Abstract
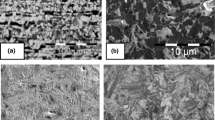
The influence of low chromium additions to a 0.25C-1.5Mn semikilled steel on microstructure, and tensile and impact behaviors of high strength rock bolt reinforcing bars has been investigated. Although chromium imparted adequate tensile properties at ambient temperature (yield stress: 624 MPa; ultimate tensile stress: 819 MPa; elongation: 12.5%) by forming transformation products such as tempered martensite, lower and upper bainite, and small amounts of acicular ferrite, it increased the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature due to coarser upper bainite in the core region of bar having larger unit crack paths. The synthesized steel is considered to be effective in realizing the desired tensile properties, and suitable for application in rock bolt, as well as other reinforced concrete structures.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standard Specifications for Roof and Rock Bolts and Accessories, ASTM F 432-04, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 2006, 01.08, p 107-121
S. Hashimoto and M. Nakamura, Effect of Microalloying Elements on Mechanical Properties of Reinforcing Bars, Trans. ISIJ Int., 2006, 46(10), p 1510–1515
H. Weise, W. Kramer, W. Bartels, and W.D. Brand, Reinforcing Steel for Reinforced Concrete and Prestressed Concrete Structures, Steel, Vol 2, 1st ed., Springer Verlag, New York, 1992, p 61–76
A.B. Yure’v, Y.F. Ivanov, V.E. Gromov, and E.V. Kozlov, Structural-Phase State of Thermostrengthened Large Diameter Reinforcement, Steel Transl., 2004, 34(6), p 69–72
B.K. Panigrahi and S.K. Jain, Impact Toughness of High Strength Low Alloy TMT Reinforcement Bar, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2002, 25(4), p 319–324
B.K. Panigrahi, Microstructure-Related Properties of Some Novel Reinforcement Bar Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (online). doi:10.1007/s11665-009-9456-0
B.K. Panigrahi, S. Srikanth, and G. Sahoo, Effect of Alloying Elements on Tensile Properties, Microstructure, and Corrosion Resistance of Reinforcing Bar Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (online). doi:10.1007/s11665-008-9336-z
Y.T. Khudik, A.V. Ivchenko, O.A. Chaikovski, S.A. Madatyan, M.I. Kostyuchenko, and J.N. Surikov, Thermomechanically Strengthened 25 G2S Reinforcing Steel of Strength Class at IVS, Steel USSR, 1988, 18(6), p 272–277
V.I. Stolyarov, V.N. Nikiten, L.J. Efron, and V.G. Laz’ko, Status and Outlook of Production Technology for 700 N/mm2 Yield Strength Weldable Steels, Steel Transl., 1993, 23(6), p 27–32
I.G. Uzlov, Y.T. Khudik, and V.T. Chernenko, Optimisation of Service Properties of Thermomechanically Strengthened Reinforcing Steel, Steel Transl., 1993, 19(11), p 500–502
W. Dahl, Mechanical Properties, Steel, Vol 1, 1st ed., Springer Verlag, New York, 1992, p 203–378
T.N. Baker, Microalloyed Steels, Science Progress, Vol 65, Blackwell Scientific Publisher, Oxford, 1978, p 493–542
M. Sarkaya, B.G. Steinberg, and G. Thomas, Optimisation of Fe/Cr/C Base Structural Steel for Improved Strength and Toughness, Met. Trans., 1982, 13A(12), p 2227–2237
W. Pitsch and G. Sauthoff, Typical Microstructures in Steel, Steel, Vol 1, 1st ed., Springer Verlag, New York, 1992, p 83
H.J. Aaronson, W.T. Reynolds, G.J. Shiflet, and G. Spanos, Bainite Viewed Three Different Ways, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(6), p 1343–1380
H. Ohtani, S. Okaguchi, Y. Fuzishiro, and Y. Ohmori, Morphology and Properties of Low Carbon Bainite, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A, p 877–888
S. Morooka, Y. Tomota, and T. Kamiyama, Heterogenous Deformation Behavior Studied by In-Situ Neutron Diffraction During Tensile Deformation for Ferrite, Martensite, and Pearlite Steel, ISIJ Int., 2008, 48(4), p 525–530
S. Barnard, G.D.W. Smith, M. Sarikaya, and G. Thomas, Carbon Atom Distribution in a Dual Phase Steel: An Atom Probe Study, Scr. Metall., 1981, 15(4), p 387–392
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, SI Metric Edition, Part 3, Chap. 9, McGraw-Hill Book Co., London, 1988, p 325–337
G. Spanos, H.S. Fang, and H.I. Aaronson, A Mechanism for the Formation of Lower Bainite, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(6), p 1381–1390
R.W.K. Honeycombe and F.B. Pickering, Ferrite and Bainite in Alloy Steels, Met. Trans., 1972, 3(5), p 1099–1112
R.W.K. Honeycombe, Structure and Strength of Alloy Steels, Climax Molybdenum Co., London, 1971, p 1–36
B.L. Bramfitt and J.G. Speer, A Perspective on the Morphology of Bainite, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(4), p 817–829
F.B. Pickering, Physical Metallurgy and Design of Steels, Chap. 6, 1st ed., Applied Science Publishers, London, 1978
D.V. Edmonds and R.C. Cochrane, Structure-Property Relationships in Bainitic Steel, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(6), p 1527–1540
B. Dogan and J.D. Boyd, Through Thickness Failure of Ti-V-N Steel, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(5), p 1177–1191
M.L. Joki, V. Vitek, and C.J. McMahon, A Microscopic Theory of Brittle Fracture in Deformable Solids: A Relation Between Ideal Work to Fracture and Plastic Work, Acta Metall., 1980, 28(11), p 1479–1488
D. Kwon and R.J. Asaro, A Study of Void Nucleation, Growth, and Coalescence in Spherodised 1518 Steel, Met. Trans., 1990, 21A(1), p 117–134
W.D. Biggs, Fracture, Physical Metallurgy, 2nd revised ed., R.W. Cahn, Ed., North Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, 1970, p 1199–1232
W.C. Leslie, The Physical Metallurgy of Steels, McGraw Hill International Book Co., New York, p 289–300
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due the management of Steel Authority of India Limited, Bhilai Steel Plant, and Research & Development Center for Iron and Steel, Ranchi, where the work was carried out. Thanks are also due Mr. C.B. Sharma, Mr. A.K. Singh, Mr. B.B. Patra, Mr. John Guria, and Mr. S.N. Hoda for microstructural and tensile tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panigrahi, B.K. Microstructure-Mechanical Property Relationships for a Fe/Mn/Cr Rock Bolt Reinforcing Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 19, 885–893 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9540-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9540-5