Abstract
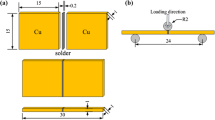
To investigate the effect of stand-off height (SOH) on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of certain solder joints, Cu/Sn9Zn/Cu solder joints with a SOH of 100 μm, 50 μm, 20 μm, and 10 μm were prepared and studied. It was found that, as the SOH is reduced, the Zn content in the solder bulk experiences a rapid decrease due to consumption by metallurgical reaction in the reflow process; hence, the microstructure of the solder bulk is changed significantly from a Sn-Zn eutectic structure to a hypoeutectic structure. By contrast, Cu content in the solder bulk experiences a rapid increase with reducing SOH, and this leads to more dissociative intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in the solder bulk. These compositional and microstructural changes induced by reducing the SOH correlate closely with the mechanical properties of the solder joints. In our study it is found that, as SOH is reduced, the tensile strength of the solder joints decreases, the fracture path of the solder joint transfers from the solder bulk into the interface between the IMC layer and the solder bulk, and the fracture mode tends to change from ductile to brittle. These findings point to a probable way to improve the mechanical properties of miniaturized solder joints by controlling the composition and dissociative IMCs in the solder bulk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.Plieninger, M.Dittes, K.Pressel, Microelectron. Reliab. 46, 1868 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.microrel.2006.08.008
F. Wu, M. He, Y. Wu, B. An, and W. Zhang, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT’06), Shanghai, China, 26–29 August (2006), pp. 1–5
A. Sharif, Y.C. Chan, and R.A. Islam, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 106, 120 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2003.09.003
L. Quan, D.R. Frear, D. Grivas, J.W. Morris Jr., J. Electron. Mater. 16, 203 (1987) doi:10.1007/BF02655488
K.H. Prakash, T. Sritharan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 379, 277 (2004) doi:10.1016/j.msea.2004.02.049
B.S. Chiou, J.H. Chang, J.G. Duh, IEEE Trans. CPMT-B 18, 537 (1995)
K. Zeng, K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 38, 55 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0927-796X(02)00007-4
M. Date, T. Shoji, M. Fujiyoshi, K. Sato, and K.N. Tu, Proceedings of the 54th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV (2004), pp. 668–674
B.I.Noh, J.M.Koo, J.W.Kim, D.G.Kim, J.D.Nam, J.Joo, S.B.Jung, Intermetallics, 14, 1375 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.intermet.2005.11.036
F.-Y. Hung, T.-S. Lui, L.-H. Chen, J.-G. You, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3865 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0463-3
Solder Data Sheet, Welco Castings, 2 Hillyard Street, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60776033), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2006AA04A110). The authors also acknowledge the Analytical and Testing Center of HUST for their analytical work, and acknowledge Peter Talbot and Huibin Zheng for their kind help with the revision of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Wang, B., Du, B. et al. Effect of Stand-Off Height on Microstructure and Tensile Strength of the Cu/Sn9Zn/Cu Solder Joint. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 860–865 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0723-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0723-5