Abstract
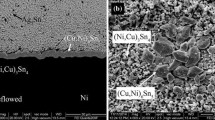
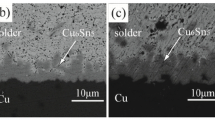
The growth kinetics of the intermetallic compound (IMC) layer formed between two low melting point solders and electrolytic Ni/Cu substrate by solid-state isothermal aging were examined. The solders were 100 In and In-48Sn. A quantitative analysis of the IMC layer thickness as a function of aging time and aging temperature was performed. Experimental results showed that the IMCs, such as In27Ni10 and Ni3(In, Sn)4), were observed for different solders. Additionally, the growth rate of these IMCs increased with the aging temperature and time. The layer growth of the IMC in the couples of indium solder alloy/electrolytic Ni system satisfied the parabolic law at a given temperature range. As a whole, because the values of the time exponent (n) are approximately 0.5, the layer growth of the IMC was mainly controlled by the diffusion mechanism over the temperature range studied. The apparent activation energies for IMC growth were 60.03 kJ/mol for In27Ni10 and 72.84 kJ/mol for Ni3(In, Sn)4.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.B. Lee, S.B. Jung, Y.E. Shin, and C.C. Shur, Mater. Trans. 42, 751 (2001).
J. Glazer, Int. Mater. Rev. 40, 65 (1995).
K. Suganuma, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 5, 55 (2001).
M. McCormack and S. Jin, JOM 45, 36 (1993).
Y.M. Liu and T.H. Chuang, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 405 (2000).
H.H. Manco, Solders and Soldering, 3rd ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1992), pp. 128–130.
C.L. Yu, S.S. Wang, and T.H. Chuang, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 488 (2002).
C.C. Lee, C.Y. Wang, and G. Matijasevic, J. Electron. Packaging 115, 201 (1993).
F.S. Shieu, C.F. Chen, J.G. Shen, and Z.C. Chang, Thin Solid Films 346, 125 (1999).
P.L. Tu, Y.C. Chan, K.C. Hung, and J.K.L. Lai, Scripta Mater. 44, 317 (2001).
G. Ghosh, Acta Mater. 48, 3719 (2000).
P. Shewmon, Diffusion in Solids, 2nd ed. (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1989) pp. 71–75.
C.E. Ho, Y.M. Chen, and C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 1231 (1999)
Chong Hua Zhong and Sung Yi, Soldering Surf. Mount Technol. 11, 44 (1999)
Ching-Yu Huang and Sinn-Wen Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 152 (2002).
Y.H. Tseng, M.S. Yeh, and T.H. Chuang, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 105 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DG., Jung, SB. The effect of isothermal aging on the thickness of intermetallic compound layer growth between low melting point solders and Ni-plated Cu substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1561–1566 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-004-0099-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-004-0099-5