Abstract
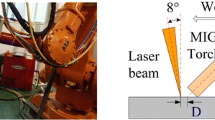
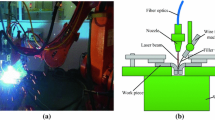
Hybrid laser–arc welding (LAW) provides an effective way to overcome problems commonly encountered during either laser or arc welding such as brittle phase formation, cracking, and porosity. The process parameters of LAW have significant effects on the bead profile and hence the quality of joint. This paper proposes an optimization methodology by combining non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) and ensemble of metamodels (EMs) to address multi-objective process parameter optimization in LAW onto 316L. Firstly, Taguchi experimental design is adopted to generate the experimental samples. Secondly, the relationships between process parameters (i.e., laser power (P), welding current (A), distance between laser and arc (D), and welding speed (V)) and the bead geometries are fitted using EMs. The comparative results show that the EMs can take advantage of the prediction ability of each stand-alone metamodel and thus decrease the risk of adopting inappropriate metamodels. Then, the NSGA-II is used to facilitate design space exploration. Besides, the main effects and contribution rates of process parameters on bead profile are analyzed. Eventually, the verification experiments of the obtained optima are carried out and compared with the un-optimized weld seam for bead geometries, weld appearances, and welding defects. Results illustrate that the proposed hybrid approach exhibits great capability of improving welding quality in LAW.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural networks
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BR:
-
Bead reinforcement
- BW:
-
Bead width
- DP:
-
Depth of penetration
- EMs:
-
Ensemble of metamodels
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithms
- GMSELOO :
-
Generalized mean square leave-one-out errors
- LAW:
-
Laser–arc welding
- LOO:
-
Leave-one-out
- MOGA:
-
Multi-objective genetic algorithm
- NN:
-
Neural networks
- NSGA:
-
Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm
- NSGA-II:
-
Improved non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm
- RBF:
-
Radial basis function
- RBFNN:
-
Radial basis function neural network
- RMAE:
-
Relative maximum absolute error
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- SVM:
-
Support vector machines
- SVR:
-
Support vector regression
References
Bendaoud, I., Matteï, S., Cicala, E., Tomashchuk, I., Andrzejewski, H., Sallamand, P., & Bouchaud, F.: Optics & Laser Technology, 2014, vol. 56, pp. 334-42.
Atabaki, M. M., Ma, J., Liu, W., & Kovacevic, R., Materials & Design, 2015, vol. 67, pp. 509-21.
Ma, N., Li, L., Huang, H., Chang, S., & Murakawa, H., Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, vol. 220, pp. 36-45.
Gao M., Chen C., Wang L., Wang Z., & Zeng X,: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 2007-20.
Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Hu, W., & Lai, X.: Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2012, vol. 50, pp. 1267-73.
Rong, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, G., Yue, C., Gu, Y., Huang, Y., Wang, C., Shao, X.: Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2015, vol. 67, pp. 94-104.
Ruggiero, A., Tricarico, L., Olabi, A. G., Benyounis, K. Y.: Optics & Laser Technology, 2011, vol. 43, pp. 82-90.
Kuo, C. F. J., Chiu, H. Y., Syu, S. S., & Vu, Q. H.: Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2014, vol. 52, pp. 250-60.
Katherasan, D., Elias, J. V., Sathiya, P., Haq, A. N.: Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2014, vol. 25, pp. 67-76.
Singh, A., Cooper, D. E., Blundell, N. J., Pratihar, D. K., Gibbons, G. J.: International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2014, vol. 27, pp. 656-74.
N.K. Lim: California State University, Long Beach, 2014.
Gao, X. D., & Zhang, Y. X.: International journal of precision engineering and manufacturing, 2014, vol. 15, pp. 399-405.
Gao, M., Chen, C., Mei, S., Wang, L., & Zeng, X.: The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, vol. 74, pp. 199-208.
Cao, X., Wanjara, P., Huang, J., Munro, C., & Nolting, A.: Materials & Design, 2011, vol. 32, pp. 3399-413.
Atabaki, M. M., Ma, J., Yang, G., & Kovacevic, R.: Materials & Design, 2014, vol. 64, pp. 573-87.
Brandizzi, M., Mezzacappa, C., Tricarico, L., & Satriano, A. A.: Welding International, 2012, vol. 26, pp. 901-9.
Gao, Z., & Ojo, O. A.: Acta Materialia, 2012, vol. 60, pp. 3153-67.
Zadeh, P. M., Toropov, V. V., & Wood, A. S. 2009: Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., 2009, vol. 38, pp. 103-15.
Taguchi, G.: International Journal of Production Research., 1978, vol. 16, pp. 521–30.
Chaki, S., Bathe, R. N., Ghosal, S., & Padmanabham, G.: J. Intell. Manuf., 2015, DOI: 10.1007/s10845-015-1187-5.
Hamarat, C., Kwakkel, J. H., Pruyt, E., & Loonen, E. T.: Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2014, vol. 46, pp. 25-39.
Shojaeefard, M. H., Akbari, M., & Asadi, P.: International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2014, vol. 15, pp. 2351-6.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., & Meyarivan, T. A. M. T.: IEEE Transactions on, 2002, vol. 15, pp. 182-97.
Sacks, J., Welch, W. J., Mitchell, T. J., & Wynn, H. P.: Statis. Sci. 1989, 4, pp. 409-23.
P. Jiang, J. Wang, Q. Zhou, and X. Zhang: Math. Probl. Eng., 2015, DOI:10.1155/2015/685958.
Zhou, Q., Shao, X., Jiang, P., Zhou, H., & Shu, L.: Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2015, vol. 59, pp. 18-35.
Zheng, J., Shao, X., Gao, L., Jiang, P., & Qiu, H.: Engineering Optimization, 2015, vol. 47, pp. 719-36.
Zheng, J., Shao, X., Gao, L., Jiang, P., & Qiu, H.: Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, vol. 41, pp. 2111-25.
Wang, G. G., & Shan, S.: Journal of Mechanical Design, 2007, vol. 129, pp. 370-80.
Acar, E.: Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, vol. 42, pp. 2703-9.
Acar, E., & Rais-Rohani, M.: Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2009, vol. 37, pp. 279-94.
Zhou, X. J., Ma, Y. Z., & Li, X. F.: Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2011, vol. 44, pp. 651-71.
Aute, V., Saleh, K., Abdelaziz, O., Azarm, S., & Radermacher, R.: Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., 2013, vol. 48, pp. 581-605.
Coello Coello, C. A.: Computers in Industry, 2000, vol. 41, pp.113-27.
Gao, Y., Olivas-Martinez, M., Sohn, H. Y., Kim, H. G., & Kim, C. W.: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 1465-75.
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China under Grant No. 2014CB046703, National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 51505163, 51323009, and 51421062, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST: Grant No. 2014TS040. The authors also would like to thank the anonymous referees for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 20, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Jiang, P., Shao, X. et al. Optimization of Process Parameters of Hybrid Laser–Arc Welding onto 316L Using Ensemble of Metamodels. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 2182–2196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0664-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0664-3