Abstract
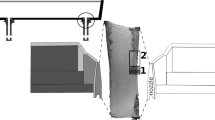
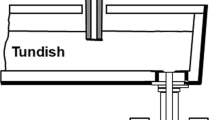
The continuous casting of Ti-alloyed Al-killed steels traditionally experiences clogging in the tundish, impeding stable operation. We studied the microstructures and mode of formation of such clogging deposits in tundish skulls recovered after long cast series. We sampled the steel skull along the whole tundish bottom from under the ladle shroud (impact zone) up to the tundish well and nozzle. The microstructures imply that the steel solidifies to the refractory (gunning mass) and remains partially solid through the entire cast. Thus, a “mushy zone” of steel loaded with solid delta ferrites is present along the margins of the steel during casting. In this mushy zone, the widely observed clusters of variably sintered alumina (NMI) accumulate, along with a substantial amount of gas bubbles acting as inclusion scavengers. The clustered alumina particles show a lognormal particle size distribution (PSD) in all locations, which becomes more pronounced if correcting for the observable sintering. Sintering of alumina size distributions linearizes a PSD, and further evolution, once the deposit is locked in place, occurs by Ostwald ripening, introducing skewness to the distributions. The observed PSDs contrast with the established log-linearity of PSDs of individual floating alumina NMI in the bulk steel, and suggest that the source of the alumina in the clogging deposits is not the passing bulk steel. However, ubiquitous sedimentary features show that the alumina particles are also not grown by reoxidation in situ. An upstream source separate from the bulk stream must be inferred, which is also required by the consistent sporadic presence of oxidic materials which cannot be derived from local sidewall reaction. In summary, the development of clogging deposits in this type of steel is an example of “slurry casting” of partially solidifying steel over thermal loss surfaces of refractories in the nozzle area.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 July 2020
This article was updated to correct errors in figure order and citations introduced during production.
References
Gao, Y. & Sorimachi, K.: ISIJ Int. (1993) 33:291-297
K.G. Rackers and B. Thomas: Proc. 78th Steelmaking Conf., Nashville, 1995, pp. 723–34.
Matsui, T., Ikemoto, T., Sawano, K., Sawada, I.: Taikabutsu Overseas, (1997) 18: 3-9
J. Smith and K. Peaslee: AISI/DOE Technology Roadmap Program Final Report, Pittsburgh, 2002, p. 229.
Andersson, M., Appelberg, J., Tilliander, A., Nakajima, K., Shibata, H., Kitamura, S., Jonsson, L., Jönsson, P.: ISIJ Intl. (2006) 46: 814-823
V. Garcia da Silva: PhD thesis, PPGEM (UFRGS), Porto Alegre, 2009, p. 98.
K. Janiszewski and Z. Kudlinski: Metal 2006 Conf., 2006, pp. 1–9.
L. Zhang and B. Thomas: XXIV. Natl. Steelmaking Symposium, Morelia, 2003, pp. 138–83.
Alekseenko, A., Baibekova, E., Kuznetsov, N., Baldaev, B., Ziborov, A., Ponomarenko, D., Ponomarenko, A.: Russian metallurgy (Metally) (2007), 7:94-97
Pack, A., Hoernes, S., Goebbels, M., Bross, R., Buhr, A.: Eur. J. Min. (2005), 17: 483-493
Khanna, R., Ikram Ul-Haq, M., Wang, Y., Seetharaman, S., Sahajwalla, V.: Met. Mat. Trans. Ser. B, (2011), 42B: 677-684
Lee JH, Kang MH, Kim SK, Kim J, Kim MS, Kang YB: ISIJ Int., 2019, 59, 749-758.
Burty, M., Peeters, L., Perrin, E., Münzer, S., Colucci, P., Salvadori, D., Schadow, F., Valcarcel, J., & Claes, J.: Rev. de Metallurgie (2005), 11:745-751
Zinngrebe, E., Van Hoek, C., Visser, H., Westendorp, A. & Jung, IH: ISIJ Intl. (2012), 52:52-61
Van Ende, MA, Guo, M., Zinngrebe, E., Dekkers, R., Proost, J., Blanpain, B. & Wollants, P.: Ironmaking Steelmaking (2009), 36:201-208
Randolph, A. & Larsen, M.: Theory of Particulate Processes, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, 1988.
Higgins, M.: Am. Miner. (2000), 85:1105-1116
Van Ende, M., Guo, M., Zinngrebe, E., Blanpain, B., Jung, IH.: ISIJ Intl. (2013), 53:1974-1982
Seo, M., Cho, JW, Kim, KC, & Kim, SH: ISIJ Intl. (2014), 54:475-481
Yang, W., Zhang, Y, Zhang, LF, Duan, H., Wang, L.: J. Iron Steel Res. Intl. (2015), 22:1069-1077
Adaba, O., Kaushik, P., Omalley, R., Lekakh, S., Von Richards, L., Mantel, E., Hall, R., Ellis, E.: Iron Steel Technol., 31, 38-49 (2017).
O. Adaba: Dissertation, University of Missouri – La Rolla, Doctoral Dissertations 2801, 2019. https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/doctoral_dissertations/2801
Zhang, L. & Pluschkell W.: Ironmaking & Steelmaking (2003), 30: 106-110
Eberl, D., Drits, V., & Srodon, J.: Am. J. Sci. (1998), 298:499-533
McCoy, B.: J. Colloid and Interface Sci. (2001), 240: 139-149
Kalisz, D., Zak, P.: Kovove Mater. (2015), 53:35-41
Ma, Z., Janke, D.: ISIJ Intl. (1998), 38: 46-52
Flemings, MC.: Metallurgical Transactions Ser. A (1991), 22A:957-981
Zhao, DG, Gao, M., Wang, SH, Wang, YF: Ironmaking Steelmaking (2016), 44:578-594
Acknowledgments
We thank Tata Steel for permission to publish. Many colleagues at Tata Steel collaborated in this work. Special thanks for their collaboration go to Frank van der Does, Corrie van Hoek, Patricia Romano Triguero, Erwin Bouwens, Henk Visser, Wouter Tiekink, Arnoud Kamperman, Bernadeta Karnasiewicz and Gert Abbel. The research also profited from discussions with colleagues outside of Tata Steel, especially In Ho Jung, Marie Aline van Ende and Joo Hyun Park. The reviewer’s efforts helped to significantly improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted July 31, 2018.
This article was updated to correct image citation and ordering errors introduced during production.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zinngrebe, E., Small, J., van der Laan, S. et al. Microstructures and Formation of Tundish Clogging Deposits in Ti-Alloyed Al-Killed Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2321–2338 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01903-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01903-y