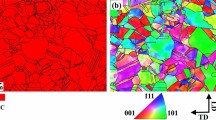
Abstract
Ultra-fine-grained (UFG) structure was developed in AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel (ASS) using cryogenic rolling followed by annealing treatments at 923 K, 973 K, 1023 K, and 1073 K (650 °C, 700 °C, 750 °C, and 800 °C) for different lengths of time. The α′-martensite to γ-austenite reversion behavior and the associated texture development were analyzed in the cryo-rolled specimens after annealing. The activation energy, Q, required for the reversion of α′-martensite to γ-austenite in the steel was estimated to be 80 kJ mol−1. TiC precipitates and unreversed triple junction α′-martensite played major roles in the development of UFG structure through the Zener pinning of grain boundaries. The optimum annealing temperature and time for the development of UFG structure in the cryo-rolled AISI 321 steel are (a) 923 K (650 °C) for approximately 28800 seconds and (b) 1023 K (750 °C) for 600 seconds, with average grain sizes of 0.22 and 0.31 µm, respectively. Annealing at 1023 K (750 °C) is considered a better alternative since the volume fraction of precipitated carbides in specimens annealed at 1023 K (750 °C) are less than those annealed at 923 K (650 °C). More so, the energy consumption during prolonged annealing time to achieve an UFG structure at 923 K (650 °C) is higher due to low phase reversion rate. The hardness of the UFG specimens is 195 pct greater than that of the as-received steel. The higher volume fraction of TiC precipitates in the UFG structure may be an additional source of hardening. Micro and macrotexture analysis indicated {110}〈uvw〉 as the major texture component of the austenite grains in the UFG structure. Its intensity is stronger in the specimen annealed at low temperatures.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wang, Y. Lin, J. Yan, D. Zen, Q. Zhang, R. Huang, and H. Fan: Surf. Coatings Technol., 2012, vol. 206, pp. 3399–3404.
D. T. Llewellyn and R. C. Hudd: STEELS-Metallurgy and Applications, 3rd ed., Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd, Oxford, UK, 1998, .
Y. Y. Chen, Y. M. Liou, and H. C. Shih: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 407, pp. 114–126.
M. Eskandari, A. Kermanpur, and A. Najafizadeh: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40, 2241–2249.
M. Eskandari, A. Najafizadeh, and A. Kermanpur: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 519, pp. 46–50.
A Di Schino, M Barteri, and J M Kenny: J Mater Sci Lett, 2002, vol. 21, 751–753.
D. L. Johannsen, A. Kyrolainen, and P. J. Ferreira: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 37A, pp. 2325-2338.
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, J. G. Speer, and D. K. Matlock: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 441, pp. 1-17.
T. J. Angel: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1954, vol. 177, pp. 165–174.
Nohara, K., Ono, Y., Ohashi, N.: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn, 1977, vol. 63, pp. 212-222.
M. Eskandari, A. Najafizadeh, A. Kermanpur, and M. Karimi: Mater. Des., 2009, vol. 30, pp. 3869–3872.
R. D. K. Misra, S. Nayak, S. A. Mali, J. S. Shah, M. C. Somani, and L. P. Karjalainen: Met. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 3–12.
R. D. K. Misra, Z. Zhang, P. K. C. Venkatasurya, M. C. Somani, and L. P. Karjalainen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 7779-7792.
S. Rajasekhara and P. J. Ferreira: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, 738-748.
H. F. G. De Abreu, S. S. De Carvalho, P. De Lima Neto, R. P. Dos Santos, V. N. Freire, P. M. D. O. Silva, and S. S. M. Tavares: Mater. Res., 2007, vol. 10, pp. 359-336.
A. Das, S. Sivaprasad, M. Ghosh, P. C. Chakraborti, and S. Tarafder: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 486, pp. 283-286.
A. K. De, D. C. Murdock, M. C. Mataya, J. G. Speer, and D. K. Matlock: Scr. Mater., 2004, vol. 50, pp. 1445-1449.
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, and Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, pp. 1431-1437.
T. Tsuchiyama, Y. Nakamura, H. Hidaka, and S. Takaki: Mater. Trans. 45, 2259 (2004).
M. C. Somani, P. Juntunen, L. P. Karjalainen, and R. D. K. Misra: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 729-744.
C. Celada-casero, B. M. Huang, M. M. Aranda, J. Yang, and D. S. Martin: Mater. Charact., 2016, vol. 118, pp. 129-141.
L. Kaufman, E. V. Clougherty, and R. J. Weiss: Acta Metall., 1963, vol. 11, pp. 323-335.
C. S. Yoo, Y. M. Park, Y. S. Jung, and Y. K. Lee: Scr. Mater., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 71-74.
M. G. Shahri, S. R. Hosseini, and M. Salehi: Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett.), 2015, vol. 28, pp. 499-504.
T. Tomida, M. Wakita, M. Yasuyama, S. Sugaya, Y. Tomota, and S. C. Vogel: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 2828-2839.
B.R. Kumar, A.K. Singh, B. Mahato, P.K. De, N.R. Bandyopadhyay, and D.K. Bhattacharya: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 429, pp. 205–11.
A. Poulon-quintin, S. Brochet, J. Vogt, and J. Glez: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 293-301.
T. Michler: Materwiss. Werksttech., 2007, vol. 38, pp. 32-35.
M. Eskandari, A. Kermanpur, and A. Najafizadeh: Mater. Lett., 2009, vol. 63, pp. 1442-1444.
J. Talonen, P. Aspegren, and H. Hänninen: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 20, pp. 1506-1512.
E. A. Wilson: Worked Examples in the Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Phase Transformations, 1st ed., The Institution of Metallurgists, London, UK, 1983, pp. 40.
W. D.Callister and D. G. Rethwisch: Materials Science and Engineering, 9th ed., Wiley, United States, 2014, pp. 368.
E. Lee, R. Banerjee, S. Kar, D. Bhattacharyya, H. L. Fraser, R. Banerjee, S. Kar, D. Bhattacharyya, and H. L. Fraser: Philos. Mag., 2007, vol. 87, pp. 3615-3627.
D. A. Porter, K. E. Easterling, and M. Y. Sherif: Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys, 3rd ed., CRC Press, FL, USA, 2009, pp. 143-146.
M. Moallemi, A. Najafizadeh, A. Kermanpur, and A. Rezaee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 530, pp. 378-381.
C. A. Apple and G. Krauss; Acta Met., 1972, vol. 20, pp. 849-856.
A. K. Jena and M. C. Chaturvedi: Phase Transformation in Materials, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1992, pp. 342.
S. Rajasekhara, L. P. Karjalainen, A. Kyröläinen, and P. J. Ferreira: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 1986-1996.
K. S. Min, K. J. Kim, and S. W. Nam: J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 370, pp. 223-229.
S. Xu, X. Q. Wu, E. H. Han, W. Ke, and Y. Katada: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 490, pp. 16-25.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Vanier Graduate Scholarship for the financial support of this study. The support of ACUREN Group Inc. for the use of Fischer Feritscope MP30E is well appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 6, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiamiyu, A.A., Szpunar, J.A., Odeshi, A.G. et al. Development of Ultra-Fine-Grained Structure in AISI 321 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 5990–6012 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4361-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4361-x