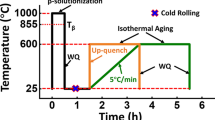
Abstract
The microstructural evolution and grain refinement mechanisms of a Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy, β-solution quenched and cold forged (CF) to strains of 0.1, 0.35, and 1.2 have been investigated using optical microscopy (OM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results showed that the stress-induced martensitic transformation became a predominant deformation mode in the metastable Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy during cold forging. These martensites α″ repeatedly divided the original β parent phase into a large number of micron-sized blocks when the forging strain was 0.1. Shear bands were observed to traverse α″/β lamellae and resulted in a significant grain refinement of the β phase, as the forging strain increased to 0.35. The degree of grain refinement inside shear bands was higher than the outside. Nanocrystalline and amorphous structures were produced in local areas of the original β phase, when the forging strain rose to 1.2. This dramatic grain refinement in the metastable Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy could be attributed to the stress-induced martensitic transformation promoting the initiation and growth of shear bands across α″/β lamellae. More dislocations were produced and accumulated inside grains to accommodate plastic deformation. The crystal structure was collapsed and an amorphous structure was formed as soon as the dislocation density was accumulated to a critical value of 1014/cm2. Moreover, some of the reverse martensitic phase transformation, α″→β, was observed to contribute to grain refinement of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy as well.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Lu and J. Lu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vols. 375-7, pp. 38–45.
N.R. Tao, Z.B. Wang, W.P. Tong, M.L. Sui, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 4603-16.
K.Wang, N.R. Tao, G. Liu, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 5281-91.
H.Q. Sun, Y.N. Shi, M.X. Zhang, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 975-82.
W. Xu, K.B. Kim, J. Das, M. Calin, B. Rellinghaus, and J. Eckert: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, vol. 89, p. 031906.
W. Xu, K.B. Kim, J. Das, M. Calin, J. Eckert: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1943-48.
W. Xu, X. Wu, M. Calin, M. Stoica, J. Eckert, K. Xia: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 1012-15.
H.W. Zhang, Z.K. Hei, G. Liu, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1871-81.
X. Wu, N. Tao, Y. Hong, G. Liu, B. Xu, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 681-91.
N.R. Tao and K. Lu: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 1039-43.
Y.S. Li, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2008, vol.56, pp. 230-41.
G.H. Xiao, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vols. 513–514, pp. 13–21.
A.W. Weeber and H. Bakker: Phys. B, 1988, vol. 153, pp. 93-135.
Y.L. Hao, S.J. Li, B.B. Sun, M.L. Sui, and R. Yang: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, vol. 98, p. 216405.
J. Koike, D.M. Parkin, and M. Nastasi: J. Mater. Res., 1990, vol. 5, pp. 1414-18.
L.E. Rehn, P.R. Okamoto, J. Pearson, R. Bhadra, and M. Grimsditch: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, vol. 98, pp. 2987-90.
M.W. Chen, J.W. Mccauley, and K.J. Hemker: Science, 2003, vol. 299, pp. 1563-66.
G.T. Terlinde, T.W. Duerig, and J.C. Williams: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 2101-15.
T.W. Duerig, J. Albercht, D. Richter, and P. Fischer: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 2161-72.
Q.Y. Sun, S.J. Song, R.H. Zhu, and H.C. Gu: J. Mater. Sci., 2002, vol. 37, pp. 2543-47.
R. Valiev: Nature Mater., 2004, vol. 3, pp. 511-16.
X. Wu, N. Tao, Y. Hong, J. Lu, and K. Lu: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2005, vol. 38, pp. 4140-43.
X.L. Wu and E. Ma: J. Mater. Res., 2007, vol. 22, pp. 2241-53.
T. Grosdidier, C. Roubaud, M.J. Philippe, and Y. Combres: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 36, pp. 21-28.
P.J. Bania: JOM, 1994, vol. 46, pp. 16-19.
D. Doraiswamy, S. Ankem: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1607-19.
W. Chen, Z.Y. Song, Q.Y. Sun, L. Xiao, W.B. She, J. Sun, and P. Ge: J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng., 2010, vol. 4, pp. 1296-1305.
S.E. Schoenfeld, S. Ahzi, and R.J. Asaro: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1995, vol. 43, pp. 415-46.
A.G. Considère: Ann. Ponts Chaussees, 1885, vol. 9, pp. 574-95.
G. Lutjering, J.C. Williams: Titanium, 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, 2003, pp. 74.
A. Mishra, B.K. Kad, F. Gregori, and M.A. Meyers: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 12-28.
D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 3495-3509.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the 973 Program of China under Grants 2007CB613804 and 2010CB631003 for financial support. We are also appreciative of the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 50831004 and 51071118. The authors would also like to thank Shengwu Guo for help with TEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 7, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Sun, Q., Xiao, L. et al. Deformation-Induced Grain Refinement and Amorphization in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 316–326 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0856-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0856-z