Abstract
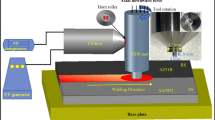
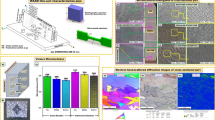
This paper is aimed to investigate the microstructure of 7005 aluminum sheets joined by friction-stir welding as well as their mechanical properties. Specimens with ten different sets of welding parameters were studied. Tensile test and fracture analysis determined that the joint of the best quality was obtained at the rotation speed of 1000 rpm matching with the travel speed of 200 mm/min, and the travel speed has more impact on the ultimate tensile strength. Optical microscope observation was applied to this high-quality specimen and gave evidence to explaining the formation of the onion ring structure. Electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) technique was employed to characterize the textures and revealed the evolution of microstructures during friction stir processing. The EBSD results showed that the grains maintain their original orientations at relatively low deformation while the orientations rotate under increasing strain. Accumulated rotation will turn the textures into mixed shear components, which finally results in grain refinement and contributes to the high quality of the joint.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zuo and P. Ni, Effect of Ti, Sc and Zr Additions on as-Cast Microstructures of 7005 Aluminum Alloy, Adv. Sci. Lett., 2011, 4(3), p 1182–1188
J. Jiang, Y. Wang, and H. Atkinson, Microstructural Coarsening of 7005 Aluminum Alloy Semisolid Billets with High Solid Fraction, Mater. Charact., 2014, 90, p 52–61
C. Huang and S. Kou, Partially Melted Zone in Aluminum Welds-Liquation Mechanism and Directional Soldification, Weld. J. N. Y., 2000, 79(5), p 113-s
A.K. Jha et al., Metallurgical Analysis of Cracking in Weldment of Propellant Tank, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2003, 10(3), p 265–273
N.R. Mandal, Aluminum Welding, Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2001
R.S. Mishra and Z. Ma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2005, 50(1), p 1–78
W. Thomas, et al., International Patent Application PCT/GB92/02203 and GB Patent Application 9125978.8. UK Patent Office, London, 6, 1991.
W.-B. Lee and S.-B. Jung, The Joint Properties of Copper by Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58(6), p 1041–1046
H.S. Park et al., Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welds of 60% Cu-40% Zn Copper Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 371(1), p 160–169
N. Afrin et al., Microstructure and Tensile Properties Of Friction Stir Welded AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 472(1), p 179–186
W. Woo et al., Texture Variation and its Influence on the Tensile Behavior of a Friction-Stir Processed Magnesium Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54(11), p 1859–1864
A.J. Ramirez and M.C. Juhas, Microstructural Evolution in Ti-6Al-4V Friction Stir Welds, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publications, Aedermannsdorf, 2003
Y. Zhang et al., Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 485(1), p 448–455
R. Nandan, T. DebRoy, and H. Bhadeshia, Recent Advances in Friction-Stir Welding-Process, Weldment Structure and Properties, Prog. Mater Sci., 2008, 53(6), p 980–1023
S. Benavides et al., Low-Temperature Friction-Stir Welding of 2024 Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 1999, 41(8), p 809–815
M.A. Sutton et al., Microstructural Studies of Friction Stir Welds in 2024-T3 Aluminum, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 323(1), p 160–166
A. Da Silva et al., Material Flow and Mechanical Behaviour of Dissimilar AA2024-T3 and AA7075-T6 Aluminium Alloys Friction Stir Welds, Mater. Des., 2011, 32(4), p 2021–2027
G. Liu et al., Microstructural Aspects of the Friction-Stir Welding of 6061-T6 Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 1997, 37(3), p 355–361
Y.S. Sato, M. Urata, and H. Kokawa, Parameters Controlling Microstructure and Hardness During Friction-Stir Welding of Precipitation-Hardenable Aluminum Alloy 6063, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33(3), p 625–635
J.-Q. Su et al., Microstructural Investigation of Friction Stir Welded 7050-T651 Aluminium, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(3), p 713–729
C.B. Fuller et al., Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Naturally Aged 7050 and 7075 Al Friction Stir Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(9), p 2233–2240
H.-B. Chen et al., The Investigation of Typical Welding Defects for 5456 Aluminum Alloy Friction Stir Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 433(1), p 64–69
K. Krishnan, On the Formation of Onion Rings in Friction Stir Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 327(2), p 246–251
P. Prangnell and C. Heason, Grain Structure Formation During Friction Stir Welding Observed by the ‘Stop Action Technique’, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(11), p 3179–3192
W. Woo et al., Texture Analysis of a Friction Stir Processed 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy Using Neutron Diffraction, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(15), p 3871–3882
R. Fonda, J. Bingert, and K. Colligan, Development of Grain Structure During Friction Stir Welding, Scr. Mater., 2004, 51(3), p 243–248
Y. Li, L. Murr, and J. McClure, Flow Visualization and Residual Microstructures Associated with the Friction-Stir Welding of 2024 Aluminum to 6061 Aluminum, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 271(1), p 213–223
Y.S. Sato et al., Microstructural Evolution of 6063 Aluminum During Friction-Stir Welding, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, 30(9), p 2429–2437
Y. Li, L. Murr, and J. McClure, Solid-State Flow Visualization in the Friction-Stir Welding of 2024 Al to 6061 Al, Scr. Mater., 1999, 40(9), p 1041–1046
D.P. Field et al., Heterogeneity of Crystallographic Texture in Friction Stir Welds of Aluminum, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(11), p 2869–2877
R. Fonda and J. Bingert, Microstructural Evolution in the Heat-Affected Zone of a Friction Stir Weld, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(5), p 1487–1499
R. Fonda and J. Bingert, Texture Variations in an Aluminum Friction Stir Weld, Scr. Mater., 2007, 57(11), p 1052–1055
U. Suhuddin et al., Grain Structure and Texture Evolution During Friction Stir Welding of Thin 6016 Aluminum Alloy Sheets, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(7), p 1962–1969
D.N. Lee, The Evolution of Recrystallization Textures from Deformation Textures, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1995, 32(10), p 1689–1694
J. Lee, T. Konno, and H. Jeong, Grain Refinement and Texture Evolution in AZ31Mg Alloys Sheet Processed by Differential Speed Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2009, 161(1), p 166–169
Y.S. Sato et al., Microtexture in the Friction-Stir Weld of an Aluminum Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(4), p 941–948
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the ardent support from Jingxu Zheng (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) for polishing the English writing and providing valuable ideas of further structure adjustments in this paper. We also thank Ruichun Luo for modifying some of figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Lu, Y., Zheng, F. et al. Microstructural Investigation of Friction-Stir-Welded 7005 Aluminum Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 4297–4306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1764-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1764-y