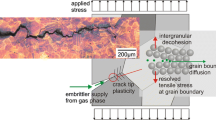
Abstract
The effects of electrochemically pre-dissolved hydrogen on room-temperature fracture initiation in Beta-C titanium (Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr wt pct) have been investigated using circumferentially notched tensile specimens. Finite element-based analysis of notch stress fields was used to define relationships between the local threshold stress for crack initiation vs total internal hydrogen concentration. The as-received, solution heat treated (ST, σy.2 pct=865 MPa) and the ST + peak-aged conditions (STA, σ y.2% pct=1260 MPa) were compared after defining the relationships between the fracture process zone hydrogen concentration, hydrogen-metal interactions (i.e., hydrostatic stress field occlusion, trapping, hydriding), and the resulting fracture initiation behavior of each. Solutionized + peak-aged (β+α) Beta-C fractured intergranularly above total hydrogen concentrations of ∼1000 wt ppm. (5.1 at. pct). A fracture mode consistent with cleavage occurred at ∼2100 wt ppm. (10.7 at. pct). Solutionized Beta-C resisted hydrogen-assisted cracking (e.g., did not crack intergranularly) but was not immune; cleavage cracking was provoked at ∼4000 wt ppm. (20.4 at. pct). Coldworked ST Beta-C (CW, σ y.2 pct=1107 MPa) did not crack intergranularly; fracture initiation behavior was similar to the ST condition regardless of specimen orientation. This suggests that high yield strength alone does not account for the susceptibility to intergranular cracking observed in the STA β+α condition. Stroke-rate studies and X-ray diffraction investigation of H partitioning suggests that equilibrium hydriding and/or irreversible trapping does not singularly control intergranular fracture initiation of the STA condition. Fractographic evidence and finite element results show that a finite plastic zone exists prior to intergranular fracture of the STA condition. This suggests that a criterion for fracture that incorporates plastic strain and stress should be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Lederich, D. Schwartz, and S. Sastry: in Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990’s, D. Eylon, R.R. Boyer, and D.A. Koss, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 159–69.
W. Gerberich, N. Moody, C. Jensen, C. Hayman, and K. Jatavallabhula: in Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I.M. Bernstein, and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 731–43.
J. Costa, D. Banerjee, and J. Williams: in Titanium Science and Technology, G. Lutjering, U. Zwicker, and W. Bunk, eds., Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde E.V., Oberursel, Germany, 1984, vol. 4, pp. 2479–87.
G. Young and J. Scully: in Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990’s, D. Eylon, R.R. Boyer, and D.A. Koss, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 147–58.
N. Paton, R. Spurling, and C. Rhodes: in Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I.M. Bernstein, and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 269–79.
A. Sedriks and J. Greene: Corrosion, 1972, vol. 28, pp. 226–30.
R. Wanhill: Br. Corr. J., 1975, vol. 10, pp. 69–78.
L. Young: Master’s Thesis, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, 1993.
M. Blackburn and W. Smyrl: in Titanium Science and Technology, R.I. Jaffee, and H.M. Burte, eds., Plenum Publishing Corp., New York, NY, 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2577–2609.
H. Nelson: Hydrogen in Metals, I.M. Bernstein, and A.W. Thompson, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974, pp. 445–64.
D. Thomas and S. Seagle: in Titanium Science and Technology, G. Lutjering, U. Zwicker, and W. Bunk, eds., Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde E.V., Oberursel, Germany, 1984, vol. 4, pp. 2533–40.
K. Shah and D. Johnson: in Hydrogen in Metals, I.M. Bernstein, and A.W. Thompson, eds. ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974, pp. 475–81.
D. Kolman and J. Scully: in Effects of the Environment on the Initiation of Crack Growth, ASTM STP 1298, W.A. Van der Sluys, R.S. Piascik, and R. Zawierucha, eds., ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1997.
L. Wolfe, C. Burnette, and M. Joosten: Mater. Performance, 1993, vol. 32, pp. 14–21.
I. Azkarate and A. Pelayo: Proc. INASMET, San Sebastian, Spain, 1992, paper no. 20009.
W. Czyrklis and M. Levy: Corrosion, 1976, vol. 32, pp. 99–102.
J. Hagemeyer, and D. Gordon: Titanium Science and Technology, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, pp. 1957–68.
B. Somerday, J. Grandle, and R. Gangloff: Proc. Tri-Services Conf. on Corrosion, Materials Laboratory, Wright Patterson Air Force Base, OH, 1994, pp. 375–92.
M. Gaudett, S. Smith, and J. Scully: in Hydrogen Effects in Materials, A. Thompson, and N. Moody, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 745–54.
A. McQuillan: Proc. R. Soc. London, 1950, vol. 204A, pp. 309–23.
W. Gerberich, K., Jatavallabhula K. Peterson, and C., Jensen: Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Fracture, ICF 5, Cannes, France 1981, pp. 989–98.
N. Nakasa and J. Liu: J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1991, vol. 55, pp. 922–27.
D. Shih and H. Birnbaum: Scripta Metall., 1986, vol. 20, pp. 1261–64.
D. Williams: J. Inst. Met., 1962–63, vol. 91, pp. 147–52.
H. Robinson, P. Frost, and W. Parris: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, pp. 464–69.
H. Nelson: NASP Government Work Package #92, NASA-Ames Research Center, Monterey, CA, 1992.
M. Gaudett and J. Scully: Scripta Metall., 1997, vol. 36, pp. 565–72.
G. Young and J. Scully: Scripta Metall., 1993, vol. 28, pp. 507–12.
D. Kolman and J. Scully: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1993, vol. 140, pp. 2771–79.
D. Kolman and J. Scully: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, vol. 141, pp. 2633–41.
J. Yu, R. Parkins, Y. Xu, G. Thompson, and G. Wood: Corr. Sci., 1987, vol. 27, pp. 141–57.
L. Young, G. Young, J. Scully, and R. Gangloff: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 1257–72.
G. Young and J. Scully: Corrosion, 1994, vol. 50, pp. 919–33.
N. Moody, S. Robinson, J. Angelo, and M, Perra: in Hydrogen Effects in Metals, A.W. Thompson and N.R. Moody, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996 pp. 967–77.
A. Stroh: Proc. R. Soc. London, 1954, vol. 223, pp. 404–14.
J. Tien, A. Thompson, I. Bernstein, and R. Richards: Metall Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A pp. 821–29.
J. Tien, S., Nair, and R. Jensen: in Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I. Bernstein, and A. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 37–56.
M. Blackburn, W. Smyrl, and J. Feeney: Stress Corrosion Cracking in High Strength Steels and in Titanium and Aluminum Alloys, B.F. Brown, ed., Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC, 1973, pp. 245–363.
G. Caskey: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1974, vol. 14, pp. 109–14.
R. Schutz and L. Covington: Corrosion, 1981, vol. 37, pp. 585–91.
B. Somerday and R. Gangloff: University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, unpublished research, 1997.
J. Waisman, G. Sines, and L. Robinson: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 291–302.
N. Paton and O. Buck: in Effect of Hydrogen on the Behavior of Materials, A.W. Thompson, and I.M. Bernstein, eds., TMS, New York, NY, 1975, pp. 83–89.
B. Cullity: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Manila, Philippines, 1976, pp. 411–15.
M. Dickson: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1969, vol. 2, pp. 176–80.
A. Troiano: Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, pp. 54–80.
J. Hancock and A. Mackenzie: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1976, vol. 24, pp. 147–69.
H. Johnson, J. Morlet, and A. Troiano: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, pp. 528–36.
K. Akhurst and T. Baker: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1059–70.
P. Doig and G Jones: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1993–89.
X. Chen and W. Gerberich: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 59–70.
P. Khadkikar, J. Lewandowski, and K. Vedula: Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 1247–55.
J. Lewandowski and A. Thompson: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 1453–62.
R. Van Stone, J. Low, and J. Shannon: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 539–52.
T. Headley and H. Rack: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 909–20.
I. Phillips, P. Poole, and L. Shreir: Corr. Sci., 1972, pp. 855–66.
J. Boyd: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 977–88.
G. Pittinato and W. Hanna: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, 2905–09.
P. Adler, R. Schulte, E. Schneid, E. Kamykowski, and F. Kuehne: Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1617–23.
T. MacKay: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, 2299–202.
O Huber, J. Gates, A. Young, M. Pobereskin, and P. Frost: Trans. AIME, 1957, vol. 5, pp. 918–23.
N. Tiner, T. Mackay, S. Asunmaa, and R. Ingersoll: Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 195–202.
R. Hertzberg: Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1989.
R. Oriani and P. Josephic: NY, Acta Metall., 1974, vol. 22, pp. 1065–74.
M. Gaudett: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, 1997.
J. Lewandowski and A. Thompson: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 1769–86.
J. Knott: Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Fracture, S. Valluri, D. Taplin, P. Rao, J. Knott, and R. Dubey, eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1984, vol. 1, pp. 83–105.
R. Chopra and J. Li: Scripta Metall., 1973, vol. 6, pp. 543–45.
H. Birnbaum: in Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior, N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1990, pp. 639–60.
S. Gahr M. Grossbeck and H. Birnbaum: Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, pp. 125–34.
M. Grossbeck and H. Birnbaum: Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, pp. 135–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudett, M.A., Scully, J.R. Part I-the effects of pre-dissolved hydrogen on cleavage and grain boundary fracture initiation in metastable beta Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr. Metall Mater Trans A 30, 65–79 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0196-4
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0196-4