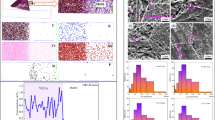
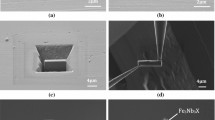
B and N can be used to increase the creep strength of advanced 9Cr power plant steels by means of microstructural stabilization and precipitation strengthening; however, the formation of boron nitride (BN) particles removes B and N from solution and reduces the strengthening effect of B and N simultaneously. In the current study, the BN precipitation/dissolution conditions in 9Cr-3W-3Co-V-Nb steels have been investigated to understand how to prevent the formation of BN. A series of austenitizing heat treatments have been designed using thermodynamic predictions as a guide in an attempt to dissolve the BN present after the production of 9Cr-3W-3Co-V-Nb type steels and to prevent also the precipitation of BN during the subsequent heat treatments. Advanced electron microscopy has been carried out to investigate the evolution of the BN particles in relation to the austenitization temperature. Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) has been used to identify the B-containing phases, and a method has been developed using secondary electron images to quantify the amount of BN present within the microstructure. It has been found that BN solubility is sensitive to the B and N levels in the steel composition, as indicated by thermodynamic calculations. However, it is proposed that austenitizing heat treatments at temperatures ranging from 1448 K to 1473 K (from 1175 °C to 1200 °C) with durations from 1 to 7 hours can effectively prevent the precipitation of BN as well as dissolving most of the BN particles formed during initial steel manufacture.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: ISIJ Int, 2001, vol. 41, pp 626-40.
F. Masuyama: ISIJ Int, 2001, vol. 41, pp 612-25.
F. Abe: Curr. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 8, pp 305-11.
S.K. Albert, M. Kondo, M. Tabuchi, F. Yin, K. Sawada and F. Abe: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp 333-43.
F. Abe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vols. 510-511. pp 64-69.
P. Mayr, I. Holzer, M. Albu, G. Kothleitner, H. Cerjak, and S.M. Allen: in Advances in Materials Technology for Fossil Power Plants, Proceedings from the Sixth International Conference, 2010, pp. 640–53.
K. Maile, Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip., 2007, vol. 84, pp 62-68.
K. Yamada, M. Igaeashi, S. Muneki and F. Abe, ISIJ int, 2002, vol. 42(7), pp 779-84.
M. Taneike, K. Sawada and F. Abe, Metall. Mater. Trans A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp 1255-62.
F. Abe: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2008, vol. 9, pp 1-15.
F. Abe: in Advances in Materials Technology for Fossil Power Plants, Proceedings from the Sixth International Conference, 2010, pp. 620–39.
K. Maruyama, K. Sawada and J. Koike: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp 641-53.
K. Sakuraya, H. Okada and F. Abe: Energy Mater., 2006, vol. 1, pp 158-66.
Thermo-Calc Software AB: TCFE6-TCS Steels/Fe-Alloys Database, Version 6.2, http://www.thermocalc.com/res/pdfDBD/tcfe6fromtcfe4.pdf.
P. Shi and B. Sundman: Thermo-Calc Software System (Thermodynamic Framework and Data), Thermocalc Software AB., 2008, pp. 2.27–2.29.
T. Horiuchi, M. Igarashi and F. Abe: ISIJ Int. 2002, vol. 42(Supplement), pp S67–S71.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the Technology Strategy Board and the valuable contributions of their partners in the collaborative project, IMPACT (Project number: TP11/CAT/6/I/BP074G): Alstom Power Ltd., Doosan Power Systems, E.ON, Goodwin Steel Castings, and the National Physical Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 13, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., MacLachlan, R., Jepson, M.A.E. et al. Microstructural Evolution of Boron Nitride Particles in Advanced 9Cr Power Plant Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 3411–3418 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1642-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1642-x