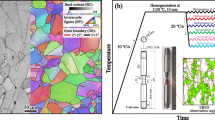
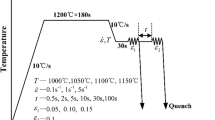
Abstract
Superalloys are being employed in more extreme conditions requiring higher strength, which requires producers to forge products to finer grain sizes with less grain size variability. To assess grain size, crystallographic texture, and substructure as a function of forging conditions, frictionless uniaxial compression testing characteristic of hot working was performed on INCOLOY 945 (Special Metals Corporation, Huntington, WV), which is a newly developed hybrid of alloys 718 and 925, over a range of temperatures and strain rates. The microstructure and texture were investigated comprehensively using light optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), electron channeling contrast imaging (ECCI), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to provide detailed insight into microstructure evolution mechanisms. Dynamic recrystallization, nucleated by grain/twin boundary bulging with occasional subgrain rotation, was found to be a dominant mechanism for grain refinement in INCOLOY 945. At higher strain rates, static recrystallization occurred by grain boundary migration. During deformation, duplex slip along {111} planes occurred until a stable 〈110〉 fiber compression texture was established. Recrystallization textures were mostly random but shifted toward the compression texture with subsequent deformation. An exception occurred at 1423 K (1150 °C) and 0.001 seconds−1, the condition with the largest fraction of recrystallized grains, where a 〈100〉 fiber texture developed, which may be indicative of preferential growth of specific grain orientations.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Sakai and J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 189-209.
M.C. Mataya, M.L. Robinson, D. Chang, M.J. Weis, G.R. Edwards, and D.K. Matlock: 29 th Mechanic. Working and Steel Process. Conf. Proceedings, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1987, vol. 25, pp. 235–48.
H. McQueen and J. Jonas: Treatise Mater. Sci. Technol., 1975, vol. 6, pp. 393-493.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Elsevier Ltd., Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2004, pp. 251-63.
N. Dudova, A. Belyakov, T. Sakai, and R. Kaibyshev: Acta Mater., 2010, no. 10, vol. 58, pp. 3624-32.
I. Shimizu: J. Struct. Geol., 2008, vol. 30, pp. 899-917.
A. Belyakov, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol. 255, pp. 139-47.
T. Sakai and M. Ohashi: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1990, vol. 6, pp. 1251-57.
J.K. Solberg, H.J. McQueen, N. Ryum, and E. Nes: Philos. Mag., A, 1989, vol. 60, p. 447.
G. Gottstein and U. Kocks: Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, pp. 175-88.
U.F. Kocks, C.N. Tomé, H. Wenk, and H. Mecking: Texture and Anisotropy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2000, pp. 181-225.
S.C. Medeiros, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, W.G. Frazier, and R. Srinivasan: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 42, pp. 17-23.
P.J. Goodhew, J. Humphreys, and R. Beanland: Electron Microscopy and Analysis, 3rd ed., Taylor & Francis, New York, NY, 2000, pp. 122-69.
S. Mannan: 7 th International Symposium on Superalloys and Derivatives, TMS, Pittsburgh, PA, 2010, pp. 629-43.
Y. Wang, W. Shao, L. Zhen, L. Yang, and X. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 497, pp. 479-86.
S.P. Coryell, K.O. Findley, and M.C. Mataya: 2010 TMS Meeting and Exhibition Proceedings, Seattle, WA, 2010, pp. 291–98.
S.P. Coryell: Master’s Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, 2010.
T. Sakai: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1995, vol. 53, pp. 349-61.
M. Hasegawa, M. Yamamoto, and H. Fukutomi: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 3939-50.
M. Frommert and G. Gottstein: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2009, vol. 506, pp. 101-10.
N. Tsuji, H. Yagi, Y. Matsubara, and Y. Saito: Ottawa, Canada, unpublished research, 2000.
B. Pratt, S. Kulkarni, D.P. Pope, C.D. Graham, and G. Noel: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1799-1804.
P.A. Beck: Acta Metall., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 230-34.
A. Merlini and P. Beck: Acta Metall., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 598-606.
H. Yoshida, B. Liebmann, and K. Lücke: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 51-56.
R.E. Smallman and R.J. Bishop: Modern Physical Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, 6th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Jordon Hill, Oxford, UK, 1999, pp. 232-45.
C. Barrett, C. Graham Jr., and J. Lommel: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 699-700.
W. Hosford: Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, 2005, pp. 131-33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 21, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coryell, S.P., Findley, K.O., Mataya, M.C. et al. Evolution of Microstructure and Texture During Hot Compression of a Ni-Fe-Cr Superalloy. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 633–649 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0889-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0889-3