Abstract
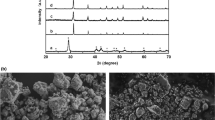
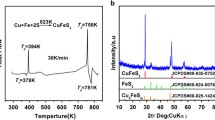
The use of microwave energy for materials processing has a major potential and real advantages over conventional heating such as (1) time and energy savings, (2) rapid heating rates (volumetric heating vs. conduction), (3) considerably reduced processing time and temperature, (4) fine microstructures and hence improved mechanical properties and better product performance, and (5) finally lower environmental impact. In this study, we investigated the use of microwave-assisted synthesis to synthesize a series of Co1−x Fe x Sb3 using this novel approach, which gave high quality materials with little or no impurities in a fraction of the time needed for conventional synthesis. X-ray diffraction analysis was used to examine the structure and the lattice parameters of the samples, while scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy was used to study the morphology of the compounds. The samples were sintered by spark plasma sintering, and the highest ZT of 0.33 was obtained for x = 0.2 at 700 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Slack and V.G. Tsoukala, J. Appl. Phys. 76, 1665 (1994).
J.W. Sharp, E.C. Jones, R.K. Williams, P.M. Martin, and B.C. Sales, J. Appl. Phys. 78, 1013 (1995).
D.T. Morelli and G.P. Meisner, Phys. Rev. B 56, 7376 (1997).
M. Martín-González, O. Caballero-Calero, and P. Díaz-Chao, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 24, 288 (2013).
B.C. Sales, D. Mandrus, and R.K. Williams, Science 272, 1325 (1996).
G.S. Nolas, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 29, 89 (1999).
G.S. Nolas, Phys. Rev. B 58, 164 (1998).
L.D. Chen, J. Mater. Res. 16, 3343 (2001).
T. Caillat, J.-P. Fleurial, A. Borshchevsky, and J. Vandersande, Phys. Rev. B 51, 9622 (1995).
G.S. Nolas, M.R. Kaeser, T. Littleton IV, and T.M. Tritt, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 51855–51857 (2000).
L. Nordström and D.J. Singh, Phys. Rev. B 53, 1103 (1996).
Y. Kawaharada, K. Kurosaki, M. Uno, and S. Yamanaka, J. Alloys Compd. 315, 193 (2001).
S.-C. Ur, J.-C. Kwon, and I.-H. Kim, J. Alloys Compd. 442, 358 (2007).
I.-H. Kim and S.-C. Ur, Mater. Lett. 61, 2446 (2007).
N. Dong, X. Jia, T.C. Su, F.R. Yu, Y.J. Tian, Y.P. Jiang, L. Deng, and H.A. Ma, J. Alloys Compd. 480, 882 (2009).
C. Zhou, J. Sakamoto, D. Morelli, X. Zhou, and G. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 063722 (2001).
S. Katsuyama, Y. Shichijo, M. Ito, K. Majima, and H. Nagai, J. Appl. Phys. 84, 6708 (1998).
X. Zhang, Q.M. Lu, J.X. Zhang, Q. Wei, D.M. Liu, and Y.Q. Liu, J. Alloys Compd. 457, 368 (2008).
J. Arreguin-Zavala, D. Vasilevskiy, S. Turenne, and R.A. Masut, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1992 (2013).
K. Biswas, S. Muir, and M.A. Subramanian, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2288 (2011).
L.J. van der Pauw, Philips Res. Rep. 13, 1 (1958).
O. Boffoué, A. Jacquot, A. Dauscher, B. Lenoir, and M. Stölzer, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 053907 (2005).
M. Rotter, ed., 25th International Conference on Thermoelectrics (EEE-Cat-No.-06TH8931, Aug 6–10, 2006, Vienna, Austria).
J. Peng, J. Yang, T. Zhang, X. Song, and Y. Chen, J Alloys Compd. 381, 313 (2004).
J. Peng, J. Yang, X. Song, Y. Chen, S. Bao, and T. Zhang, Front. Mater. Sci. China 1, 177 (2007).
X. Xia, P. Qiu, X. Huang, S. Wan, Y. Qiu, X. Li, and L. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. (2013). doi:10.1007/s11664-013-2820-8.
J.X. Zhang, Q.M. Lu, K.G. Liu, L. Zhang, and M.L. Zhou, Mater. Lett. 58, 1981 (2004).
K.-H. Park, J.-Y. Jung, S.-C. Ur, and I.-H. Kim, Phys. Scr. T139, 014009 (2010).
M.Y. Tafti, M. Saleemi, A. Jacquot, M. Jägle, M. Muhammed, and M.S. Toprak, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1543 (2013). doi:10.1557/opl.2013.947.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the European Project “NEXTEC” FP7-NMP-201-1.2-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ioannidou, A.A., Rull, M., Martin-Gonzalez, M. et al. Microwave Synthesis and Characterization of the Series Co1−x Fe x Sb3 High Temperature Thermoelectric Materials. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 2637–2643 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3197-z