Abstract
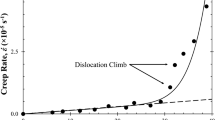
Because of the high homologous operation temperature of solders used in electronic devices, time and temperature dependent relaxation and creep processes affect their mechanical behavior. In this paper, two eutectic lead-free solders (96.5Sn-3.5Ag and 91Sn-9Zn) are investigated for their creep and stress relaxation behavior. The creep tests were done in load-control with initial stresses in the range of 10-22 MPa at two temperatures, 25 and 80°C. The stress relaxation tests were performed under constant-strain conditions with strains in the range of 0.3-2.4% and at 25 and 80°C. Since creep/relaxation processes are active even during monotonie tensile tests at ambient temperatures, stress-strain curves at different temperatures and strain rates provide insight into these processes. Activation energies obtained from the monotonic tensile, stress relaxation, and creep tests are compared and discussed in light of the governing mechanisms. These data along with creep exponents, strain rate sensitivities and damage mechanisms are useful for aiding the modeling of solder interconnects for reliability and lifetime prediction. Constitutive modeling for creep and stress relaxation behavior was done using a formulation based on unified creep plasticity theory which has been previously employed in the modeling of high temperature superalloys with satisfactory results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Mei, J.W. Morris, Jr. and M.C. Shine, J. Electron. Packaging 113, 109 (1991).
D. Tribula and J.W. Morris, Jr., J. Electron. Packaging, 112, 87 (1990).
D.S. Stone, J. Electron. Packaging 112, 100 (1990).
J.K. Tien, B.C. Hendrix and A.I. Attarwala, J. Electron. Packaging 113, 115 (1991).
A.I. Attarwala, J.K. Tien, G.Y. Msada and G. Dody, J. Electron. Packaging 114, 109 (1992).
E.W. Hare and R.G. Stang, J. Electron. Mater. 24,473 (1995).
G.S. Murty, J. Mater. Sci. 8, 611 (1973).
Z. Mei and J.W. Morris, J. Electron. Mater. 21, 599 (1992).
D.L. McDowell, M.P. Miller and D.C. Brooks, ASTM STP 1153, (Philadelphia, PA: ASTM, 1994), p. 42.
John H. Lau, ed., Thermal Stress and Strain in Microelectronics Packaging, (New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1993), p. 67.
Z. Guo, A.F. Sprecher and H. Conrad, J. Electron. Packaging 114, 112 (1992).
George E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1986), p. 295.
Robert E. Reed-Hill and Reza Abbaschian, Physical Metallurgy Principles, 3rd ed. (Boston: PWS-Kent Publishing Co., 1992), p. 836.
W. Lange and D. Bergner, Phys. Stat. Sol. 2, 1410 (1962).
N.H. Natchtrieb and G.S. Handler, J. Chem. Phys. 23, 1569 (1955).
H. Mavoori and J. Chin, Proc. 45th Electronic Comp. and Tech. Conf. 1, (New York: IEEE, 1995), p. 990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mavoori, H., Chin, J., Vaynman, S. et al. Creep, stress relaxation, and plastic deformation in Sn-Ag and Sn-Zn eutectic solders. J. Electron. Mater. 26, 783–790 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-997-0252-z
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-997-0252-z