Abstract
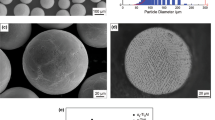
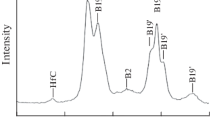
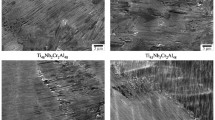
Ti51Ni49 compacts consolidated with persistent liquid-phase sintering usually contain Ti2Ni networks at the grain boundaries, which cause adverse effects on mechanical properties. With 0.5 and 1.0 at pct B additions, fine TiB forms during heating and sintering and acts as a nucleation site for Ti2Ni to precipitate within the grain during cooling. The resultant uniform distribution of TiB and Ti2Ni impedes grain growth and prevents the formation of continuous Ti2Ni precipitates at grain boundaries. As a result, a significant increase in tensile elongation, and not a decrease, as in most as-cast titanium alloys, is obtained because of these changes. The tensile strength also increases, without deterioration of the shape memory characteristics. The tensile strength and elongation are close to those of wrought TiNi alloys.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Igharo and J.V. Wood: Powder Metall., 1985, vol. 28. pp. 131-39.
D.G. Morris and M.A. Morris: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1989, vol. 110, pp. 139-49.
N. Zhang, P.B. Khosrovabadi, J.H. Lindenhovius, and B.H. Kolster: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1992, vol. 150, pp. 263-70.
J.C. Hey and A.P. Jardine: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, vol. 188, pp. 291-300.
S.M. Green, D.M. Grant, and N.R. Kelly: Powder Metall., 1997, vol. 40, pp. 43-47.
F.C. Yen and K.S. Hwang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 5296-5305.
F.C. Yen, K.S. Hwang, S.K. Wu, and S.H. Wu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 2431-41.
J. Mentz, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2006, vol. 8, pp. 247-52.
L. Zhang, C. Xie, and J. Wu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vols. 438–440, pp. 905-10.
J. Mentz, J. Frenzel, M.F.-X. Wagner, K. Neuking, G. Eggeler, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 491, pp. 270-78.
H.F. Lopez, A. Salinas, and H. Calderón: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 717-29.
H. Kato, T. Koyari, M. Tokizane, and S. Miura: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 1351-58.
J. Mentz, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vols. 481–482, pp. 630-34.
C. Zener: Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1948, vol. 175, pp. 15-51.
Y. Suzuki, Y. Xu, S. Morito, K. Otsuka, and K. Mitose: Mater. Lett., 1998, vol. 36, pp. 85-94.
J. Zhu, A. Kamiya, T. Yamada, W. Shi, and K. Naganuma: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 339, pp. 53-62.
V.K. Chandravanshi, R. Sarkar, P. Ghosal, S.V. Kamat, and T.K. Nandy: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 936-46.
D.J. Mceldowney, S. Tamirisakandala, and D.B. Miracle: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 1003-15.
J. Frenzel, E.P. George, A. Dlouhy, Ch. Somsen, M.F.-X Wagner, and G. Eggeler: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 3444-58.
H.C. Lin and S.K. Wu: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 26, pp. 59-62.
M. Binnewies and E. Milke: Thermochemical Data of Elements and Compounds, 2nd ed., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2002, pp. 102-16.
M.H. Mueller and H.W. Knott: Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 674-78.
H.T. Takeshita, H. Tanaka, N. Kuriyama, T. Sakai, I. Uehara, and M. Haruta: J. Alloy Compd., 2000, vol. 311, pp. 188-93.
R.W. Cahn and P. Haasen: Physical Metallurgy, 3rd ed., Elsevier Science, Atlanta, GA, 1983, pp. 1650-51.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China for their financial support of this work under contract NSC97-2221-E002-033-MY3. We also thank Professor Shyi-Kaan Wu for providing the DSC instrument and tensile test machine, and Chung-Yuan Kao and Yuan-Tzu Lee for their assistance in EPMA analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 13, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yen, FC., Hwang, KS. Microstructures, Mechanical Properties, and Shape Memory Characteristics of Powder Metallurgy Ti51Ni49 Modified with Boron. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 687–696 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0894-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0894-6