Abstract
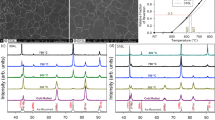
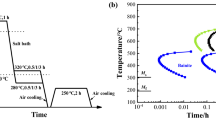
It is well known that a significant amount of retained austenite can be obtained in steels containing high additions (>1 pct) of Si, where bainite is the predominant microconstituent. Furthermore, retained austenite with optimum characteristics (volume fraction, composition, morphology, size, and distribution), when present in ferrite plus bainite microstructures, can potentially increase strength and ductility, such that formability and final properties are greatly improved. These beneficial properties can be obtained largely by transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP). In this work, the effect of a microalloy addition (0.035 pct Nb) in a 0.22 pct C-1.55 pct Si-1.55 pct Mn TRIP steel was investigated. Niobium was added to enable the steel to be processed by a variety of thermomechanical processing (TMP) routes, thus allowing the effects of prior austenite grain size, austenite recrystallization temperature, Nb in austenite solid solution, and Nb as a precipitate to be studied. The results, which were compared with those of the same steel without Nb, indicate that the retained austenite volume fraction is strongly influenced by both prior austenite grain size and the state of Nb in austenite. Promoting Nb(CN) precipitation by the change in TMP conditions resulted in a decrease in the V RA . These findings are rationalized by considering the effects of changes in the TMP conditions on the subsequent transformation characteristics of the parent austenite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.F. Zackay, E.R. Parker, D. Fahr, and R. Busch: Trans. ASM, 1967, vol. 60, pp. 253–59.
B.R. Banerjee, J.M. Capenos, and J.J. Hauser: Application of Fracture Toughness Parameters to Structural Metals, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Inc., New York, NY, 1966, pp. 373–406.
R. Entin: in Decomposition of Austenite by Diffusional Processes, V.F. Zackay and H.I. Aaronson, eds., Interscience, New York, NY, 1962, pp. 295–311.
A. Zarei-Hanzaki: Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, 1994.
G. Thomas and J.Y. Koo: in Structure and Properties of Dual-Phase Steels, R.A. Kot and J.W. Morris, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979, pp. 183–201.
K.I. Sugimoto, N. Usui, M. Kobayashi, and S.I. Hashimoto: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 1311–18.
O. Matsumura, Y. Sakuma, and H. Takechi: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 1014–20.
Y. Sakuma, S. Matsumura, and H. Takechi: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 489–98.
K.I. Sugimoto, M. Misu, M. Kobayashi, and H. Shirasawa: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 775–82.
A. Zarei-Hanzaki, P.D. Hodgson, and S. Yue: 33rd Mechanical Working and Steel Processing Conf., ISS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 459–66.
B.D. Cullity: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc., Reading, MA, 1978.
C.F. Jatczak, J.A. Larson, and S.W. Shin: Retained Austenite and Its Measurements by X-ray Diffraction, Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc., Warrendale, PA, 1980, p. 9.
G.E. Lucas: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1105–19.
A. Zarei-Hanzaki, R. Pandi, P.D. Hodgson, and S. Yue: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 2657–65.
J.R. Bradley, H.I. Aaronson, K.C. Russell, and W.C. Johnson: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1955–61.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, Transformation, Microstructure and Properties, The Institute of Materials, London, 1992, p. 173.
C.M. Sellars: Hot Working and Forming Processes, The Metals Society, London, 1980, pp. 3–15.
S. Bandoh, O. Matsumura, and Y. Sakuma: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1988, vol. 28, pp. 569–74.
A. Zarei-Hanzaki, P.D. Hodgson, and S. Yue: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1995, vol. 35 (1), pp. 79–85.
Y. Sakuma, D.K. Matlock, and G. Krauss: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1221–32.
P. Brozzo, G. Buzzichelli, A. Mascanzoni, and M. Mirabile: Met. Sci., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 123–29.
A.K. Sinha: Ferrous Physical Metallurgy, Butterworth and Co., Stoneham, MA, 1989, p. 315.
M.H. Richman, D.A. Thomas, and M. Cohen: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 814–16.
K.C. Russell: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 5–17.
H. Baumgart, H.F. de Boer, and F. Heisterkamp: Niobium, Conf. Proc., H. Stuart, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 883–915.
W.J. Liu: Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, 1987.
I. Weiss and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 831–40.
A.J. DeArdo, J.M. Gray, and L. Meyer: Proc. Int. Symp. on Niobium, H. Stuart, ed., AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 685–759.
S. Okaguchi, K. Fujiwara, and T. Hashimoto: Physical Metallurgy of Direct-Quenched Steels, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 169–77.
M.H. Thomas and G.M. Michal: in Solid-Solid Phase Transformation, H.L. Aaronson, D.E. Loughlin, R.F. Sekerka, and C.M. Wayman, eds., AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 469–78.
J.R. Bradley and H.I. Aaronson: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1729–41.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., F.Z. Li, C.K. Shui, and H.I. Aaronson: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1433–63.
R.B.G. Yeo: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 884–90.
R.K. Amin and F.B. Pickering: Thermomechanical Processing of Microalloyed Austenite, AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 377–403.
S. Okaguchi, T. Hashimoto, and H. Ohtani: Proc. Int. Conf. on Physical Metallurgy of Thermomechanical Processing of Steel and Other Metals (THERMEC-88), I. Tamura, ed., ISIJ, Tokyo, 1988, pp. 330–36.
A.J. Goldman and W.D. Robertson: Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, pp. 1265–75.
G.R. Speich, A.J. Schwoeble, and W.C. Leslie: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2031–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanzaki, A.Z., Hodgson, P.D. & Yue, S. Retained austenite characteristics in thermomechanically processed Si-Mn transformation-induced plasticity steels. Metall Mater Trans A 28, 2405–2414 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0197-0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0197-0