Abstract
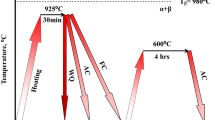
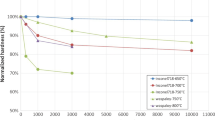
This research studies the effect of double aging heat treatment on the short-term creep behavior of the superalloy Inconel 718. The superalloy, received in the solution treated state, was subjected to an aging treatment which comprises a solid solution at 1095 °C for 1 h, a first aging step of 955 °C for 1 h, then aged at 720 and 620 °C, 8 h each step. Creep tests at constant load mode, under temperatures of 650, 675, 700 °C and stress of 510, 625 and 700 MPa, were performed before and after heat treatment. The results indicate that after the double aging heat treatment creep resistance is increased, influenced by the presence of precipitates γ′ and γ″ and its interaction with the dislocations, by grain size growth (from 8.20 to 7.23 ASTM) and the increase of hardness by approximately 98%. Creep parameters of primary and secondary stages have been determined. There is a breakdown relationship between \(\dot{\upvarepsilon }_{\text{s}}\) and stress at 650 °C of Inconel 718 as received, around 600 MPa. By considering the internal stress values, effective stress exponent, effective activation energy, and TEM images of Inconel 718 double aged, it is suggested that the creep mechanism is controlled by the interaction of dislocations with precipitates. The fracture mechanism of Inconel 718 as received is transgranular (coalescence of dimples) and mixed (transgranular-intergranular), whereas the Inconel 718 double aged condition crept surfaces evidenced the intergranular fracture mechanism.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.S. Sims, N. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel, Superalloys II, High Temperature Materials for Aerospace and Industrial Power, Willey, New York, 1987
F. Schubert, Temperature and Time Dependent Transformation: Application to Heat Treatment of High Temperature Alloys, ASM, Metals Park, 1983, p 3
G.R. Leverant and B.H. Kear, The Mechanism of Creep in Gamma Prime Precipitation-Hardened Nickel-Base Alloys at Intermediate Temperatures, Metall. Trans., 1970, 1, p 491–498
L.K. Singhal and M.L. Vaidya, Generation of Dislocations in a Precipitation Hardened Alloy, Metall. Trans., 1970, 1, p 1044–1045
J.K. Tien, B.H. Kear, and G.R. Leverant, On the High Activation Energy for Steady State Creep of Particle Strengthened Systems, Scr. Metall., 1972, 6, p 135–140
R. Lagneborg and B. Bergman, The Stress/Creep Rate Behavior of Precipitation-Hardened Alloys, Met. Sci., 1976, 10(1), p 20–28
L. Rémy, Precipitation Behavior and Creep Rupture of 706 Type Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1979, 38, p 227–239
O.D. Sherby and J. Weertman, Diffusion-Controlled Dislocation Creep: A Defense, Acta Metall., 1979, 27, p 387–400
K. Shiozawa and J.R. Weertman, The Nucleation of Grain Boundary Voids in a Nickel-Base Superalloy During High Temperature Creep, Scr. Metall., 1982, 16, p 735–739
B.F. Dyson and M. Mclean, Particle Coarsening, σ0 and Tertiary Creep, Acta Metall., 1983, 31, p 17–27
O.D. Sherby and E.M. Taleff, Influence of Grain Size, Solute Atoms and Second-Phase Particles on Creep Behavior of Polycrystalline Solids, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, A322, p 89–99
H. De Cicco, M.I. Luppo, L.M. Gribaudo, and J. Ovejero-García, Microstructural Development and Creep Behavior in A286 Superalloy, Mater. Charact., 2004, 52, p 85–92
A. Soula, Y. Renollet, D. Boivin, J.-L. Pouchou, D. Locq, P. Caron, and Y. Bréchet, Analysis of High-Temperature Creep Deformation in a Polycrystalline Nickel-Base Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, A510–511, p 301–306
R. Merabtine, J.P. Dallas, and M. Cornet, Creep Strengthening of Ni3(Al, Si) Intermetallic Alloy by Ductile Precipitates, Intermetallics, 2005, 13, p 179–186
S. Li, J. Tao, T. Sugui, and H. Zhuangqi, Influence of Precipitate Morphology on Tensile Creep of a Single Crystal Nickel-Base Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 454–455, p 461–466
A.A. Tavassoli, On the Anomalous Stress-Dependence of Creep Rate in Precipitation Strengthened Alloys, Nucl. Eng. Des., 1979, 54, p 279–287
B. Pieraggi and J.F. Uginet, Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, TMS, Warrendale, 1994, p 535–544
W.R. Sun, H.R. Guan, M. Wang, Z.G. Wang, L.F. Huang, and Z.Q. Hu, Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, TMS, Warrendale, 2005, p 399–407
X. Xie, Q. Liang, J. Dong, W. Meng, and Z. Xu, Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, TMS, Warrendale, 1994, p 711–720
G.D. Smith and S.J. Patel, Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, TMS, Warrendale, 2005, p 135–154
S. Azadian, L.-Y. Wei, and R. Warren, Delta Phase Precipitation in Inconel 718, Mater. Charact., 2004, 53, p 7–16
Z.F. Zhou and B.A. Parker, On the High-Stress Region Stress Exponent During Creep, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1995, 32, p 1889–1893
C.-M. Kuo, Y.-T. Yang, H.-Y. Bor, C.-N. Wei, and C.-C. Tai, Aging Effects on the Microstructure and Creep Behavior of Inconel 718 Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, A510–511, p 289–294
American Society for Testing and Materials, E21-05, Standard Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests of Metallic Materials, ASTM, Philadelphia, 2005
American Society for Testing and Materials, E139-11, Standard Practice for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials, ASTM, Philadelphia, 2011
Heat Treater’s Guide, Practices and Procedures for Nonferrous Alloys, ASM International, The Materials Information Society, Materials Park, 1996
D.A.P. Reis, C.R.M. Silva, M.C.A. Nono, M.J.R. Barboza, F. Piorino-Neto, and E.A.C. Perez, Effect of Environment on the Creep Behavior of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 399, p 276–280
F.R.N. Nabarro and H.L. De Villiers, The Physics of Creep, Taylor and Francis Ltd., London, 1995
B. Kaplan, A. Blomqvist, C. Arhammar, M. Selleby, and S. Norgren, Structural Determination of (Cr,Co)7C3. Proceedings of the 18th Plansee Seminar, Reutte, Austria, 2013, pp. HM104/1–HM104/12.
J.R. Davis, ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt and Their Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, 2000
M.F. Ashby, C. Gandhi, and D.M.R. Taplin, Fracture-Mechanism Maps and Their Construction for f.c.c. Metals and Alloys, Acta Mater., 1979, 27, p 699–729
Y. Han and M.C. Chaturvedi, Steady State Creep Deformation of Superalloy Inconel 718, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1987, 89, p 25–33
W. Chen and M.C. Chaturvedi, The Effect of Grain Boundary Precipitates on the Creep Behavior of Inconel 718, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, 183, p 81–89
D.F. Paulonis, J.M. Oblak, and D.S. Duvall, Precipitation in Nickel-Base Alloy 718, Trans. ASM, 1969, 62(3), p 611–622
R. Cozar and A. Pineau, Morphology of y’ and y” Precipitates and Thermal Stability of Inconel 718 Type Alloys, Metall. Trans., 1973, 4(1), p 47–59
G. Venkataraman and F. Cosandey, Creep Behavior of Ni-Cr Alloys with Trace Additions of Cerium, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1987, 93, p 175–179
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all the financial support gave from CAPES and technical/scientifical advice from LME/LNNano/CNPEM Process Number 15053. Especial thanks to Tarcila Sugahara and Fabiano Emmanuel Montoro. This work is dedicated to the memory of Prof. Carlos de Moura Neto.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Prof. Carlos de Moura Neto.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caliari, F.R., Candioto, K.C.G., Couto, A.A. et al. Effect of Double Aging Heat Treatment on the Short-Term Creep Behavior of the Inconel 718. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 2307–2317 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2051-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2051-2