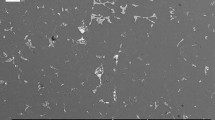
During heat treatment, the work piece experiences a range of heating rates depending upon the sizes and types of furnace. When the Al-Si-Mg cast alloy is heated to the solutionizing temperature, recrystallization takes place during the ramp-up stage. The effect of heating rate on recrystallization in the A356 (Al-Si-Mg) alloy was studied using dilatometric and calorimetric methods. Recrystallization in as-cast Al-Si alloys is a localized event and is confined to the elasto-plastic zone surrounding the eutectic Si phase; there is no evidence of recrystallization in the center of the primary Al dendritic region. The size of the elasto-plastic zone is of the same order of magnitude as the Si particles, and recrystallized grains are observed in the elasto-plastic region near the Si particles. The coefficient of thermal expansion of Al is an order of magnitude greater than Si, and thermal stresses are generated due to the thermal mismatch between the Al phase and Si particles providing the driving force for recrystallization. In contrast, recrystallization in Al wrought alloy (7075) occurs uniformly throughout the matrix, stored energy due to cold work being the driving force for recrystallization in wrought alloys. The activation energy for recrystallization in as-cast A356 alloy is 127 KJ/mole. At a slow heating rate of 4.3 K/min, creep occurs during the heating stage of solution heat treatment. However, creep does not occur in samples heated at higher heating rates, namely, 520, 130, and 17.3 K/min.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Sanders, Jr.: J. Met., 2001, vol. 53 (2), pp. 21–25.
M.N. Becker: J. Met., 1999, vol. 51 (11), pp. 26–38.
ASM Handbook, vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1991, pp. 159–61.
L. Pedersen and L. Arnberg: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 525–32.
S. Shivkumar, S. Ricci, B. Steenhoff, D. Apelian, and G. Sigworth: AFS Trans., 1989, vols. 89–138, pp. 791–810.
M.H. Mulazimoglu, A. Zaluska, F. Paray, and J.E. Gruzleski: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 1289–95.
P.N. Crepeau: AFS Trans., 1996, vol. 103, pp. 361–66.
S.K. Chaudhury and D. Apelian: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 763–78.
S.K. Chaudhury and D. Apelian: J. Mater. Sci., 2006, vol. 41, pp. 4684–90.
S.K. Chaudhury, L. Wang, and D. Apelian: AFS Trans., 2004, vol. 112, pp. 1–16.
M. Slamova, M. Karlik, M. Cieslar, B. Chalupa, and P. Merle: Kovove Mater., 2002, vol. 40 (6), pp. 389–401.
M. Slamova, M. Karlik, M. Cieslar, B. Chalupa, and P. Merle: Kovove Mater., 2003, vol. 41 (1), pp. 51–62.
X. Peng, J. Yang, Y. Chen, and Y. Yin: Int. J. Solids Struct., 2003, vol. 40 (26), pp. 7385–97.
S. Sarkar, M.A. Wells, and W.J. Poole: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 421 (1–2), pp. 276–85.
C.F. Yeung and W.B. Lee: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1998, vol. 82 (1–3), pp. 102–06.
J.S. Venrano, S.M. Bruemmer, L.M. Pawlowski, and I.M. Robertson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 238 (1), pp. 101–07.
Y.B. Kim, Y.H. Chung, K.K. Cho, and M.C. Shin: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 36 (1), pp. 111–16.
S. Shankar, Y. Riddle, and M.M. Makhlouf: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 705–07.
H. Kissinger: Anal. Chem., 1957, vol. 29, pp. 1702–06.
W. Sha: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2903–10.
C.S. Park, M.H. Kim, and C. Lee: J. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 36 (14), pp. 3579–87.
X. Zhou, R. Fougeres, and A. Vincent: J. Phys: III France, 1992, vol. 2 (11), pp. 2185–2201.
D. Brooksbank and K.W. Andrews: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1972, vol. 210, pp. 246–55.
Acknowledgments
Research sponsored by the Assistant Secretary for Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Office of Freedom CAR and Vehicle Technologies, as part of the High Temperature Materials Laboratory User Program, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, managed by UT–Battelle, LLC, for the United States Department of Energy, under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725. The support from corporate members of the Advanced Casting Research Center of the Metal Processing Institute at WPI is deeply appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 24, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhury, S.K., Warke, V., Shankar, S. et al. Localized Recrystallization in Cast Al-Si-Mg Alloy during Solution Heat Treatment: Dilatometric and Calorimetric Studies. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3160–3169 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0716-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0716-x