in case of CGW samples, formation of nanoshear bands accommodates the applied strain during cyclic loading, thereby facilitating dislocation accumulation along with subgrain formations, leading to the high fatigue life. The deformed or broken impurity phase particles found in the deformed samples along with the precipitates that were formed during warm rolling also play a prominent role in enhancing the fatigue strength. These tiny particles hindered the dislocation movement by effectively pinning it at grain boundaries, thereby improving the resistance of crack propagation under cyclic load.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Cavaliere, Fatigue Properties and Crack Behavior of Ultra-Fine and Nanocrystalline Pure Metals, Int. J. Fatigue, 2009, 31, p 1476–1489
N. Hansen, Hall–Petch Relation and Boundary Strengthening, Scripta Mater., 2004, 51, p 801–806
I.F. Mohamed, S. Lee, K. Edalati, Z. Horita, S. Hirosawa, K. Matsuda, and D. Terada, Aging Behavior of Al 6061 Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion and Subsequent Aging, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46, p 2664–2673
A.P. Zhilyaev, K. Oh-Ishi, T.G. Langdon, and T.R. McNelley, Microstructural Evolution in Commercial Purity Aluminum During High-Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 410, p 277–280
B.B. Straumal, B. Baretzky, A.A. Mazilkin, F. Phillipp, O.A. Kogtenkova, M.N. Volkov, and R.Z. Valiev, Formation of Nanograined Structure and Decomposition of Supersaturated Solid Solution During High Pressure Torsion of Al-Zn and Al-Mg Alloys, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 4469–4478
X. Yang, J. Yi, S. Ni, Y. Du, and M. Song, Microstructural Evolution and Structure–Hardness Relationship in an Al-4 wt.% Mg Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 1909–1915
C. Xu, Z. Horita, and T.G. Langdon, The Evolution of Homogeneity in an Aluminum Alloy Processed Using High-Pressure Torsion, Acta Mater., 2008, 56, p 5168–5176
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, Z. Jin, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine Grained 7075 Al Alloy Processed by ECAP and Their Evolutions During Annealing, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 4589–4599
S.Y. Chang, K.S. Lee, S.H. Choi, and D.H. Shin, Effect of ECAP on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Commercial 6061 Al Alloy Produced by Powder Metallurgy, J. Alloys Compd., 2003, 354, p 216–220
M. Zha, Y. Li, R.H. Mathiesen, R. Bjørge, and H. Roven, J, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Behavior of a Binary Al-7Mg Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2015, 84, p 42–54
L.J. Zheng, H.X. Li, M.F. Hashmi, C.Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, and M.G. Zeng, Evolution of Microstructure and Strengthening of 7050 Al Alloy by ECAP Combined with Heat-Treatment, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 171, p 100–107
M. Namdar and S. Jahromi, J, Influence of ECAP on the Fatigue Behavior of Age-Hardenable 2xxx Aluminum Alloy, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2015, 22, p 285–291
P.N. Rao, D. Singh, and R. Jayaganthan, Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Al 6061 Alloy Processed by Multidirectional Forging at Liquid Nitrogen Temperature, Mater. Des., 2014, 56, p 97–104
R.Z. Valiev, Y. Estrin, Z. Horita, T.G. Langdon, M.J. Zechetbauer, and Y.T. Zhu, Producing bulk Ultrafine-Grained Materials by Severe Plastic Deformation, JOM, 2006, 58, p 33–39
O.S. Sitdikov, Comparative Analysis of Microstructures Formed in Highly Alloyed Aluminum Alloy During High-Temperature Equal-Channel Angular Pressing and Multidirectional Forging, Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res., 2016, 7, p 149–157
D. Fuloria, N. Kumar, S. Goel, R. Jayaganthan, S. Jha, and D. Srivastava, Tensile Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Zircaloy-4 Processed Through Rolling at Different Temperatures, Mater. Des., 2016, 103, p 40–51
A. Joshi, N. Kumar, K.K. Yogesha, R. Jayaganthan, and S.K. Nath, Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution in Al 2014 Alloy Processed Through Multidirectional Cryo forging, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 1–15
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, S.H. Lee, and Y. Minamino, ARB (Accumulative Roll-Bonding) and Other New Techniques to Produce Bulk Ultrafine Grained Materials, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2003, 5, p 338–344
M. Ruppert, M. Strebl, H.W. Höppel, and M. Göken, Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine-Grained AlZnMg (Cu)-Alloys AA7020 and AA7075 Processed by Accumulative Roll Bonding, J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50, p 4422–4429
H. Xie, M.P. Wang, W. Chen, and Y. Jia, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Texture Evolution of Aluminum Alloy 7005 by Accumulative Roll Bonding, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 1199–1210
H.W. Höppel, J. May, and M. Göken, Enhanced Strength and Ductility in Ultrafine-Grained Aluminium Produced by Accumulative Roll Bonding, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 781–784
M.Z. Quadir, O. Al-Buhamad, L. Bassman, and M. Ferry, Development of a Recovered/Recrystallized Multilayered Microstructure in Al Alloys by Accumulative Roll Bonding, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 5438–5448
J.Y. Huang, Y.T. Zhu, H. Jiang, and T.C. Lowe, Microstructures and Dislocation Configurations in Nanostructured Cu Processed by Repetitive Corrugation and Straightening, Acta Mater., 2001, 49, p 1497–1505
V. Rajinikanth, G. Arora, N. Narasaiah, and K. Venkateswarlu, Effect of Repetitive Corrugation and Straightening on Al and Al–0.25 Sc Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, p 301–304
N. Thangapandian, S.B. Prabu, and K.A. Padmanabhan, Effects of Die Profile on Grain Refinement in Al-Mg Alloy Processed by Repetitive Corrugation and Straightening, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 649, p 229–238
A. Krishnaiah, U. Chakkingal, and H.S. Kim, Mechanical Properties of Commercially Pure Aluminium Subjected to Repetitive Bending and Straightening Process, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2008, 61, p 165–167
P.S. Pao, H.N. Jones, S.F. Cheng, and C.R. Feng, Fatigue Crack Propagation in Ultrafine Grained Al-Mg Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2005, 27, p 1164–1169
A. Vinogradov, A. Washikita, K. Kitagawa, and V.I. Kopylov, Fatigue life of Fine-Grain Al-Mg-Sc Alloys Produced by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 349, p 318–326
A. Vinogradov, S. Nagasaki, V. Patlan, K. Kitagawa, and M. Kawazoe, Fatigue Properties of 5056 Al-Mg Alloy Produced by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Nanostruct. Mater., 1999, 11, p 925–934
V. Patlan, A. Vinogradov, K. Higashi, and K. Kitagawa, Overview of Fatigue Properties of Fine Grain 5056 Al-Mg Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 300, p 171–182
J.H. Cha, H.H. Cho, W.H. Kim, S.I. Kwun, and D.H. Shin, The Low Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Equal-Channel Angular Pressed Al 5052 Alloy, Key Eng. Mater., 2008, 385, p 725–728
G. Khatibi, J. Horky, B. Weiss, and M.J. Zehetbauer, High Cycle Fatigue Behaviour of Copper Deformed by High Pressure Torsion, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, 32, p 269–278
S.K. Panigrahi and R. Jayaganthan, A Study on the Mechanical Properties of Cryorolled Al-Mg-Si Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 480, p 299–305
K.K. Yogesha, N. Kumar, A. Joshi, R. Jayaganthan, and S.K. Nath, A Comparative Study on Tensile and Fracture Behavior of Al-Mg Alloy Processed Through Cryorolling and Cryo Groove Rolling, Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal., 2016, 5, p 251–263
S. Malekjani, P.D. Hodgson, P. Cizek, I. Sabirov, and T.B. Hilditch, Cyclic Deformation Response of UFG 2024 Al Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2011, 33(5), p 700–709
D. Singh, P. Nageswara Rao, and R. Jayaganthan, High Cyclic Fatigue Behaviour of Ultrafine Grained Al 5083 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, 30, p 1835–1842
U.G. Kang et al., The Improvement of Strength and Ductility in Ultra-Fine Grained 5052 Al Alloy by Cryogenic-and Warm-Rolling, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45, p 4739–4744
Y.B. Lee, D.H. Shin, and W.J. Nam, Effect of Annealing Temperature on Tensile Behavior of 5052 Al Alloy Deformed at Cryogenic Temperature, J. Mater. Sci., 2005, 40, p 1313–1315
P.N. Rao, D. Singh, and R. Jayaganthan, Effect of Annealing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al 6061 Alloy Processed by Cryorolling, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29, p 76–82
S.K. Panigrahi and R. Jayaganthan, Development of Ultrafine-Grained Al 6063 Alloy by Cryorolling with the Optimized Initial Heat Treatment Conditions, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 2172–2180
T.S. Srivatsan, S. Anand, S. Sriram, and V.K. Vasudevan, The High-Cycle Fatigue and Fracture Behavior of Aluminum Alloy 7055, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 281(1), p 292–304
C.D. Beachem, Electron Fractographic Studies of Mechanical Fracture Processes in Metals, J. Basic Eng., 1965, 87, p 299–306
L. Yan and J. Fan, In-Situ SEM Study of Fatigue Crack Initiation and Propagation Behavior in 2524 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Des., 2016, 110, p 592–601
D. Singh, P. Nageswara Rao, and R. Jayaganthan, Effect of Deformation Temperature on Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine Grained Al-Mg Alloys Processed by Rolling, Mater. Des., 2013, 50, p 646–655
A. Gholinia, F.J. Humphreys, and P.B. Prangnell, Production of Ultra-Fine Grain Microstructures in Al-Mg Alloys by Coventional Rolling, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 4461–4476
D. Singh, P. Nageswara Rao, and R. Jayaganthan, Microstructures and Impact Toughness Behavior of Al 5083 Alloy Processed by Cryorolling and Afterwards Annealing, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2013, 20, p 759–769
S. Malekjani, P.D. Hodgson, N.E. Stanford, and T.B. Hilditch, Shear Bands Evolution in Ultrafine-Grained Aluminium Under Cyclic Loading, Scripta Mater., 2013, 68(10), p 821–824
U.G. Gang, S.H. Lee, and W.J. Nam, The Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a 5052 Aluminium Alloy by the Application of Cryogenic Rolling and Warm Rolling, Mater. Trans., 2009, 50(1), p 82–86
W. Bo, X.H. Chen, F.S. Pan, J.J. Mao, and F.A.N.G. Yong, Effects of Cold Rolling and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA 5052 Aluminum Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2015, 25(8), p 2481–2489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yogesha, K.K., Joshi, A. & Jayaganthan, R. Fatigue Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained 5052 Al Alloy Processed Through Different Rolling Methods. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 2826–2836 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2705-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2705-8