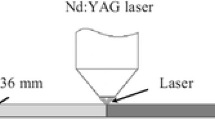
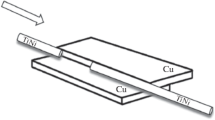
Abstract
As interest increases in incorporating Nitinol alloys in different microapplications and devices, the development of effective procedures for laser microwelding (LMW) these alloys becomes necessary. Laser welding processes applied to Nitinol have been shown to lower strength, induce inclusions of intermetallic compounds (IMCs), and alter the pseudoelastic and shape memory effects. Inconsistency in reported weld properties has also suggested that further studies are required. The current study details the mechanical, microstructural, and phase transformation properties of Nd:YAG LMW crossed Ti-55.8 wt pct Ni Nitinol wires. The effects of surface oxide on joint performance were also investigated. Fracture strength, weld microstructure, and phase transformation temperatures at varying peak power inputs were studied and compared to the unaffected base metal. Results showed good retention of strength and pseudoelastic properties, while the fusion zone exhibited higher phase transformation temperatures, which altered the active functional properties at room temperature.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
INSTRON is a trademark of Instron, Canton, MA.
References
J.V. Humbeeck: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2001, vol. 3 (11), pp. 837–50.
X.J. Yan, D.Z. Yang, and X.P. Liu: Mater. Charact., 2007, vol. 58, pp. 262–66.
X.J. Yan, D.Z. Yang, and M. Qi: Mater. Charact., 2006, vol. 57, pp. 58–63.
Y. Zhou: Microjoining and Nanojoining, Woodhead Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2008.
B. Tam: M.A.Sc Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010.
P. Scholossmacher, T. Haas, and A. Schüssler: J. Phys. Coll. C5, 1997, pp. 251–56.
Y. Ogata, M. Takatugu, T. Kunimasa, K. Uenishi, and K.F. Kobayashi: Mater. Trans., 2004, vol. 45, pp. 1070–76.
Y.T. Hsu, Y.R. Wang, S.K. Wu, and C. Chen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 569–76.
A. Tuissi, S. Besseghini, T. Ranucci, F. Squatrito, and M. Pozzi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vols. A273–A275, pp. 813–17.
A. Falvo, F.M. Furgiuele, and C. Maletta: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 412, pp. 235–40.
Y.G. Song, W.S. Li, L. Li, and Y.F. Zheng: Mater. Lett., 2008, vol. 62, pp. 2325–28.
M.I. Khan and Y. Zhou: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 6235–38.
X. Li, J. Xie, and Y. Zhou: J. Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 40, pp. 3437–43.
T.W. Duerig, K.N. Melton, D. Stockel, C.M. Wayman: Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1990.
G.S. Firstov, R.G. Vitchev, H. Kumar, B. Blanpain, and J. Van Humbeeck: Biomaterials, 2002, vol. 23 (24), pp. 4863–71.
V.G. Chuprina and I.M. Shalya: Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 2002, vol. 41 (1–2), pp. 85–89.
S.K. Sadrnezhaad and S.B. Raz: Mater. Manuf. Process., 2008, vol. 23 (7), pp. 640–50.
B. Tam, M.I. Khan, and Y. Zhou: MPMD 2009, ASM International, Minneapolis, MN, 2009.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2002
H. Sehitoglu, R. Hamilton, D. Canadinc, X.Y. Zhang, K. Gall, I. Karaman, Y. Chumlyakov, and J.J. Maier: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 5–13.
F.J. Gil, J.M. Manero, and J.A. Planell: J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 2526–30.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada. The authors are also thankful to Mr. Dennis W. Norwich, Memry Corporation, for the kind donation of material examined in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 10, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tam, B., Khan, M.I. & Zhou, Y. Mechanical and Functional Properties of Laser-Welded Ti-55.8 Wt Pct Ni Nitinol Wires. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 2166–2175 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0639-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0639-6