Abstract
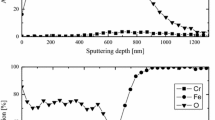
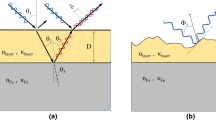
The hot rolling of austenitic stainless steels in Steckel Mills introduces particular characteristics to the development of oxides scales and surface structures. In this work, the formation of oxide structures during multipass hot rolling of 302 steel was studied under different sets of processing parameters in a laboratory system designed for the simulation of the Steckel process. The resulting surface structures were characterized by a set of complementary techniques involving scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and glow discharge optical spectroscopy (GDOS). The surface analysis revealed two alternative surface structures: one consisting in a thin protective oxide layer rich in Cr2O3 and the other consisting in thick complex structures containing several successive nonprotective oxide scale and metal layers resulting from a cyclic oxidation pattern involving stages of protective oxidation, chemical breakaway, and duplex oxidation. The critical condition that determined the activation of one mechanism or the other was identified associated with the parabolic rate constant for Cr2O3 growth and the diffusivity of Cr in the alloy. The effects of changes in temperature, deformation, and furnace atmosphere are discussed. Alternatives for controlling scale development are presented.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments Corp., Mahwah, NJ.
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
Siemens is a trademark of Siemens United Kingdom, Surrey, UK.
References
S. Kramer, G. Kneppe, D. Rosenthal: Iron Steel Eng., 1997, vol. 74, pp. 17–26
D. Blazevic: Internal Technical Report, International Association of Steckel Mill Operators (IASMO), Tornio, Finland, 1992
J. Robertson: Corr. Sci., 1991, vol. 32, 4, pp. 443–65
G.C. Wood: Corr. Sci., 1962, vol. 2, pp. 167–78
B. Ozturk, R. Matway: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, 2, pp. 169–75
S.J. Cobo: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom, 2005
H.E. Evans, A.T. Donaldson, T.C. Gilmour: Oxid. Met., 1999, vol. 52 (5–6), pp. 379–402
H.E. Evans, D.A. Hilton, R.A. Holm: Oxid. Met., 1976, vol. 10 (3), pp. 149–61
P. Kofstad: High Temperature Corrosion, Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1988, pp. 206–18
D. Caplan, M.J. Graham, M. Cohen: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1972, vol. 119 (9), pp. 1205–15
S.C. Kuiry, S. Seal, S.K. Bose, S.K. Roy: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34 (7), pp. 599–606
J.C. Langevoort, T. Fransen, P.J. Gellings: Oxid. Met., 1984, vol. 21 (5–6), pp. 271–84
C. Ostwald, H. Grabke: Corr. Sci., 2004, vol. 46, 5, pp. 1113–27
S.J. Allen, M.J. Dean: Behaviour of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments, The Metals Society, London, 1979, pp. 139–47
K.P. Lillerud, P. Kofstad: Oxid. Met., 1982, vol. 17 (3–4), pp. 177–94
P. Kofstad: Microscopy of Oxidation, The Institute of Metals, London, 1991, pp. 2–9
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the financial support provided by the Materials Forum, The University of Sheffield, and the collaboration of industrial partners Outokumpu and VAI UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 21, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobo, S., Rainforth, W. Factors Affecting the Development of Oxide Scales on Austenitic Stainless Steels during Hot Rolling in Steckel Mills. Metall Mater Trans A 39, 2486–2494 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9577-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9577-3