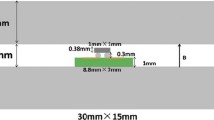
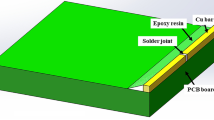
Morphological changes from electromigration were examined on microsized Sn-Ag-Cu, pure Sn, and single-crystal Sn solder interconnects. It was found that both grain structure and alloying had a strong influence on the form of electromigration damage. In polycrystal Sn, grain boundary grooves were the primary form of electromigration damage, while in single-crystal Sn interconnects wavy surface relief appeared following electromigration. Alloying with Ag and Cu encouraged formation of Sn hillocks and Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound (IMC) segregation. The grain boundary grooves were related to the divergence of the vacancy concentration at grain boundaries, which induced Sn grain tilting or sliding. Removal of the grain boundaries in the single-crystal interconnect made surface diffusion the primary electromigration mechanism, resulting in wavy surface relief after long electromigration time. In Sn-Ag-Cu alloy, directional flow of Cu caused Cu6Sn5 IMC segregation, which produced large compressive stress, driving the stressed grains to grow into hillocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Zeng and K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 38, 55 (2002).
K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003).
Y.C. Chan and D. Yang, Prog. Mater. Sci. 55, 428 (2010).
L. Zhang, Z.G. Wang, and J.K. Shang, Scripta Mater. 56, 381 (2007).
H.Y. Liu, Q.S. Zhu, L. Zhang, Z.G. Wang, and J.K. Shang, J. Mater. Res. 5, 1172 (2010).
H.Y. Liu, Q.S. Zhu, Z.G. Wang, and J.K. Shang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 1467 (2011).
F. Ren, J.W. Nah, K.N. Tu, B.S. Xiong, L.H. Xu, and H.L. Pang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 141914 (2006).
X.J. Wang, Q.S. Zhu, Z.G. Wang, and J.K. Shang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26, 737 (2010).
S. Branderburg and S. Yeh, Proceeding of Surface Mount International Conference and Exposition, San Jose, CA (1998).
Q.L. Yang and J.K. Shang, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1363 (2005).
Y.C. Hu, Y.H. Lin, C.R. Kao, and K.N. Tu, J. Mater. Res. 18, 2544 (2003).
Y.H. Lin, Y.C. Hu, C.R. Kao, and K.N. Tu, Acta Mater. 53, 2029 (2005).
W.J. Boettinger, C.E. Johnson, L.A. Bendersky, K.W. Moon, M.E. Williams, and G.R. Stafford, Acta Mater. 53, 5033 (2005).
H. Gan and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 063514 (2005).
A.T. Wu and T.C. Hsieh, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 121921 (2008).
A.T. Wu, K.N. Tu, J.R. Lloyd, N. Tamura, B.C. Valek, and C.R. Kao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 2490 (2004).
H.Y. Hsiao and C. Chen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 152105 (2007).
A.T. Huang, A.M. Gusak, K.N. Tu, and Y.S. Lai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 141911 (2006).
B.F. Dyson, T.R. Anthony, and D. Turnbull, J. Appl. Phys. 38, 3408 (1967).
K.N. Tu, Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter 49, 2030 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Q.S., Liu, H.Y., Wang, Z.G. et al. Surface Morphology of Sn-Rich Solder Interconnects After Electrical Loading. J. Electron. Mater. 41, 741–747 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-1932-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-1932-x