Abstract
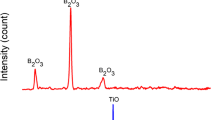
Because of the excellent thermal and mechanical properties of engineering ceramics, they have been used as structural materials or composite matrixes and reinforcements in recent years. Alumina, titanium diboride, and zirconium diboride have found important uses in the past two decades. In this study, Al2O3/(ZrB2 + TiB2) ceramic composite powders were fabricated in situ and mechanical activation by milling was used to assist combustion synthesis (CS). A mixture of Al, ZrO2, TiO2, and B2O3 powders were used as raw materials. Mechanical activation was done using ball milling of different durations. Afterward, combustion was initiated using microwaves on the activated mixtures. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy were used to investigate the purity and microstructure of the products. XRD analysis of the samples in the final stages of the process revealed that Al2O3/(ZrB2 + TiB2) composite powder was successfully fabricated using mechanical activation and CS, but that the CS reaction did not occur in unmilled samples. It was shown that increasing milling time from 3 to 10 hours increased purity and homogeneity of the products to the point that no noticeable impurity existed in the samples milled for 10 hours.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.K. Mishra, S.K. Das, L.C. Pathak: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 426(1–2), pp. 229–234.
S.K. Mishra, S.K. Das, V. Sherbacov: Compos. Sci. Technol., 2007, 67(11–12), pp. 2447–2453.
D.D. Radev, D. Klissurski: Mater. Synth. Process., 2001, 9(3), pp. 131–136.
S.K. Mishra, P.K.P. Rupa, S.K.Das, V. Shcherbakov: Compos. Sci. Technol., 2007, 67(7–8), pp. 1734–1739.
S.P. Ray: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, 23A, pp. 2381–2385.
S.K. Mishra, S.K. Das, P. Ramachandrara, D. Belov, S. Mamyan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34A, pp. 1979–1983.
K.C. Patil, S.T. Aruna, T. Mimani: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2002, 6(6), pp. 507–512.
H.E. Camurlu, F. Magliab: J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 478(1–2), pp. 721–725.
S. Niyomwas, N. Chaichana, N. Memongkol: Sci. Technol. 2008, 30, pp. 233–238.
V. Sundaram, K.V. Logan, R.F. Speyer: Mater. Res. 1997, 12(07), pp. 1681–1684.
R. Taherzadeh Mousavian, S. Sharafi, and M.H. Shariat: Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater., 2011, vol. 29 (2), pp. 281–88.
L. Takacs: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2002, 47(4), pp. 355–414.
P. Mossino: Ceram. Int., 2004, 30(3), pp. 311–332.
L. Takacs, V. Soika, P. Balaz: Solid State Ionics, 2001, 141–142, pp. 641–647.
P. Millet, T. Hwang: Mater. Sci., 1996, 31(2), pp. 351–355.
N. Setoudeh, N.J. Welham: Alloys Compd., 2006, 420(1–2), pp. 225–28.
N.J. Welham: Miner. Eng., 1999, 12(10), pp. 1213–24.
E. Balakrishnan: Appl. Math. Decis. Sci. 2001, 5(3), pp. 151–164.
S. Gedenvanishili, D. Agrawal, and R. Roy: Mater. Sci. Lett., 1999, vol. 18 (9), pp. 665–68.
D.K. Agrawal: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 1998, vol. 3, pp. 480–85.
D.K. Agrawal: Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc., 2006, vol. 65 (3), pp. 129–44.
M. Gupta and E.W. Leong: Microwaves and Metals, Chap. 3, Wiley, New York, 2008.
B.L. Hays: Microwave Synthesis, Chap. 1, CEM Publishing, Berkshire, 2002.
D.R. Gaskell: Introduction to Thermodynamics of Materials, 5th edition, Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, 2003.
E. Mohammad Sharifi, F. Karimzadeh, and M.H. Enayati: Adv. Powder Technol., 2010, vol. 22 (4), pp. 526–31.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Farzad Azimi for his support in all steps of this work and students Sepideh Farhadinia and Ali Safapour for their help. The authors also thank Mrs. Mojhgan Bandabdi for her help in correcting the language of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 18, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farhadinia, F., Sedghi, A. Fabrication of Al2O3/(ZrB2 + TiB2) Composite Using MACS and Microwaves. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 3125–3129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2246-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2246-9