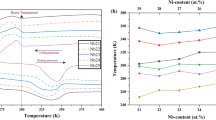
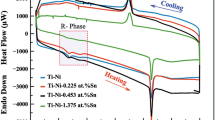
Abstract
Owing to their unique properties, NiTi-based shape memory alloys (SMAs) are highly attractive candidates for a lot of functional engineering applications like biomedical implants (stents), actuators, or coupling elements. Adding a third element is an effective measure to adjust or stabilize the phase transformation behavior to a certain extent. In this context, addition of alloying elements, which are low soluble or almost insoluble in the NiTi matrix is a promising approach and—with the exception of adding Nb—has rarely been reported in the literature so far, especially if the manufacturing of the net-shaped parts of these alloys is aspired. In the case of addition of elemental Nb, broadening of hysteresis between austenitic and martensitic phase transformation temperatures after plastic deformation of the Nb phase is a well-known effect, which is the key of function of coupling elements already established on the market. In the present study, we replaced Nb with additions of elemental Ag and W, both of which are almost insoluble in the NiTi matrix. Compared with Nb, Ag is characterized by higher ductility in combination with lower melting point, enabling liquid phase sintering already at moderate temperatures. Vice versa, addition of W might act in opposite manner considering its inherent brittleness combined with high melting temperature. In the present study, hot isostatic pressing was used for manufacturing such alloys starting from prealloyed NiTi powder and with the additions of Nb, Ag, and W as elemental powders. Microstructures, interdiffusion phenomena, phase transformation behaviors, and impurity contents were investigated aiming to better understand the influence of insoluble phases on bulk properties of NiTi SMAs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Saito, T. Wachi, and S. Hanada, A Study on the Machinability of a Ti Ni Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, 161, p 91–96
Y. Furuya, A. Sasaki, and M. Taya, Enhanced Mechanical Properties of TiNi Shape Memory Fiber/Al Matrix Composite, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1993, 34, p 224–227
M. Taya, Y. Yamamda, R. Watanabe, S. Shibata, and T. Mori, Strengthening Mechanism of TiNi Shape Memory Fiber/Al Matrix Composite, SPIE, 1992, 1916, p 373–383
S. Miyazaki, K. Otsuka, and Y. Suzuki, Transformation Pseudoelasticity and Deformation Behavior in a Ti-506 at% Ni Alloy, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1981, 15, p 287–292
J. Frenzel, E.P. George, A. Dlouhy, C. Somsen, M.X.F. Wagner, and G. Eggeler, Influence of Ni on Martensitic Transformations in NiTi Shape Memory Alloys, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 3444–3458
T.H. Nam, D.W. Chung, J.P. Noh, and H.W. Lee, Phase Transformation Behavior and Wire Drawing Properties of Ti-Ni-Mo Shape Memory Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36, p 4181–4188
T. Kurita, H. Matsumoto, K. Sakamoto, K. Tanji, and H. Abe, Effect of Aluminium on the Transformation of NiTi Alloy, J. Alloys Comp., 2005, 396, p 193–196
S. Besseghini, E. Villa, and A. Tuissi, NiTiHf Shape Memory Alloy: Effect of Aging and Thermal Cycling, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1999, A273–275, p 390–394
H. Hosoda et al., Martensite Transformation Temperatures and Mechanical Properties of Ternary NiTi Alloy with Offstoichiometric Compositions, Intermetallics, 1998, 6, p 291–301
F.J. Gil and J.A. Planell, Thermal Efficiencies of NiTiCu Shape Memory Alloys, Thermochim. Acta, 1999, 327, p 151–154
W. Siegert et al., Influence of Nb Content and Processing Conditions on Microstructure and Functional Properties of NiTiNb Shape-Memory Alloys, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2002, 394–395, p 361–364
V. Petzoldt, Formgedächtnistechnik Tiefbohren und Mikrofräsen von NiTi: Schriftenreihe ISF 2006
T.W. Duerig and K.N. Melton, Wide Hysteresis NiTiNb Alloys, The Martensitic Transformation in Science and Technology, E. Hornbogen and N. Jost, Ed., DGM Informationsgesellschaft mbH, Oberursel, 1989, p 191–198
C.S. Zhang et al., Effects of Deformation on the Transformation Hysteresis and Shape Memory Effect in a Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1990, 24, p 1807–1812
L.C. Zhao, T.W. Duerig, S. Justi, K.N. Melton, J.L. Proft, W. Yu, and C.M. Wayman, The Study of Niobium-Rich Precipitates in a NiTiNb Shape Memory Alloy, Scr. Metall., 1990, 24, p 221–225
A. Bansiddhi and D.C. Dunand, Shape-Memory NiTi-Nb Foams, J. Mater. Res., 2009, 24, p 2107–2117
T. Wu and M.H. Wu, NiTiNb Plugs for Sealing High Pressure Fuel Passages in Fuel Injector Applications, in Proceedings of International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies (SMST 2000), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2000, p 235–240
X. Zhao, X. Yan, Y. Yang, and H. Xu, Wide Hysteresis NiTi(Nb) Shape Memory Alloys with Low Nb Content (4.5 at.%), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 438–440, p 575–578
K.T. Oh, U.K. Joo, G.H. Park, C.J. Hwang, and K.N. Kim, Effect of Silver Addition on the Properties of Nickel-Titanium Alloys for Dental Application, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2006, 76, p 306–314
H. Enami, M. Hara, and H. Maeda, Effect of W Addition on the Martensitic Transformation and Shape Memory Behavior of the TiNi-Base Alloy, J. Phys. IV Fr., 1995, 5(C8), p 629–633
X.J. Yan, H. Gugel, S. Huth, and W. Theisen, Microstructures and Properties of Laser Cladding NiTi Alloy with W for Biomedical Applications, Mater. Lett., 2011, 65, p 2934–2936
D.S. Grummon, J.A. Shaw, and J. Foltz, Fabrication of Cellular Shape Memory Alloy Materials by Reactive Eutectic Brazing Using Niobium, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 438, p 1113–1118
S.F. Hsieh, S.K. Wu, H.C. Lin, and C.H. Yang, Transformation Sequence and Second Phases in Ternary Ti-Ni-W Shape Memory Alloys with Less Than 2 at% W, J. Alloys Comp., 2005, 387, p 121–127
C. Zamponi, M. Wuttig, and E. Quandt, Ni-Ti-Ag Shape Memory Thin Films, Scr. Mater., 2007, 56, p 1075–1077
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, R. Zarnetta, and A. Ludwig, The Effects of Grain Size on the Phase Transformation Properties of Annealed (Ti/Ni/W) Shape Memory Alloy Multilayers, Scr. Mater., 2011, 64, p 1047–1050
P.J.S. Buenconsejo, A. Siegel, A. Savan, S. Thienhaus, and A. Ludwig, Preparation of 24 Ternary Thin Film Materials Libraries on a Single Substrate on One Experiment for Irreversible High-Throughput Studies, ACS Combin. Sci., 2012, 14, p 25–30
http://jmmedical.com/resources/221/Nitinol-Technical-Properties.html. Accessed 15 April 2012
http://www.goodfellow.com/E/Niobium.html. Accessed 15 April 2012
http://www.goodfellow.com/E/Silver.html. Accessed 15 April 2012
http://www.goodfellow.com/G/wolfram.html. Accessed 15 April 2012
L. Krone, J. Mentz, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, D. Stöver, M. Wagner, G. Eggeler, D. Christ, S. Reese, D. Bogdanski, M. Köller, S.A. Esenwein, G. Muhr, O. Prymak, and M. Epple, The Potential of Powder Metallurgy for the Fabrication of Biomaterials on the Basis of Nickel-Titanium: A Case Study with a Staple Showing Shape Memory Behaviour, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2005, 7, p 613–619
J. Mentz, J. Frenzel, M.F.X. Wagner, K. Neuking, G. Eggeler, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver, Powder Metallurgical Processing of NiTi Shape Memory Alloys with Elevated Transformation Temperatures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 491, p 270–278
M. Bram, M. Bitzer, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver, Reproducibility Study of NiTi Parts Made by Metal Injection Moulding, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., 2012. doi:10.1007/s11665-012-0264-6.
J. Mentz, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver, Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Powder Metallurgical NiTi Shape Memory Alloys, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2006, 8, p 247–252
J. Mentz, L. Krone, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver, Influence of Heat Treatment on Properties of Hot Isostatic Pressed (HIP) NiTi, Int. Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies, SMST, 3-7 October 2004, Baden–Baden, Germany, 2006, p 489–494
J. Mentz, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, D. Stöver, Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Powder Metallurgical NiTi by Reduction of Impurity Phases, International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies SMST, 7-11 May 2006, B. Berg, M.R. Mitchell, J. Proft, Eds., Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2008, p 399–408
J. Khalil-Allafi, A. Dlouhy, and G. Eggeler, Ni4Ti3-Precipitation During Aging of NiTi Shape Memory Alloys and Its Influence on Martensitic Phase Transformations, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 4255–4274
W. Tang, B. Sundmann, R. Sandström, and C. Quiu, New Modelling of the B2 Phase and its Associated Martensitic Transformation in the Ti-Ni System, Acta Mater., 1999, 47, p 3457–3468
J. Di, L. Wen-xi, D. Zhr-zhong, H. Ming, and W. De-fa, Influence on Phase Composite and Mechanical Properties of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2003, 13, p 917–921
W. Siegert, K. Neuking, M. Mertmann, and G. Eggeler, First Cycle Shape Memory Effect in the Ternary NiTiNb System, J. Phys. IV Fr., 2003, 112, p 739–742
M. Piao, K. Otsuka, S. Miyazaki, and H. Horikawa, Mechanism of the As Temperature Increase by Pre-deformation in Thermoelastic Alloys, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1993, 10, p 919–929
A.P. Cysne Barbosa, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver, Fabrication of Titanium Implants with a Gradient in Porosity by 2-Component MIM, Powder Inject. Mould. Int. PIM, 2012, 6, p 69–73
H.A. Wriedt, The O-W (Oxygen-Tungsten) System, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr., 1989, 10, p 368–384
H. Okamoto, C-W (Carbon-Tungsten), J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2008, 29, p 543–544
K. Otsuka and X. Ren, Physical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-Based Shape Memory Alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2005, 50, p 511–678
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the research centre SFB 495 (shape memory technology) of Ruhr-Universität Bochum. Financial supports as well as contributions of Dr. D. Sebold (SEM images) and Mr. D. Rose (DSC-measurements) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies 2011, held November 6-9, 2011, in Hong Kong, China, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bitzer, M., Bram, M., Buchkremer, H.P. et al. Phase Transformation Behavior of Hot Isostatically Pressed NiTi-X (X = Ag, Nb, W) Alloys for Functional Engineering Applications. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 21, 2535–2545 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0375-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0375-0