Abstract
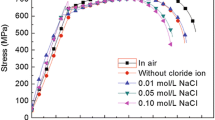
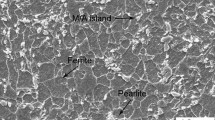
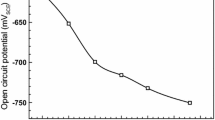
In this work, the local corrosion at crack tip on an API 5L X46 pipeline steel specimens was investigated under various applied loads in a near-neutral pH solution. Electrochemical measurements, including potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, combined with micro-electrochemical technique and surface characterization, were conducted to investigate the effect of stress on local anodic solution of the steel at the crack tip. The stress corrosion cracking of the steel was dominated by an anodic dissolution mechanism, while the effect of hydrogen was negligible. The applied load (stress) increased the corrosion rate at the crack tip, contributing to crack propagation. The deposit of corrosion products at the crack tip could protect somewhat from further corrosion. At sufficiently large applied loads such as 740 N in the work, it was possible to generate separated cathode and anode, further accelerating the crack growth.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.F. Cheng, Stress Corrosion Cracking of Pipelines, Wiley, Hoboken, 2013
National Energy Board, Stress Corrosion Cracking on Canadian Oil and Gas Pipelines, Calgary, AB, 1996
M. Javidi and S. Bahalaou, Horeh, Investigating the Mechanism of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Near-Neutral and High pH Environments for API, 5L X52 Steel, Corros. Sci., 2014, 80, p 213–220
X.Y. Zhang, S.B. Lambert, and R. Sutherby, Transgranular Stress Corrosion Cracking of X-60 Pipeline Steel in Simulated Ground Water, Corrosion, 1999, 55, p 297–305
B.Y. Fang, E.H. Han, J.Q. Wang, and W. Ke, Stress Corrosion Cracking of X-70 Pipeline Steel in Near Neutral pH Solution Subjected to Constant Load and Cyclic Load Testing, Corros. Eng., Sci. Technol., 2007, 42, p 123–129
Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, and Y.F. Cheng, Mechanistic aspect of Near-Neutral pH Stress Corrosion Cracking of Pipelines under Cathodic Polarization, Corros. Sci., 2012, 55, p 54–60
G. Liang, X. Peng, E.S. Juan, and Y.F. Cheng, Strain Aging of X100 Steel in Service and the Enhanced Susceptibility of Pipelines to Stress Corrosion Cracking, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 3778–3782
Y.F. Cheng, Analysis of Electrochemical Hydrogen Permeation Through X-65 Pipeline Steel and its Implications on Pipeline Stress Corrosion Cracking, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2007, 32, p 1269–1276
H.B. Xue and Y.F. Cheng, Hydrogen Permeation and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of X80 Pipeline Steel Weld, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 170–175
G.A. Zhang and Y.F. Cheng, Micro-Electrochemical Characterization of Corrosion of Pre-Cracked X70 Pipeline Steel in a Concentrated Carbonate/Bicarbonate Solution, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 960–968
X. Tang and Y.F. Cheng, Micro-Electrochemical Characterization of the Effect of Applied Stress on Local Anodic Dissolution Behavior of Pipeline Steel under Near-Neutral pH Condition, Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54, p 1499–1505
Y.F. Cheng, Fundamentals of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction and its Implications on Near-Neutral pH Stress Corrosion Cracking of Pipelines, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, p 2661–2667
A. Turnbull, The Solution Composition and Electrode Potential in Pits, Crevices and Crack, Corros. Sci., 1983, 8, p 833–870
I. Dmytrakh, Corrosion Fracture of Structural Metallic Materials: Effect of Electrochemical Conditions in Crack, Strain Int. J. Exp. Mech., 2011, 47, p 427–435
Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, and Y.F. Cheng, Effect of Strain Rate on Cathodic Reaction During Stress Corrosion Cracking of X70 Steel in a Near-Neutral pH Solution, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20, p 1242–1246
ASTM, E647-15, Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fatigue Crack Growth Rates, West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
R.N. Parkins, W.K. Blanchard, and B.S. Delanty, Transgranular Stress Corrosion Cracking of High-Pressure Pipelines in Contact with Solutions of Near Neutral pH, Corrosion, 1994, 50, p 394–408
ASTM, E8/E8M Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
ASTM G59-97, Standard Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization Resistance Measurements, West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
C.F. Dong, Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, and Y.F. Cheng, Effects of Hydrogen-Charging on the Susceptibility of X100 Pipeline Steel to Hydrogen-Induced Cracking, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2009, 34, p 9879–9884
L.Y. Xu and Y.F. Cheng, Corrosion of X100 Pipeline Steel under Plastic Strain in a Neutral pH Bicarbonate Solution, Corros. Sci., 2012, 64, p 145–152
L.Y. Xu and Y.F. Cheng, An Experimental Investigation of Corrosion of X100 Pipeline Steel under Uniaxial Elastic Stress in a Near-Neutral pH Solution, Corros. Sci., 2012, 59, p 103–109
G.Z. Meng, C. Zhang, and Y.F. Cheng, Effects of Corrosion Product Deposit on the Subsequent Cathodic and Anodic Reactions of X-70 Steel in Near-Neutral pH Solution, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, p 3116–3122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Cheng, Y.F. Effect of Stress on Corrosion at Crack Tip on Pipeline Steel in a Near-Neutral pH Solution. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 4988–4995 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2369-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2369-9