Abstract
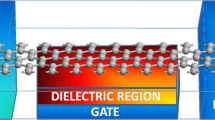
Modeling of a graphene nanoribbon field effect transistor (GNRFET) as a frequency doubler has been extensively explored for developing future communication applications. For its analysis, different types of modifications are applied to the GNRFET model simulated in a Hewlett simulation program with an integrated circuit. The model is demonstrated for its frequency response and conversion gain. It uses an intrinsic GNRFET for frequency doubling which clearly shows a distortionless sinusoidal output at a peak frequency of 20.6 MHz for an applied input of 10.3 MHz. However, after applying doping at different fractions of 0.3%, 3% and 30% in the transistor model, signal decay appears at 30% doping fractions. Results are also shown for increasing the number of dimers (N), increasing the number of channels for conduction and the impact of changing the dielectric constant on the doubler model performance. It is found that as the channel width increases, an increase in the conversion gain from − 26.05 dB to − 20 dB results from an increase in N from 8 to 20 dimer lines. Further, if four graphene nanoribbon (GNR) channels are used in the doubler operation instead of one GNR channel, then a high conversion gain of − 16.47 dB as compared to − 26.05 dB for an individual GNR channel is also calculated. Regarding the impact of different dielectrics, it is revealed that, similar to a conventional transistor, a graphene transistor with a high-K-value dielectric presents the highest gain, but with a high distortion in the output signal. However, using a conventional silicon dioxide (SiO2) dielectric having a low K value gives lower conversion gain, but ideal frequency doubling in the output is attained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. Choudhury, Y. Yoon, J. Guo, and K. Mohanram, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10, 727 (2011).
T. Palacios, A. Hsu, and H. Wang, IEEE Commun. Mag. 48, 122 (2010).
F. Schwierz, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 487 (2010).
P. Sharma, S. Singh, S. Gupta, and I. Kaur, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 7668 (2017).
M.E. Ramón, K.N. Parrish, S.F. Chowdhury, C.W. Magnuson, H.C. Movva, R.S. Ruoff, S.K. Banerjee, and D. Akinwande, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11, 877 (2012).
H. Wang, A. Hsu, K.K. Kim, J. Kong, and T. Palacios, in Proceedings of the IEEE Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (IEEE, 2010), pp 23.6.1–23.6.4.
H. Wang, D. Nezich, J. Kong, and T. Palacios, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30, 547 (2009).
C. Cheng, B. Huang, X. Mao, Z. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Z. Geng, P. Xue, and H. Chen, Sci. Rep. 7, 46605 (2017).
H. Wang, A. Hsu, J. Wu, J. Kong, and T. Palacios, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 906 (2010).
C. Chen, S. Lee, V.V. Deshpande, G.-H. Lee, M. Lekas, K. Shepard, and J. Hone, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 923 (2013).
Y.-Y. Chen, A. Rogachev, A. Sangai, G. Iannaccone, G. Fiori, D. Chen, in Proceedings of the Design, Automation and Test in Europe (EDA Consortium) (2013), pp 1789–1794.
Z. Hu, D. Prasad Sinha, J. Ung Lee, and M. Liehr, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 194507 (2014).
P. Vimala and N.B. Balamurugan, J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 9, 649 (2014).
H. Wang, A.L. Hsu, and T. Palacios, IEEE Microw. Mag. 13, 114 (2012).
J.W. Chung, W.E. Hoke, E.M. Chumbes, and T. Palacios, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 195 (2010).
Y.-M. Lin, K.A. Jenkins, A. Valdes-Garcia, J.P. Small, D.B. Farmer, and P. Avouris, Nano Lett. 9, 422 (2008).
M.E. Ramón, K.N. Parrish, S.F. Chowdhury, C.W. Magnuson, H.C. Movva, R.S. Ruoff, S.K. Banerjee, and D. Akinwande, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11, 877 (2012).
M. Gholipour, Y.-Y. Chen, A. Sangai, N. Masoumi, and D. Chen, IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2, 650 (2016).
H. Liu, Y. Liu, and D. Zhu, J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3335 (2011).
S.S. Chauhan, P. Srivastava, and A.K. Shrivastava, Solid State Commun. 154, 69 (2013).
Y. Liang, X. Liang, Z. Zhang, W. Li, X. Huo, and L. Peng, Nanoscale 2015, 10954 (2015).
J. Zheng, L. Wang, R. Quhe, Q. Liu, H. Li, D. Yu, W.-N. Mei, J. Shi, Z. Gao, and J. Lu, Sci. Rep. 3, 1314 (2013).
W.-X. Wang, M. Zhou, X. Li, S.-Y. Li, X. Wu, W. Duan, and L. He, Phys. Rev. B 93, 241403 (2016).
D.Y. Jung, S.Y. Yang, H. Park, W.C. Shin, J.G. Oh, B.J. Cho, and S.-Y. Choi, Nano Converg. 2, 11 (2015).
P. Sharma, S. Singh, S. Gupta, and I. Kaur, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 2883 (2018).
L. Liao, J. Bai, Y.-C. Lin, Y. Qu, Y. Huang, and X. Duan, Adv. Mater. 22, 1941 (2010).
I. Meric, C.R. Dean, N. Petrone, L. Wang, J. Hone, P. Kim, and K.L. Shepard, in Proceedings of the IEEE (2013), pp. 1609–1619.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Gupta, S. & Kaur, I. Design and Simulation of a Frequency Doubler Using Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistors for Communication Devices. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 3043–3049 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07068-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07068-y



