Abstract
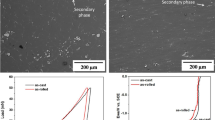
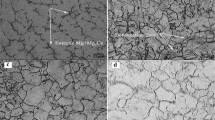
Microstructure, bio-corrosion behavior, and corrosion residual strength in 0.9 wt.% NaCl solution of the fine-grained Mg-4Zn alloy sheet prepared by high strain rate rolling are systematically investigated. The as-rolled alloy has fine homogenous dynamic recrystallization grains with the average grain size of 4.5 μm. It has different bio-corrosion behavior from the as-cast and is the most corrosion resistant except for pure Mg. Its in vitro strength loss is about 19% after 7 days immersion (the as-cast, 62%), and corrosion residual strength after 15 days immersion is 205 MPa. Its in vitro strength loss after 15, 30, and 60 days immersion are 24, 37, and 38% respectively. The as-rolled Mg-4Zn alloy is featured with the slighter in vitro loss of mechanical integrity due to uniform bio-corrosion and is desirable for the usage in the field of bone fixation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.P. Staiger, A.M. Pietak, J. Huadmai, and G. Dias, Magnesium and Its Alloys as Orthopedic Biomaterials: A Review, Biomaterials, 2006, 27, p 1728–1734
L. Tan, X. Yu, P. Wan, and K. Yang, Biodegradable Materials for Bone Repairs: A Review, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29, p 503–513
I. Popov, D. Starosvetsky, and D. Shechtman, Initial Stages of Corrosion Within Mg-Zn-Y-Zr Alloy in 1g/l NaCl Solution, J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35, p 1–8
G. Song, Control of Biodegradation of Biocompatible Magnesium Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 1696–1701
M.B. Kannan and R.K.S. Raman, In Vitro Degradation and Mechanical Integrity of Calcium-Containing Magnesium Alloys in Modified-Simulated Body Fluid, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, p 2306–2314
H. Li, Q.M. Peng, X.J. Li, K. Li, Z.S. Han, and D.Q. Fang, Microstructures, Mechanical and Cytocompatibility of Degradable Mg-Zn Based Orthopedic Biomaterials, Mater. Design, 2014, 58, p 43–51
J. Kubásek, D. Vojtěch, J. Lipov, and T. Ruml, Structure, Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior and Cytotoxicity of Biodegradable Mg-X (X=Sn, Ga, In) Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2013, 33, p 2421–2432
F. Rosalbino, S. De Negri, A. Saccone, E. Angelini, and S. Delfino, Bio-corrosion Characterization of Mg-Zn-X(X=Ca, Mn, Si) Alloys for Biomedical Applications, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 21, p 1091–1098
W.W. He, E.L. Zhang, and K. Yang, Effect of Y on the Bio-corrosion Behavior of Extruded Mg-Zn-Mn Alloy in Hank’s Solution, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2010, 10, p 167–174
S.X. Zhang, J.N. Li, Y. Song, C.L. Zhao, X.N. Zhang, C.Y. Xie, Y. Zhang, H.R. Tao, Y.H. He, Y. Jiang, and Y.J. Bian, In Vitro Degradation, Hemolysis and MC3T3-E1 Cell Adhesion of Biodegradable Mg-Zn Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2009, 29, p 1907–1912
B.P. Zhang. Research on Mg-Zn-Ca Alloys as Degradable Materials, Doctor Thesis, Harbin University of Technology, 2010.
Y.H. Gu, S. Bandopadhyay, C.F. Chen, C.Y. Ning, and Y.J. Guo, Long-Term Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism of Microarc Oxidation Coated AZ31 Mg Alloys for Biomedical Applications, Mater. Design, 2013, 46, p 66–75
H. Zhao, S. Cai, S.X. Niu, R.Y. Zhang, X.D. Wu, G.H. Xu, and Z.T. Ding, The Influence of Alkali Pretreatments of AZ31 Magnesium Alloys on Bonding of Bioglass-Ceramic Coatings and Corrosion Resistance for Biomedical Applications, Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(3), p 4590–4600
H.M. Wong, K.W.K. Yeung, K.O. Lam, V. Tam, P.K. Chu, K.D.K. Luk, and K.M.C. Cheung, A Biodegradable Polymer-Based Coating to Control the Performance of Magnesium Alloy Orthopaedic Implants, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, p 2084–2096
X.N. Gu, Y.F. Zheng, S.P. Zhong, T.F. Xi, J.Q. Wang, and W.H. Wang, Corrosion of, and Cellular Responses to Mg-Zn-Ca Bulk Metallic Glasses, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, p 1093–1103
B. Zberg, P.J. Uggowitzer, and J.F. Löffler, MgZnCa Glasses Without Clinically Observable Hydrogen Evolution for Biodegradable Implants, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, p 887–891
H. Wang, Y. Estrin, and Z. Zúberová, Bio-corrosion of a Magnesium Alloy with Different Processing Histories, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, p 2476–2479
S. Koleini, M.H. Idris, and H. Jafari, Influence of Hot Rolling Parameters on Microstructure and Biodegradability of Mg-1Ca Alloy in Simulated Body Fluid, Mater. Design, 2012, 33, p 20–25
Z. Wei, S. Tian, and N.N. Aung, Effect of Heat Treatment on Corrosion Behaviour of Magnesium Alloy AZ91D in Simulated Body Fluid, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 1035–1041
M. Alvarez-Lopez, M.D. Pereda, J.A. del Valle, M. Fernandez-Lorenzo, M.C. Garcia-Alonso, O.A. Ruano, and M.L. Escudero, Corrosion Behaviour of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy with Different Grain Sizes in Simulated Biological Fluids, Acta Biomater., 2010, 6, p 1763–1771
Z.W. Ren, S.K. Guan, Y.F. Sun, et al. Microstructure and Properties of Biomagnesium Alloy by High Pressure Torsion, The 12th Chinese Conference on Biomaterials, December 4-7, 2009, China, E-23
J. Fan, X. Qiu, X.D. Niu, Z. Tian, W. Sun, X.J. Liu, Y.D. Li, W.R. Li, and J. Meng, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, In Vitro Degradation and Cytotoxicity Evaluations of Mg-1.5Y-1.2Zn-0.44Zr Alloys for Biodegradable Metallic Implants, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2013, 33, p 2345–2352
G.B. Hamu, D. Eliezer, and L. Wagner, The Relation Between Severe Plastic Deformation Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 468, p 222–229
S.Q. Zhu, H.G. Yan, J.H. Chen, Y.Z. Wu, J.Z. Liu, and J. Tian, Effect of Twinning and Dynamic Recrystallization on the High Strain Rate Rolling Process, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63(10), p 985–988
S.Q. Zhu, H.G. Yan, J.H. Chen, Y.Z. Wu, B. Su, Y.G. Du, and X.Z. Liao, Feasibility of High Strain-Rate Rolling of a Magnesium Alloy Across a Wide Temperature Range, Scr. Mater., 2012, 67, p 404–407
S.Q. Zhu, H.G. Yan, J.H. Chen, Y.Z. Wu, Y.G. Du, and X.Z. Liao, Fabrication of Mg-Al-Zn-Mn Alloy Sheets with Homogeneous Fine-Grained Structures Using High Strain-Rate Rolling in a Wide Temperature Range, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559(1), p 765–772
M. Erinc, W. Sillekens, Magnesium Technology 2009, E.A. Nyberg, S.R. Agnew, N.R. Neelameggham, et al, Eds., Springer, Hamburg, 2009, p 209-214.
M.T. Pérez-Prado, J.A. del Valle, and O.A. Ruano, Achieving High Strength in Commercial Mg Cast Alloys Through Large Strain Rolling, Mater. Lett., 2005, 59, p 3299–3303
K. Kubota, M. Mabuchi, and K. Higashi, Review Processing and Mechanical Properties of Fine-Grained Magnesium Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 1999, 34, p 2255–2262
G.Q. Li, G.H. Wu, Y. Fan, and W.J. Ding, Effect of the Main Alloying Elements on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium Alloys, Foundry Technol., 2006, 27(1), p 81–82. (in Chinese)
Y.W. Song, E.H. Han, D.Y. Shan, C.D. Yim, and B.S. You, The Effect of Zn Concentration on the Corrosion Behavior of Mg-xZn Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2012, 65, p 322–330
N.N. Aung and W. Zhou, Effect of Grain Size and Twins on Corrosion Behaviour of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 589–594
E. Koç, M.B. Kannan, M. Ünal, and E. Candan, Influence of Zinc on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium–Zinc Binary Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 648, p 291–296
J.S. Liao, M. Hotta, and N. Yamamoto, Corrosion Behavior of Fine-Grained AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Corros. Sci., 2012, 61, p 208–214
Q. Wang, Y.H. Liu, X.Y. Zhu, S. Li, S. Yu, L. Zhang, and Y.L. Song, Study on the Effect of Corrosion on the Tensile Properties of the 1.0 wt.% Yttrium Modified AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 517(1), p 239–245
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the support of the Natural Science Foundation Project of China (51571089), the Young Teacher Growth Fund of Hunan University (531107021095) and the National SIT Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Z., Chen, J., Yan, H. et al. Microstructure, Bio-corrosion Behavior, and Corrosion Residual Strength of High Strain Rate Rolled Mg-4Zn Alloy Sheet. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1974–1985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2041-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2041-4