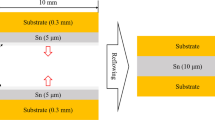
The drying and densification behavior of a nanosilver paste was studied by shrinkage and weight-loss measurements to provide fundamental understanding on the sintering behavior of the nanomaterial for packaging power devices and modules. The measured shrinkage behavior was found to be in good agreement with the weight-loss behavior of the paste as measured by thermogravitational analysis, and the comparison offered direct evidence of ~10% shrinkage contributed by late-stage densification of silver nanoparticles (NPs). It was found that sintered silver joints could be achieved without cracks or delamination under a ramp-soak temperature profile for bonding small-area chips, e.g., 3 mm × 3 mm or smaller. However, for bonding large-area chips, e.g., 5 mm × 5 mm or larger, rapid evaporation of the entrapped organic species caused the chips to delaminate, leading to large longitudinal cracks at the joint interface. Finally, examination of the microstructure evolution of the silver die-attach material revealed that binder molecules inhibited necking of the silver NPs and delayed densification during the sintering process of the nanosilver paste.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Schwarzbauer, U.S. patent 4,810,672 (March 1989).
H. Schwarzbauer and R. Kuhnert, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 27, 93 (1991).
U. Scheuermann and U. Hecht, PCIM, Nuremberg, PE4.5, 59 (2002).
R. Amro, J. Lutz, J. Rudzki, R. Sittig and M. Thoben, the 18th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & IC’s, Naples (2006).
P. Beckedahl, PCIM, Nuremberg, 5 (2007).
C. Göbl, P. Beckedahl and H. Braml, Automotive Power Electron., Paris, 1 (2006).
L. Dupont, G. Coquery, K. Kriegel, and A. Melkonyan, Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 1375 (2009).
U. Scheuermann, Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 1319 (2009).
L. Feller, S. Hartmann, and D. Schneider, Microelectron. Reliab. 48, 1161 (2008).
C. Göbl and J. Faltenbacher, CIPS, Nurnberg (2010).
T. Licht, R. Speckels and M. Thoben, CIPS, Nurnberg (2010).
J.G. Bai, Z.Z. Zhang, J.N. Calata, and G.-Q. Lu, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 29, 589 (2006).
J.G. Bai, T.G. Lei, J.N. Calata, and G.-Q. Lu, J. Mater. Res. 22, 7 (2007).
J.G. Bai and G.-Q. Lu, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 6, 436 (2006).
T. Wang, X. Chen, Lu. G-Q, and T.G. Lei, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 1333 (2007).
X. Chen, R. Li, K. Qi, and G.-Q. Lu, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1574 (2008).
T.G. Lei, J.N. Calata, Lu. G-Q, X. Chen, and S. Luo, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 33, 98 (2010).
T. Wang, T. G. Lei, G-Q. Lu, X. Chen and L. Guido, ICEPT-HDP, Beijing, 581 (2009).
J.N. Calata, T.G. Lei, and G.-Q. Lu, Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 34, 95 (2009).
A. Sin, B. El Montaser, P. Odier, and F. Weiss, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1928 (2002).
V.V. Srdic, M. Winterer, and H. Hahn, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 1853 (2000).
S. Takayuki, H. Naoto, and K. Katsutoshi, Nanotechnology 14, 487 (2003).
S.B. Fuller, E.J. Wilhelm, and J.M. Jacobson, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 11, 54 (2002).
N.B. Bell, C.B. DiAntonio, and D.B. Dimos, J. Mater. Res. 17, 2423 (2002).
G-Q Lu, G. Lei and J. N. Calata, USPTO Class: 4,273,833 (2009).
J.W. Choe, J.N. Calata, and G.-Q. Lu, J. Mater. Res. 10, 986 (1995).
L.H. Liang, C.M. Shen, S.X. Du, W.M. Liu, X.C. Xie, and H.J. Gao, Phys. Rev. B 70, 205419 (2004).
C. Huang, M.F. Becker, J.W. Keto, and D. Kovara, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 054308 (2007).
S. Iwama and T. Sahashi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 19, 1039 (1980).
M. Yeadon, J.C. Yang, R.S. Averback, J.W. Bullard, D.L. Olynick, and J.M. Gibson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 1631 (1997).
Y.C. Lin and J.H. Jean, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87, 187 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhao, M., Chen, X. et al. Shrinkage and Sintering Behavior of a Low-Temperature Sinterable Nanosilver Die-Attach Paste. J. Electron. Mater. 41, 2543–2552 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2134-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2134-2