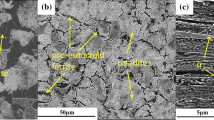
Abstract
The microstructural stability of ultrafine-grained (UFG) interstitial-free (IF) steel under cyclic loading was investigated. The samples were extracted from material processed along two different equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) routes (4C and 4E) at room temperature. Low-cycle fatigue tests were carried out in addition to electron and optical microscopy in order to characterize the microstructural evolution induced by cyclic deformation. The results revealed substantial differences in microstructure resulting from different processing routes. Specifically, the volume fraction of high-angle grain boundaries (HAGBs) and low-angle grain boundaries (LAGBs) varied significantly depending on the processing route. The different microstructural characteristics stemming from different ECAE routes expressively influence the fatigue response. Route-4C-processed material displays cyclic softening, while processing along route 4E leads to microstructural stability under cyclic loading. This highly route-dependent trend in the cyclic stress-strain response is attributed to the instability of the LAGBs and stability of HAGBs during cyclic deformation, which is further supported by electron backscattering diffraction results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Niendorf, D. Canadinc, H.J. Maier, I. Karaman, S.G. Sutter: Int. J. Mater. Res., 2006, 97:1328–36
R.Z. Valiev, A.V. Korznikov, R.R. Mulyukov: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, 168:141–48
R.Z. Valiev, I.V. Alexandrov, Y.T. Zhu, T.C. Lowe: J. Mater. Res., 2002, 17:5–8
H.W. Höppel, J. May, M. Göken: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6:219–22
H.J. Maier, P. Gabor, N. Gupta, I. Karaman, M. Haouaoui: Int. J. Fatigue, 2006, 28:243–50
M. Haouaoui, I. Karaman, and H.J. Maier: Acta Mater., 2006, 54:5477–88
I. Karaman, G.G. Yapici, Y.I. Chumlyakov, I.V. Kireeva: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 410–411:243–47
I. Karaman, A.V. Kulkarni, Z.P. Luo: Phil. Mag. A, 2005, 85:1729–45
C.C. Koch, K.M. Youssef, R.O. Scattergood, K.L. Murty: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2005, 7:787–94
A.P. Zhilyaev, G.V. Nurislamova, B.-K. Kim, M.D. Baró, J.A. Szpunar, T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 2003, 51:753–65
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, N. Tsuji, T. Sakai: Acta Mater., 1999, 47:579–83
J. Huang, Y.T. Zhu, D.J. Alexander, X. Liao, T.C. Lowe, R.J. Asaro: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 371:35–39
O.V. Mishin, D.J. Jensen, N. Hansen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 342:320–28
R.Z. Valiev, T.G. Langdon: Progr. Mater. Sci., 2006, 51:881–981
V.M. Segal: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 197:157–64
Y.T. Zhu, T.C. Lowe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 291:46–53
D.H. Shin, K.-T. Park: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 410–411:299–302
J.T. Wang, C. Xu, Z.Z. Du, G.Z. Qu, T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 410–411:312–15
Y. Fukuda, K. Oh-ishi, Z. Horita, T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 2002, 50:1359–68
German Standard DIN EN 10130: 1999–02
M.A. Meyers, A. Mishra, D.J. Benson: Progr. Mater. Sci., 2006, 51:427–556
H.W. Höppel, M. Kautz, C. Xu, M. Murashkin, T.G. Langdon, R.Z. Valiev, H. Mughrabi: Int. J. Fatigue, 2006, 28:1001–10
H.-K. Kim, M.-I. Choi, C.-H. Chung, D.-H. Shin: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 340:243–50
S.V.S. Narayana Murty, S. Torizuka, K. Nagai, T. Kitai, Y. Kogo: Scripta Mater., 2005, 53:763–68
R.E. Barber, T. Dudo, P.B. Yasskin, K.T. Hartwig: Scripta Mater., 2004, 51:373–77
V.M. Segal, R.E. Goforth, and K.T. Hartwig: U.S. Patent No. 5,400,633, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 1995
H. Mughrabi, H.W. Höppel, M. Kautz, R.Z. Valiev: Z. Metallkd., 2003, 94:1079–83
S. Li, A.A. Gazder, I.J. Beyerlein, E.V. Pereloma, C.H.J. Davies: Acta Mater., 2006, 54:1087–100
M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 332:97–109
I. Samajdar, B. Verlinden, P. van Houtte, D. Vanderschueren: Scripta Mater., 1997, 37:869–74
F. Scholz, J.H. Driver, E. Woldt: Scripta Mater., 1999, 40:949–54
T. Niendorf: University of Paderborn, 2006, unpublished research
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Dorothee Niklasch for her help with the AFM measurements, Mr. Sergej Tschumak for his help with the transmission electron microscopy analysis, and Mr. Felix Rubitschek for his assistance with the fatigue experiments. The German part of this study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, within the Research Unit Program “Mechanische Eigenschaften und Grenzflächen ultrafeinkörniger Werkstoffe.” The U.S. part of the work was supported by the National Science Foundation, Contract No. CMS 01-34554, Solid Mechanics and Materials Engineering Program, Directorate of Engineering (Arlington, VA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made in the symposium entitled “Ultrafine-Grained Materials: from Basics to Application,” which occurred September 25–27, 2006 in Kloster Irsee, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niendorf, T., Canadinc, D., Maier, H. et al. On the Microstructural Stability of Ultrafine-Grained Interstitial-Free Steel under Cyclic Loading. Metall Mater Trans A 38, 1946–1955 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9154-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9154-1