Abstract
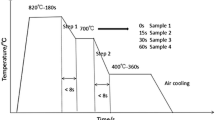
The influence of isothermal bainitic transformation (IBT) time on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-dip galvanized TRIP steel with 0.20C-1.50Mn-1.2Al-0.26Si was investigated using optical microscopy, x-ray diffraction (XRD), Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), dilatometry, and mechanical testing. This steel has high tensile strength of over 780 MPa with elongation more than 22%. The microstructure of the steel mainly consisted of ferrite, bainite, retained austenite, and martensite. The metastable austenite remaining after bainitic transformation will be transformed into martensite at the final cooling stage. The IBT time affects retained austenite content. When the IBT increased from 10 to 60 s, the amount of retained austenite increased from 9.40 to 15.42%, correspondingly. The IBT time also affects the strain hardening behavior. The n value characteristics of samples for IBT time from 10 to 30 s are similar to those of DP steel; however, the n value of specimen with IBT of 60 s shows features typical of TRIP steel.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. De Cooman, Structure-Properties Relationship in TRIP Steels Containing Carbide-Free Bainite, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, 8(3–4), p 285–303
B. Mintz, Hot Dip Galvanising of Transformation Induced Plasticity and Other Intercritically Annealed Steels, Int. Mater. Rev., 2001, 46(4), p 169–197
V.F. Zackay, E.R. Parker, D. Fahr, and R.A. Busch, The Enhancement of Ductility in High-Strength Steels, ASM Trans. Quart., 1967, 60(2), p 252–259
O. Matsumura, Y. Sakuma, and H. Takechi, Trip and Its Kinetic Aspects in Austempered 0.4C-1.5Si-0.8Mn Steel, Scripta Metall., 1987, 21(10), p 1301–1306
P.J. Jacques, E. Girault, A. Mertens, B. Verlinden, J. van Humbeeck, and F. Delannay, The Developments of Cold-rolled TRIP-Assisted Multiphase Steels. Al-Alloyed TRIP-Assisted Multiphase Steels, ISIJ Int., 2001, 41(9), p 1068–1074
H.T. Jiang, H.B. Wu, D. Tang, and Q. Liu, Influence of Isothermal Bainitic Processing on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Characterization of TRIP Steel, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing Miner. Metall., Mater., 2008, 15(5), p 574–579
E.M. Bellhousea and J.R. McDermid, Analysis of the Fe-Zn Interface of Galvanized High Al-Low Si TRIP Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 491(1–2), p 39–46
E.M. Bellhouse, A.I.M. Mertens, and J.R. McDermid, Development of the Surface Structure of TRIP Steels Prior to Hot-Dip Galvanizing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 463(1–2), p 147–156
L. Li, B.C. De Cooman, R.D. Liu, J. Vleugels, M. Zhang, and W. Shi, Design of TRIP Steel with High Welding and Galvanizing Performance in Light of Thermodynamics and Kinetics, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2007, 14(6), p 37–41
A.K. De, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock, Color Tint-Etching for Multiphase Steels, Adv. Mater. Process., 2003, 161(2), p 27–30
K. Sugimotom, M. Misu, M. Kobayashi, and H. Shirasawa, Effects of Second Phase Morphology on Retained Austenite Morphology and Tensile Properties in a TRIP-Aided Dual-Phase Steel Sheet, ISIJ Int., 1993, 33(7), p P775–P782
S.J. Kim, C.G. Lee, T.H. Lee, and C.S. Oh, Effect of Cu, Cr and Ni on Mechanical Properties of 0.15 wt.% C TRIP-Aided Cold Rolled Steels, Scripta Mater., 2003, 48(5), p 539–544
Y. Sakuma, D.K. Matlock, and G. Krauss, Intercritically Annealed and Isothermally Transformed 0.15 Pct C Steels Containing 1.2 Pct Si-1.5 Pct Mn and 4 Pct Ni: Part I. Transformation, Microstructure, and Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1992, 23(A), p 1221–1232
M.H. Saleh and R. Priestner, Retained Austenite in Dual-Phase Silicon Steels and Its Effect on Mechanical Properties, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, 113(1–3), p 587–593
Acknowledgment
This investigation was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50804005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Tang, D., Jiang, H. et al. Influence of Isothermal Bainite Transformation Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hot-Dip Galvanized TRIP Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 997–1002 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9714-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9714-1