Abstract
The microstructure evolution of 0.20C-2.00Mn-2.00Si steel treated by the thermomechanical process to manufacture hot-rolled, transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel based on dynamic transformation of undercooled austenite was investigated using a Gleeble 1500 (Dynamic Systems, Inc., Poestenkill, NY) hot simulation test machine in combination with light microscope (LM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The mechanical properties of this steel with different multiphase microstructures were also analyzed using room-temperature tensile tests. The results indicated that the multi-phase microstructures consisting of fine-grained ferrite with a size of 1–3 μm, bainite packets, and retained austenite and martensite were formed for the used steel by a thermo-mechanical process involving dynamic transformation of undercooled austenite, controlled cooling, isothermal bainite treatment and water-quenching. With the increase in the strain of hot deformation of undercooled austenite, the fraction of ferrite increased, that of bainite decreased, and that of martensite increased. At the same time, the fraction of retained austenite (RA), as well as the carbon content of RA, first increased and then decreased. For the used steel treated by such process, the tensile strength is about 1200 MPa with a total elongation of about 20 pct, and the product of tensile strength and total elongation can be up to 25,000 MPa × pct.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
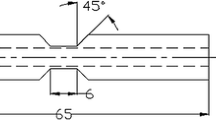
Such a special compression sample is designed to obtain a relatively large sample for tensile tests using the Gleeble 1500 hot simulation test machine, for which a cylindrical sample of 6 to 10 mm in diameter and 10 to 15 mm in length is commonly used and is not suitable for preparing a sample for tensile tests.
References
P.J. Jacques: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 259–65.
J. Bouquerel, K. Verbeken, and B.C. De Cooman: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1443–56.
P.J. Jacques, Q. Furnemont, F. Lani, T. Pardoen, and F. Delannay: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 3695–3705.
A.K. Srivastava, G. Jha, N. Gope, and S.B. Singh: Mater. Charact., 2006, vol. 57, pp. 127–35.
A. Wasilkowska, P. Tsipouridis, E.A. Werner, A. Pichler, and S. Traint: J. Mater. Proc. Tech., 2004, vols. 157–158, pp. 633–36.
I.B. Timokhina, P.D. Hodgson, and E.V. Pereloma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 1599–1609.
S. Hashimoto, S. Ikeda, K. Sugimoto, and S. Miyake: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 1590–98.
W.Y. Yang, L.F. Li, Y.Y. Yin, Z.Q. Sun, and X.T. Wang: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, vols. 654–656, pp. 250–53.
E. De Moor, P.J. Gibbs, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: Iron Steel Technol., 2010, vol. 7, pp. 133–44.
G.A. Thomas, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: Iron Steel Technol., 2008, vol. 5, pp. 209–17.
E. De Moor, J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, J.H. Kwak, and S.B. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 137–44.
D.W. Suh, S.J. Park, T.H. Lee, C.S. Oh, and S.J. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 397–408.
P.J. Gibbs, E. De Moor, M.J. Merwin, B. Clausen, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 3691–3702.
Z.Q. Sun, W.Y. Yang, J.J. Qi, and A.M. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 334A, pp. 201–06.
P. Jacqes, E. Girault, P. Harlet, and F. Delannay: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1061–67.
M. Onink, C.M. Brakman, F.D. Tichelaar, E.J. Mittermeijer, A.G.S. Vanderzwa, J.H. Root, and N.B. Konyer: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 29, pp. 1011–16.
R.F. Zhou, W.Y. Yang, R. Zhou, and Z.Q. Sun: J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 2005, vol. 12, pp. 507–11.
S.C. Hong, S.H. Lim, K.J. Lee, D.H. Shin, and K.S. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 394–99.
H.W. Xu, W.Y. Yang, and Z.Q. Sun: J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 2008, vol. 15, pp. 556–60.
H.W. Luo, L. Zhao, S.O. Kruijver, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1219–27.
E. Girault, P. Jacques, Ph. Harlet, K. Mols, J. Van Humbeeck, E. Aernoudt, and F. Delannay: Mater. Charact., 1998, vol. 40, pp. 111–18.
Y.I. Son, Y.K. Lee, K. Park, C.S. Lee, and D.H. Shin: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 3125–34.
I.B. Timokhina, P.D. Hodgson, and E.V. Pereloma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 2331–41.
J. Chiang, B. Lawrence, J.D. Boyd, and A.K. Pilkey: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528A, pp. 4516–21.
H.W. Xu, W.Y. Yang, and Z.Q. Sun: J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 2008, vol. 15, pp. 556–60.
K. Asoo, Y. Tomota, S Harjo, and Y. Okitsu: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 145–50.
R. Blonde, E. Jimenez-Melero, L. Zhao, J.P. Wright, E. Bruck, S. van der Zwaag, and N.H. van Dijk: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 565–77.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from The National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB630801) and the State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 2, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhang, X., Yang, W. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Low-Carbon Mn-Si Multiphase Steel Based on Dynamic Transformation of Undercooled Austenite. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 4337–4345 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1785-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1785-9