Abstract
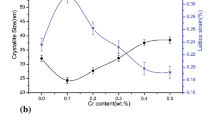
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the effect of dynamic recovery on the mechanical properties of copper (Cu) during surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) at both room temperature (RT) and cryogenic temperature (CT). Copper sheets were processed by SMAT at RT and at CT for 5, 15, and 30 min, respectively. The Cu samples after SMAT at RT for 30 min exhibited better ductility but lower strength than the samples after SMAT at CT for 30 min due to dynamic recovery. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that decreasing temperature during SMAT led to an increase in the twin and dislocation densities. In addition, a thicker gradient structure layer with finer grains was obtained in the SMAT-processed Cu samples at CT than at RT. The results indicated that SMAT at CT can effectively suppress the occurring of dynamic recovery and produce ultrahigh strength pure copper without seriously sacrificing its ductility.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Lugo, N. Llorca, J.M. Cabrera, and Z. Horita, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Pure Copper Deformed Severely by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing and High Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 477(1), p 366–371
Sh.R. Bahadori, K. Dehghani, and F. Bakhshandeh, Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties of Pure Copper Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Cold Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 583, p 36–42
K. Lu and J. Lu, Nanostructured Surface Layer on Metallic Materials Induced by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 375–377, p 38–45
Y.S. Li, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu, Microstructural Evolution and Nanostructure Formation in Copper During Dynamic Plastic Deformation at Cryogenic Temperatures, Acta Mater., 2008, 56(2), p 230–241
K. Wang, N.R. Tao, G. Liu, J. Lu, and K. Lu, Plastic Strain-Induced Grain Refinement at the Nanometer Scale in Copper, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(19), p 5281–5291
K.A. Darling, M.A. Tschopp, A.J. Roberts, J.P. Ligda, and L.J. Kecskes, Enhancing Grain Refinement in Polycrystalline Materials Using Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment at Cryogenic Temperatures, Scr. Mater., 2013, 69(6), p 461–464
O. Grassel, L. Kruger, G. Frommeyer, and L.W. Meyer, High Strength Fe-Mn-(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP Steels Development—Properties—Application, Int. J. Plast., 2000, 16(10), p 1391–1409
G. Frommeyer, U. Brux, and P. Neumann, Supra-ductile and High-Strength Manganese-TRIP/TWIP Steels for High Energy Absorption Purposes, ISIJ Int., 2003, 43(3), p 438–446
X.Y. San, X.G. Liang, L.P. Cheng, C.J. Li, and X.K. Zhu, Effect of Stacking Fault Energy on Mechanical Behavior of Cold-Forging Cu and Cu Alloys, Mater. Des., 2013, 35, p 480–483
C.B. Cater and I.L.F. Ray, On the Stacking-Fault Energies of Copper Alloys, Philos. Mag., 1977, 35(1), p 189–200
L. Lu, Z.S. You, and K. Lu, Work Hardening of Polycrystalline Cu with Nanoscale Twins, Scr. Mater., 2012, 66(11), p 837–842
Y.T. Zhu, X.Z. Liao, and X.L. Wu, Deformation Twinning in Nanocrystalline Materials, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2012, 57(1), p 1–62
X.L. Wu, P. Jiang, L. Chen, J.F. Zhang, F.P. Yuan, and Y.T. Zhu, Synergetic STRENGTHENING by Gradient Structure, Mater. Res. Lett., 2014, 2(4), p 185–191
E. Ma, Y.M. Wang, Q.H. Lu, and L. Lu, Strain Hardening and Large Tensile Elongation in Ultrahigh-Strength Nano-twinned Copper, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(21), p 4932–4934
L.H. Qian, S.C. Wang, Y.H. Zhao, and K. Lu, Microstrain Effect on Thermal Properties of Nanocrystalline Cu, Acta Mater., 2002, 50(13), p 3425–3434
S. Ni, Y.B. Wang, X.Z. Liao, R.B. Figueiredo, H.Q. Li, Y.H. Zhao, E.J. Lavernia, S.P. Ringer, T.G. Langdon, and Y.T. Zhu, Strain Softening in Nanocrystalline Ni-Fe Alloy Induced by Large HPT Revolutions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(13), p 4807–4811
K. Edalati, J.M. Cubero-Sesin, A. Alhamidi, I.F. Mohamed, and Z. Horita, Influence of Severe Plastic Deformation at Cryogenic Temperature on Grain Refinement and Softening of Pure Metals: Investigation Using High-Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 613, p 103–110
H.P. Klug and L.E. Alexander, X-ray Diffraction Procedures, Wiley-VCH, New York, 1974, p 618–677
Y.H. Zhao, K. Zhang, and K. Lu, Structure Characteristics of Nanocrystalline Element Selenium with Different Grain Sizes, Phys. Rev. B, 1997, 56(22), p 322–329
Y.H. Zhao, H.W. Sheng, and K. Lu, Microstructure Evolution and Thermal Properties in Nanocrystalline Fe During Mechanical Attrition, Acta Mater., 2001, 49(2), p 365–375
R. Smallman and K. Westmacott, Stacking Faults in Face-Centred Cubic Metals and Alloys, Philos. Mag., 1957, 2(7), p 669–683
G. Williamson and R. Smallman, Dislocation Densities in Some Annealed and Cold-Worked Metals from Measurements on the X-ray Debye-Scherrer Spectrum, Philos. Mag., 1956, 1(1), p 34–46
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, and Z. Horita, Determining the Optimal Stacking Fault Energy for Achieving High Ductility in Ultrafine-Grained Cu-Zn Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 493(1), p 123–129
Y.H. Zhao, K. Lu, and K. Zhang, Microstructure Evolution and Thermal Properties in Nanocrystalline Cu During Mechanical Attrition, Phys. Rev. B, 2002, 66(8), p 085404
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, Z. Jin, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine Grained 7075 Al Alloy Processed by ECAP and Their Evolutions During Annealing, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(15), p 4589–4599
L. Lu, R. Schwaiger, Z.W. Shan, M. Dao, and K. Lu, Nano-sized Twins Induce High Rate Sensitivity of Flow Stress in Pure Copper, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(7), p 2169–2179
J. Guo, K. Wang, and L. Lu, Tensile Properties of Cu with Deformation Twins Induced by SMAT, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22(6), p 789–792
X.L. Wu, P. Jiang, L. Chen, F.P. Yuan, and Y.T. Zhu, Extraordinary Strain Hardening by Gradient Structure, Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA, 2014, 111(20), p 7197–7201
Y.M. Wang and E. Ma, Temperature and Strain Rate Effects on the Strength and Ductility of Nanostructured Copper, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83(15), p 3165–3167
K. Edalati, T. Fujioka, and Z. Horita, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Pure Cu Processed by High-Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 497(1), p 168–173
X.Y. San, X.G. Liang, L.P. Cheng, C.J. Li, and X.K. Zhu, Temperature Effect on Mechanical Properties of Cu and Cu Alloys, Mater. Des., 2012, 35, p 480–483
K. Hanazaki, N. Shigeiri, and N. Tsuji, Change in Microstructures and Mechanical Properties During Deep Wire Drawing of Copper, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(21), p 5699–5707
L. Lu, L.B. Wang, B.Z. Ding, and K. Lu, High-Tensile Ductility in Nanocrystalline Copper, J. Mater. Res., 2000, 15(02), p 270–273
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51561015 and 51361017). We also greatly appreciate prof. Y. T. Zhu from North Carolina State University for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Wen, C., Yang, X. et al. Ultrahigh Strength Copper Obtained by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment at Cryogenic Temperature. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 5058–5064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1797-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1797-2