Abstract
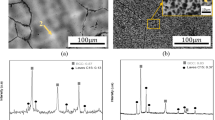
This article compares chromium evaporation characteristics of chromia- and alumina-forming alloys at high temperatures [1123 K and 1223 K (800 °C to 950 °C)] in humid air (3 and 12 pct H2O) and presents a mechanistic understanding of variation in chromium evaporation on the basis of their oxide scale morphologies. For this study, an alloy from each of the distinct chromia-forming, alumina-forming, and chromia-alumina transition characteristics was selected (i.e., an alumina-forming alloy (Aluchrom YHf), a chromia-forming alloy (AISI 310S-austentic stainless steel), and an alloy that undergoes transition from chromia to alumina formation (Nicrofer6025 HT)). For generating baseline chromium evaporation data, pure chromium oxide was also tested. The chromium evaporation rate decreased in the order pure chromium oxide > AISI 310S > Nicrofer6025 HT > Aluchrom YHf. Surface morphologies, cross sections, and chemical characteristics of oxide scales were examined by scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and focused ion beam. The variation in chromium evaporation of different alloys is explained on the basis of physical and chemical characteristics of the oxide scales.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Blum: CFI-Ceram. Forum Int., 2009, vol. 86, pp. E17-22.
S. Farhad and F. Hamdullahpur: J. Power Sources, 2009, vol. 193, pp. 632-38.
T.A. Adams and P.I. Barton: Aiche J., 2010, vol. 56, pp. 3120-36.
Y. Hao and D.G. Goodwin: J. Power Sources, 2008, vol. 183, pp. 157-63.
P. Kazempoor, V. Dorer and F. Ommi: Inl. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2009, vol. 34, pp. 8630-44.
K. Lobachyov and H.J. Richter: J. Energy Resour. Technol.-Trans. ASME, 1996, vol. 118, pp. 285-92.
J.W. Fergus: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 397, pp. 271-83.
A. Lashtabeg and S.J. Skinner: J. Mater. Chem., 2006, vol. 16, pp. 3161-70.
M.L. Liu, M.E. Lynch, K. Blinn, F.M. Alamgir and Y. Choi: Mater. Today, 2011, vol. 14, pp. 534-46.
M.C. Williams, J. Strake, and W. Sudoval: J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 159, pp.1241–47.
M.C. Williams, J.P. Strakey and W.A. Surdoval: Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2005, vol. 2, pp. 295-300.
E. Fontell, T. Kivisaari, N. Christiansen, J.B. Hansen and J. Palsson: J. Power Sources, 2004, vol. 131, pp. 49-56.
S.E. Veyo, L.A. Shockling, J.T. Dederer, J.E. Gillett and W.L. Lundberg: J. Eng. Gas. Turbines Power-Trans. ASME, 2002, vol. 124, pp. 845-9.
S.P. Jiang, J.P. Zhang and X.G. Zheng: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2002, vol. 22 (3), pp. 361-73.
H. Yokokawa, T. Horita, N. Sakai, K. Yamaji, M.E. Brito, Y.P. Xiong and H. Kishimoto: Solid State Ionics, 2006, vol. 177, pp. 3193-8.
K. Hilpert, D. Das, M. Miller, D.H. Peck and R. Weiβ: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, pp. 3642–47.
H. Ebrahimifar and M. Zandrahimi: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2011, vol. 206, pp. 75-81.
K. L. Wang, Y. J. Liu and J. W. Fergus: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, vol. 94 (12), pp. 4490–5.
M. Stanislowski, E. Wessel, K. Hilpert, T. Markus, L. Singheiser and W.J. Quadakkers: Solid State Ionics, 2008, vol. 179, pp. 2406-15.
W.N. Liu, X. Sun, E.V. Stephens and M.A. Khaleel: J. Power Sources, 2008, vol. 189 (2), pp. 1044-50.
R. Trebbels, T. Markus and L. Singheiser: J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 7, pp. 011013-6.
M. Stanislowski, E. Wessel, K. Hilpert, T. Markus and L. Singheiser: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, vol. 154, pp. A295-306.
G.R. Holcomb and D.E. Alman: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2006, vol. 15, pp. 394-8.
K. Gerdes and C. Johnson: J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol., 2009, vol. 6, pp. 011018-5.
M. Stanislowski, J. Froitzheim, L. niewolak, W.J. Quadakkers, K. Hilpert, T. Markus and L. Singheiser: J. Power Sources, 2007, vol. 164, pp. 578-89.
E. J. Opila, D. L. Myers, N. S. Jacobson, I. M. B. Nielsen, D.F. Johnson, J. K. Olminsky and M.D. Allendorf: J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, vol. 111, pp. 1971-80.
B.B. Ebbinghaus: Combust. Flame, 1993, vol. 93, pp. 119-37.
C. Gindorf, L. Singheiser and K. Hilpert: Steel Res., 2001, vol. 72, pp. 528-33.
Y.W. Kim and G. R. Belton,: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1811-6.
G. C. Fryburg, R. A. Miller, F. J. Kohl and C. A. Stearns: J. Electrochem. Soc, 1977, vol. 124, pp. 1738-43.
H. Kurokawa, C.P. Jacobson, L.C. De Jonghe, and S.J. Visco: Solid State Ionics, 2007, vol. 178, pp. 287–96.
M. Machkova, A. Zwetanova, V. Kozhukharov and S. Raicheva: J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metallurgy, 2008, vol. 43 (1), pp. 53-8.
J. R. Regina, J. N. DuPont and A. R. Marder: Oxid. Metals, 2004, vol. 61, pp. 69-90.
G. Berthome, E. NDah, Y. Wouters, A. Galerie, Materials and Corrosion, 2005, vol 56(6), pp. 389-392.
P. S. Santosa, H. S. Santos and S.P. Toledo: Mater. Res., 2000, vol. 3, pp. 104-14.
J.A. Nychka and D.R. Clarke: Oxid. Metals, 2005, vol. 63, pp. 325-52.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from the US Department of Energy and the Rolls Royce Fuel Cell Systems under Award Number DE-FE0000303. The authors also acknowledge Dr. S. Bhowmick for technical assistance, Mr. R. Ristau for the FIB analysis, and Mr. Peter Menard and Mark Drobney for laboratory support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 21, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, L., Verma, A., Goettler, R. et al. Oxide Scale Morphology and Chromium Evaporation Characteristics of Alloys for Balance of Plant Applications in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Metall Mater Trans A 44 (Suppl 1), 193–206 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1492-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1492-y