Abstract
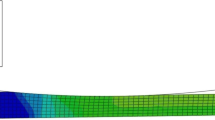
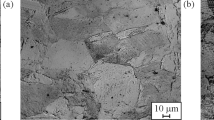
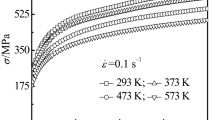
In this work, microstructural evolutions and mechanical properties of AISI 304L stainless steel were studied after rolling operations at elevated temperatures. Rolling experiments were conducted under warm and hot rolling conditions in the range of 600-1000 °C employing different reductions. Then, the developed microstructures and the mechanical properties of the steel were evaluated by means of uniaxial tensile testing, metallographic observations, and x-ray diffraction method. Besides, two-dimensional finite element analysis coupled with artificial neural network modeling was developed to assess thermo-mechanical behavior of the steel during and after rolling. The results show that inhomogeneities in strain and temperature distributions are reduced under warm rolling conditions. Static recrystallization can be operative under hot rolling conditions and relatively low reduction, i.e., reduction of 25%. However, for the case of higher reductions, the rate of recrystallization decreases considerably owing to severe temperature drop in the plate being rolled. Furthermore, the rolled plates show negative strain rate sensitivity while this phenomenon is affected by the rolling temperature.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.L. Roberts, Hot Rolling of Steels, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1983
S.L. Semiatin and J.H. Holbrook, Plastic Flow Phenomenology of 304L Stainless Steel, Metall. Trans. A, 1983, 14, p 1681–1695
P. Dadras, Flow Stress Equations for Type 304 Stainless and AISI, 1055 Steel, ASME Trans. J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1055, 107(1985), p 97–100
H.J. McQueen, S. Yue, N.D. Ryan, and E. Fry, Hot Working Characteristics of Steels in Austenitic State, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, 83, p 293–310
M. El Wahabi, J.M. Cabrera, and J.M. Prado, Hot Working of Two AISI, 304 Steels: A Comparative Study, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 343, p 116–125
K.J.R. Rasmussen, T. Burns, P. Bezkorovainy, and M.R. Bambach, Numerical Modelling of Stainless Steel Plates in Compression, J. Constr. Steel Res., 2003, 59, p 1345–1362
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, C. Phaniraj, and A.K. Bhaduri, Flow Behavior and Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of AISI, Type 316 L(N) Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 8565–8572
G.Q. Hou and L. Zhu, Influence of Strain Rate on Hot Ductility of Austenitic Stainless Steel Slab, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29, p 568–572
A.J. McLaren and C.M. Sellars, Modelling Distribution of Microstructure During Hot Rolling of Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1992, 8, p 1090–1094
S. Venugopal, S. Venugopal, P.V. Sivaprasad, M. Vasudevan, S.L. Mannan, S.K. Jha, P. Pandey, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Validation of Processing Maps for 304L Stainless Steel Using Hot Forging, Rolling and Extrusion, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1995, 59, p 343–350
S. Cho and Y. Loo, Hot Rolling Simulations of Austenitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Sci, 2001, 36, p 4267–4272
A. Di Schino, J.M. Kenny, I. Salvatori, and G. Abbruzzese, Modelling Primary Recrystallization and Grain Growth in a Low Nickel Austenitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36, p 593–601
S. Kim, Y. Lee, and B. Jang, Modeling of Recrystallization and Austenite Grain Size for AISI, 316 Stainless Steel and Its Application to Hot Bar Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 357, p 235–239
A. Belyakov, T. Sakai, and H. Miura, Grain Refinement in a 304 Stainless Steel Caused by Multiple Deformation at 0.5Tm, ISIJ Int., 2000, 40(Supplement), p SI64–SI68
R.L. Higginson and C.M. Sellars, The Effect of Strain Path Reversal During Hot Rolling on Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 338, p 323–330
S. Frechard, A. Redjaimia, E. Lach, and A. Lichtenberger, Mechanical Behavior of Nitrogen-Alloyed Austenitic Stainless Steel Hardened by Warm Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 415, p 219–224
M. Tikhonova, V. Dudko, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev, The Formation of Fine-Grained Structure in S304H-Type Austenitic Stainless Steel During Hot-to-Warm Working, Mater. Sci. Forum., 2012, 715–716, p 380–385
A.F. Padilha and P.R. Rios, Decomposition of Austenite in Austenitic Stainless Steel, ISIJ Int., 2002, 42, p 325–337
A.K. De, J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, D.C. Murdock, M.C. Mataya, and R.J. Comstock, Jr., Deformation-Induced Phase Transformation and Strain Hardening in Type 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, 37, p 1875–1896
S. Kobayashi, S. Oh, T. Altan, Metal Forming and the Finite Element Method, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1989, Chapters 6–7.
P. Tong and N. Rossettos, Finite Element Method: Basic Technique and Implementation, MIT Press, Cambridge, 1977
J.G. Lenard, M. Pietrzyk, and L. Cser, Mathematical Physical Simulation, of the Properties of Hot Rolled Products, Elsevier, New York, 1999 (Chapter 5)
R.M. Golden, Mathematical Methods for Neural Network Analysis and Design, MIT Press, Cambridge, 1996
Y.C. Lin, J. Zhang, and J. Zhong, Application of Neural Networks to Predict the Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of a Low Alloy Steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 752–758
K.H. Huebner and E.A. Thornton, The Finite Element Method for Engineers, 2nd ed., Wiley, New York, 1982
S.J. Chen and A.A. Tseng, Spray and Jet Cooling in Steel Rolling, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 1992, 13, p 358–369
Y. Prasad and S. Sasidhara, Hot Working Guide: A Compendium of Processing Maps, ASM International, Materials Park, 1997
Y.F. Shen, X.X. Li, X. Sun, Y.D. Wang, and L. Zuo, Twinning and Martensite in a 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 552, p 514–522
J. Talonen, P. Nenonen, G. Pape, and H. Hanninen, Effect of Strain Rate on the Strain-Induced-Martensite Transformation and Mechanical Properties Of Austenitic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans., 2005, 36, p 421–432
H.C. Shin, T.K. Ha, and Y.W. Chang, Kinetics of Deformation Induced Martensitic Transformation in a 304 Stainless Steel, Scripta Mater., 2001, 45, p 823–829
G.E. Dieter, H.A. Kuhn, and S.L. Semiatin, Ed., Handbook of Workability and Process Design, ASM International, Materials Park, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourabdollah, P., Serajzadeh, S. A Study on Deformation Behavior of 304L Stainless Steel During and After Plate Rolling at Elevated Temperatures. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 885–893 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2475-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2475-8