Abstract
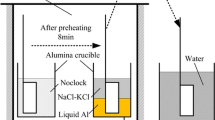
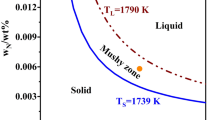
The dissolution behavior of Ti in liquid Fe has been investigated experimentally and theoretically within the framework of inclusion formation in steel. In the experimental study, Ti cylinders have been immersed into liquid Fe and, subsequently, water-quenched. Macroscopic observation of quenched samples shows the initial solidification of an Fe shell around the Ti. Microstructural analysis of the Fe-Ti interfacial area with a scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer reveals that a reaction zone develops in a three-step process: formation of a first liquid eutectic layer rich in Ti, formation of a second eutectic layer rich in Fe, and then mixing of both layers. The reaction zone grows in thickness up to 40 pct of the original sample radius and dissolves both parts of the Ti sample and the Fe shell. A simplified, one-dimensional, implicit finite volume model has been used to describe these phenomena theoretically. Good qualitative agreement is achieved between experiment and model. The model has been used to estimate the influence of original addition size, preheating, convection, and superheating on the required melt-back time.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Argyropoulos and R.I.L. Guthrie: Can. Metall. Q., 1979, vol. 18(3), pp. 267–81.
P.G. Sismanis and S.A. Argyropoulos: Can. Metall. Q., 1988, 27(2), pp. 123–33.
S.A. Argyropoulos and P.G. Sismanis: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22(4), pp. 417–27.
L. Zhang and F. Oeters: Melting and Mixing of Alloying Agents in Steel Melts, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf, Germany, 1999.
S.A. Argyropoulos: Ph.D. Dissertation, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, 1981.
S.A. Argyropoulos and R.I.L. Guthrie: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15(1), pp. 47–58.
P. Gardin, J.-F. Domgin, M. Simonnet, and J. Lehmann: Revue Metallurgie, 2008, vol. 105(2), pp. 84–91.
J. Szekely and Y.K. Chuang: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1972, vol. 27(12), pp. 2300–04.
S.A. Argyropoulos and H.F. Hu: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1996, vol. 39(5), pp. 1005–21.
S.A. Argyropoulos and P.G. Sismanis: Steel Res., 1997, vol. 68(8), pp. 345–54.
K.C.H. Kumar, P. Wollants, and L. Delaey: Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem., 1994, vol. 18(2), pp. 223–34.
L.F.S. Dumitrescu, M. Hillert, and N. Saunders: J. Phase Equilibria, 1998, vol. 19(5), pp. 441–48.
G. Cacciamani, J. De Keyzer, R. Ferro, U.E. Klotz, J. Lacaze, and P. Wollants: Intermetallics, 2006, vol. 14(10–11), pp. 1312–25.
C.A. Sims: Electric Furnace Steelmaking, AIME, New York, NY, 1967.
L. Pandelaers, F. Verhaeghe, B. Blanpain, and P. Wollants: Defect Diffusion Forum, 2008, vol. 273–276, pp. 467–73.
H.S. Carslaw and J.C. Jaeger: Conduction of Heat in Solids, Oxford University Press, Clarendon, Oxford, 1984.
S.C. Gupta: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1990, vol. 33(4), pp. 593–602.
S.V. Patankar; Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere, Washington, DC, 1980.
Y.S. Touloukian: Thermal Conductivity: Metallic Elements and Alloys, IFI/Plenum, New York, NY, 1978.
Y.S. Touloukian and E.H. Buyco: Specific Heat: Metallic Elements and Alloys, IFI/Plenum, New York, NY, 1978.
N. Mehdipour, A. Boushehri, and H. Eslami: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2005, vol. 351(16–17), pp. 1333–37.
M.J. Assael, K. Kakosimos, R.M. Banish, J. Brillo, I. Egry, R. Brooks, P. N. Quested, K.C. Mills, A. Nagashima, Y. Sato, and W.A. Wakeham: J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 2006, vol 35(1), pp. 285–300.
D.Y. Povolotskiy, V.E. Roshchin, and A.N. Keys: Russ. Metall., 1970, vol. 5, pp. 162–64.
T.A. Engh: Principles of Metal Refining, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1992.
P.F. Paradis, T. Ishikawa, and S. Yoda: Int. J. Thermophys., 2002, vol. 23(3), pp. 825–42.
G.H. Rodway and J.D. Hunt: J. Mater. Sci., 1988, vol. 23(3), pp. 814–22.
Acknowledgments
L. Pandelaers acknowledges the financial support from the IWT Grant SB-61446. F. Verhaeghe acknowledges the support of the Research Foundation - Flanders (FWO - Vlaanderen) through a postdoctoral fellowship. L. Pandelaers also would like to thank J. Fransaer for the constructive discussions as well as ArcelorMittal Research and Development for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 22, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandelaers, L., Verhaeghe, F., Blanpain, B. et al. Interfacial Reactions During Titanium Dissolution in Liquid Iron: A Combined Experimental and Modeling Approach. Metall Mater Trans B 40, 676–684 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9273-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9273-8