Abstract
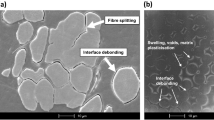
Modeling and prediction of the damage evolution in particle reinforced composites is a complex problem. Microstructure characters such as the particle morphologies, sizes, and distribution significantly affect the damage evolution in composites. A numerical simulation has been performed to investigate the damage evolution of SiCp/AA2009 composites. Tensile deformation in SiCp/AA2009 composites was simulated using the microstructure-based model constructed from the metallograph. Matrix damage, particle cracking, and interface debonding were simulated combining the ductile damage model, the normal stress criterion, and the maximum stress ratio criterion. The simulation results show that under tensile loading, damage initiates at the interface, and then propagates along the weakest direction. The simulation microstructures agree well with experimental results in which interface debonding, particle cracking, and matrix damage co-exist. In addition, the effects of component properties on the damage evolution are examined for various situations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Wang, W. Liang, and L. Zhou, Finite Element Simulation of the Failure Process of Single Fiber Composites Considering Interface Properties, Compos. B Eng., 2012, 45(1), p 573–580
S. Rudraraju, A. Salvi, K. Garikipati, and A.M. Waas, Experimental Observations and Numerical Simulations of Curved Crack Propagation in Laminated Fiber Composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2012, 72(10), p 1064–1074
B. Cox and Q. Yang, In Quest of Virtual Tests for Structural Composites, Science, 2006, 314(5802), p 1102–1107
J. Williams, J. Segurado, J. Lorca, and N. Chawla, Three Dimensional (3D) Microstructure-Based Modeling of Interfacial Decohesion in Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 557(15), p 113–118
J. Boselli, P. Pitcher, P. Gregson, and I. Sinclair, Numerical Modelling of Particle Distribution Effects on Fatigue in Al/SiCp Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 300(1), p 113–124
M. Li, S. Ghosh, T.N. Rouns, H. Weiland, O. Richmond, and W. Hunt, Serial Sectioning Method in the Construction of 3D Microstructures for Particle-Reinforced MMCs, Mater. Charact., 1998, 41(2), p 81–95
S. Ghosh and S. Moorthy, Three Dimensional Voronoi Cell Finite Element Model for Microstructures with Ellipsoidal Heterogeneities, Comput. Mech., 2004, 34(6), p 510–531
P. Kenesei, H. Biermann, and A. Borbely, Structure-Property Relationship in Particle Reinforced Metal-Matrix Composites Based on Holotomography, Scr. Mater., 2005, 53(7), p 787–791
L. Babout, E. Maire, and R. Fougeres, Damage Initiation in Model Metallic Materials: X-ray Tomography and Modelling, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(8), p 2475–2487
L.L. Mishnaevsky, Jr., Automatic Voxel-Based Generation of 3D Microstructural FE Models and Its Application to the Damage Analysis of Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 407(1), p 11–23
X. Deng and N. Chawla, Modeling the Effect of Particle Clustering on the Mechanical Behavior of SiC Particle Reinforced Al Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(17), p 5731–5734
J. Llorca, S. Suresh, and A. Needleman, An Experimental and Numerical Study of Cyclic Deformation in Metal-Matrix Composites, Metall. Trans. A, 1992, 23(3), p 919–934
J.C. Shao, B.L. Xiao, Q.Z. Wang, Z.Y. Ma, and K. Yang, An Enhanced FEM Model for Particle Size Dependent Flow Strengthening and Interface Damage in Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2011, 71(1), p 39–45
J. Segurado and J. LLorca, Computational Micromechanics of Composites: The Effect of Particle Spatial Distribution, Mech. Mater., 2006, 38(8), p 873–883
B. McWilliams, T. Sano, J. Yu, A. Gordon, and C. Yen, Influence of Hot Rolling on the Deformation Behavior of Particle Reinforced Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 577(10), p 54–63
W. Xu, X. Sun, D. Li, S. Ryu, and M.A. Khaleel, Mechanism-Based Representative Volume Elements (RVEs) for Predicting Property Degradations in Multiphase Materials, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2013, 68(2), p 152–159
A.L. Gurson, Continuum Theory of Ductile Rupture by Void Nucleation and Growth. Part I. Yield Criteria and Flow Rules for Porous Ductile Media, Division of Engineering, Brown University, Providence, RI, 1975
V. Tvergaard, Influence of Voids on Shear Band Instabilities Under Plane Strain Conditions, Int. J. Fract., 1981, 17(4), p 389–407
V. Tvergaard and A. Needleman, Analysis of the Cup-Cone Fracture in a Round Tensile Bar, Acta Metall., 1984, 32(1), p 157–169
H.-Y. Jeong, A New Yield Function and a Hydrostatic Stress-Controlled Void Nucleation Model for Porous Solids with Pressure-Sensitive Matrices, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2002, 39(5), p 1385–1403
Hibbitt, Karlsson, Sorensen. ABAQUS/Explicit: User’s Manual, Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen Incorporated, 2001
J. Segurado and J. LLorca, A Computational Micromechanics Study of the Effect of Interface Decohesion on the Mechanical Behavior of Composites, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(18), p 4931–4942
L.P. Canal, J. Segurado, and J. LLorca, Failure Surface of Epoxy-Modified Fiber-Reinforced Composites Under Transverse Tension and Out-of-Plane Shear, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2009, 46(11), p 2265–2274
Hibbitt, Karlsson, Sorensen. ABAQUS: Theory Manual, Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen Incorporated, 1997
P.P. Camanho and C.G. Davila, Mixed-Mode Decohesion Finite Elements for the Simulation of Delamination in Composite Materials, NASA Tech. Paper, 2002, 211737(1), p 1–37
Z.Y. Liu, Q.Z. Wang, B.L. Xiao, Z.Y. Ma, and Y. Liu, Effects of Double Extrusion on the Microstructure and Tensile Property of the P/M Processed SiCp/AA2009 Composites, Acta Metall. Sin., 2010, 46(9), p 1121–1127
G. Tursun, U. Weber, E. Soppa, and S. Schmauder, The Influence of Transition Phases on the Damage Behaviour of an Al/10 vol.% SiC Composite, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2006, 37(1), p 119–133
H. Zhang, K. Ramesh, and E. Chin, Effects of Interfacial Debonding on the Rate-Dependent Response of Metal Matrix Composites, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(17), p 4687–4700
M. Kiser, F. Zok, and D. Wilkinson, Plastic Flow and Fracture of a Particulate Metal Matrix Composite, Acta Mater., 1996, 44(9), p 3465–3476
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China under Grant No. 2012CB619600 and National High-tech R&D Program under Grant No. 2013AA030700. The authors would like to thank J. C. Shao and Q. Z. Wang for their helpful suggestion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kan, Y., Liu, Z.G., Zhang, S.H. et al. Microstructure-Based Numerical Simulation of the Tensile Behavior of SiCp/Al Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 1069–1076 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0805-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0805-7