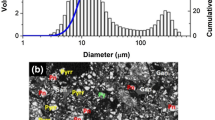
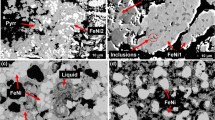
Abstract
The fluidized bed sulfation roasting process followed by water leaching was investigated as an alternative process to treat nickel sulfide concentrate for nickel production. The effects of several roasting parameters, such as the sulfation gas flow rate, roasting temperature, the addition of Na2SO4, and the roasting time, were studied. 79 pct Ni, 91 pct Cu, and 95 pct Co could be recovered with minimal dissolution of Fe of 4 pct by water leaching after two-stage oxidation-sulfation roasting under optimized conditions. The sulfation roasting mechanism was investigated, showing that the outermost layer of sulfate melt and the porous iron oxide layer create a favorable sulfation environment with high partial pressure of SO3. Sulfation of the sulfide core was accompanied by the conversion of the sulfide from Ni1−x S to Ni7S6 as well as inward diffusion of the sulfation gas.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Schonewille, M. Boissoneault, D. Ducharme, and J. Chenier: 44th Annual Conference of Metallurgists: Nickel and Cobalt 2005, Calgary, Canada, 2005, pp. 479–98.
Inco Limited: Moving Towards Sustainability, 2005 Good Neighbours Report on Health, Safety, Environment and Community, Inco Limited, Toronto, Canada, 2005.
A. Roine: HSC Chemistry, version 6.12 for Windows, Outokumpu Research Oy, Pori, Finland, 2007.
P.G. Thornhill: U.S. Patent 2,813,016, November 12, 1957.
A.W. Fletcher and M. Shelef: Unit Process in Hydrometallurgy. Group C: Plant Operating Practice—Economics—General, New York Gordon and Breach Science, New York, NY, 1965, pp. 946–70.
A. W. Fletcher and M. Shelef: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1964, vol. 230, pp. 1721-1724.
J. G. Dunn: Thermochim. Acta, 1997, vol. 300, pp. 127-139.
M. C. B. Hotz and T. R. Ingraham: Can. Metall. Q., 1966, vol. 5, pp. 237-244.
P.J. Saikkonen: U.S. Patent 4,464,344, August 7, 1984.
M. C. B. Hotz and T. R. Ingraham: Can. Metall. Q., 1965, vol. 4, pp. 295-302.
W.K. Sproule, P.E. Queneau, and G.C. Nowlan Jr: Canada Patent CA 593622, March 1, 1960.
P.G. Thornhill: U.S. Patent 2 930 604, March 29, 1960.
K. L. Luthra: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1647-1654.
N. Zubryckyj, D. J. I. Evans and V. N. Mackiw: J. Met., 1965, vol. 17, pp. 478-486.
P.G. Thornhill: AIME Trans., 1961, vol. 14L, pp. 337–44.
J.R. Boldt, Jr.: The Winning of Nickel, Longmans Canada, Toronto, 1967, pp. 331–36.
N. Birks, G. H. Meier and F. S. Pettit: Introduction to The High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals, pp. 205-252, Cambridge University Press, United States of America, 2006.
J. M. Toguri: Can. Metall. Q., 1975, vol. 14, pp. 323-338.
M. C. B. Hotz, R. C. Kerby and T. R. Ingraham: Can. Metall. Q., 1968, vol. 7, pp. 205-210.
P.J. Saikkonen and J.K. Rastas: 25th Annual Conference of Metallurgists, Toronto, ON, Canada, 1986, pp 278–90.
K. T. Jacob: Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 1987, vol. 40, pp. 383-388.
D. Yu, T.A. Utigard, and M. Barati: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013. DOI:10.1007/s11663-013-9958-x.
P.G. Thornhill and L.M. Pidgeon: J. Met., 1957, vol. 9, pp. 989-995.
A. K. Misra and D. P. Whittle: Oxid. Met., 1984, vol. 22, pp. 1-33.
F.K. Crundwell, M.S. Moats, V. Ramachandran, T.G. Robinson and W.G. Davenport: In Extractive Metallurgy of Nickel, Cobalt and Platinum-Group Metals, pp. 67-83, Elsevier, Oxford, 2011.
D. Yu, M. Zhu, T. A. Utigard, and M. Barati: Miner. Eng., 2013. DOI:10.1016/j.mineng.2013.03.018.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Xstrata Process Support (Sudbury, ON, Canada) for providing the concentrate and both Xstrata and Vale for sponsoring the project. We acknowledge the constructive comments received from Dr. Gus Van Weert of ORETOME Ltd. The funding for this research was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 24, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, D., Utigard, T.A. & Barati, M. Fluidized Bed Selective Oxidation-Sulfation Roasting of Nickel Sulfide Concentrate: Part II. Sulfation Roasting. Metall Mater Trans B 45, 662–674 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9959-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9959-9