Abstract
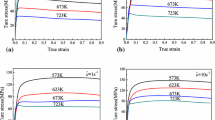
In this study, artificial neural network (ANN) was used to model the hot deformation behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy during compression test, in the strain rate range of 0.0003-1 s−1 and temperature range of 200-450 °C. The inputs of the model were temperature, strain rate, and strain, while the output of the model was the flow stress. The feed-forward back-propagation network with two hidden layers was built and successfully trained at different deformation domains by Levenberg-Marquardt training algorithm. Comparative analysis of the results obtained from the hyperbolic sine, the power law constitutive equations, and the ANN shows that the newly developed ANN model has a better performance in predicting the hot deformation behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Tiryakioglu, J.T. Staley, Physical Metallurgy and the Effect of Alloying Additions in Aluminum Alloys, Handbook of Aluminum. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, 2003
L. Jin-feng, P. Zhuo-wei et al., Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behaviors and Microstructures of 7075 Aluminum Alloy with Various Aging Treatments, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2008, 18, p 755–762
I.J. Polmear, Light Alloys from Traditional Alloys to Nanocrystals, 4th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann-Elsevier, Oxford, 2006
M.A. Choudhry and M. Ashraf, Effect of Heat treatment and Stress Relaxation in 7075 Aluminum Alloy, Alloys Compd., 2007, 437, p 113–116
S.L. Semiatin and J.J. Jonas, Formability and Workability of Metals Plastic instability and flow localization, American Society for Metals, Materials Park, OH, 1984
N. Ravichandran and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Dynamic Recrystallization During Hot Deformation of Aluminum: A Study Using Processing Maps, Metall. Trans., 1991, 22A, p 2339–2348
S.C. Medeiros, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, W.G. Frazier et al., Microstructural Modeling of Metadynamic Recrystallization in Hot Working of IN718 Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, A293, p 198–207
C.M. Sellars and W.J.Mc.G. Tegart, Hot Workability, Int. Metall., 1972, 17, p 1–24
A. Jenab and A. Karimi Taheri, Evaluation of Low Strain Rate Constitutive Equation of 7075 Aluminum Alloy at Hight Temperature, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, 27, p 1067–1072
M. Zhou and M.P. Clode, Constitutive Equation for Modeling Flow Softening Due to Dynamic Recovery and Heat Generation During Plastic Deformation, Mech. Mater., 1998, 27, p 63–76
A. Gholamzadeh and A. Karimi Taheri, The Prediction of Hot Flow Behavior of Al-6%Mg Alloy, Mech. Res. Commun., 2009, 36, p 252–259
R. Kapoor, D. Pal, and J.K. Chakravartty, Use of Artificial Neural Networks to Predict the Deformation Behavior of Zr-2.5Nb-0.5Cu, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2005, 169, p 199–205
S. Mandal, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, and K.P.N. Murthy, Constitutive Flow Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steels Under Hot Deformation: Artificial Neural Network Modelling to Understand, Evaluate and Predict, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2006, 14, p 1053–1070
Y.C. Lin, J. Zhang, and J. Zhong, Application of Neural Networks to Predict the Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of a Low Alloy Steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 752–758
A. Mahamood Hassan, A. Alrashdan, M.T. Hayajneh, and A. Turki Mayyas, Prediction of Density, Porosity and Hardness in Aluminum-Copper-Based Composite Materials Using Artificial Neural Network, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 894–899
I.S. Jalham, Modeling Capability of the Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to Predict the Effect of the Hot Deformation Parameters on the Strength of Al-Base Metal Matrix Composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2003, 63, p 63–67
L.X. Kong, P.D. Hodgson, and D.C. Collinson, Extrapolative Prediction of the Hot Strength of Austenitic Steels with a Combined Constitutive and ANN Model, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 102, p 84–89
J. Liu, H. Chang, T.Y. Hsu, Xu. Zuyao, and Xueyu. Ruan, Prediction of the Stress of High-Speed Steel During Hot Deformation Using a BP Artificial Neural Network, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 103, p 200–205
H.R. Hafizpour, M. Sanjari, and A. Simchi, Analysis of the Effect of Reinforcement Particles on the Compressibility of Al-SiC Composite Powders Using a Neural Network Model, Mater. Des., 2009, 30, p 1518–1523
W.S. Lee, W.C. Sue et al., The Strain Rate and Temperature Dependence of the Dynamic Impact Properties of 7075 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 100, p 116–122
J. Sheikh-Ahmad and J. Twomey, ANN Constitutive Model for High Strain-Rate Deformation of Al 7075-T6, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 186, p 339–345
H.E. Hu, L. Zhen, L. Yang et al., Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of 7050 Aluminum Alloy During High Temperature Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2008, A 488, p 64–71
T. Seshacharyulu, S.C. Medeiros, W.G. Frazier, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Microstructural Mechanisms During Hot Working of Commercial Grade Ti-6Al-4V with Lamellar Starting Structure, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, A 325, p 112–125
S.L. Semiatin, V. Seetharaman, and I. Weiss, Hot Workability of Titanium and Titanium Aluminide Alloys—An Overview, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, A243, p 1–24
J. May, H.W. Höppel, and M. Göken, Strain Rate Sensitivity of Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum Processed by Severe Plastic Deformation, Scripta Mater., 2005, 53, p 189–194
R.C. Picua, G. Vincze, F. Ozturk, J.J. Gracio, F. Barlat, and A.M. Maniatty, Strain Rate Sensitivity of the Commercial Aluminum Alloy AA5182-O, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 390, p 334–343
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2004
K.-L. Du and M.N.S. Swamy, Neural Networks in a Softcomputing Framework, Springer-Verlag London Limited, Berlin, 2006
P.M. Dixit and U.S. Dixit, Modeling of Metal Forming and Machining Processes by Finite Element and Soft Computing Methods, Brian Derby, Springer-Verlag London Limited, Berlin, 2008
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the research board and the Department of Materials Science and Engineering of Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, for the provision of research facilities used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenab, A., Karimi Taheri, A. & Jenab, K. The Use of ANN to Predict the Hot Deformation Behavior of AA7075 at Low Strain Rates. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 22, 903–910 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0332-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0332-y