Abstract
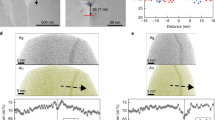
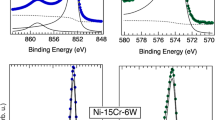
The mechanism of selective internal oxidation (SIO) for intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) of nickel-base alloys has been investigated through a series of experiments using high-purity alloys and a steam environment to control the formation of NiO on the surface. Five alloys (Ni-9Fe, Ni-5Cr, Ni-5Cr-9Fe, Ni-16Cr-9Fe, and Ni-30Cr-9Fe) were used to investigate oxidation and intergranular cracking behavior for hydrogen-to-water vapor partial pressure ratios (PPRs) between 0.001 and 0.9. The Ni-9Fe, Ni-5Cr, and Ni-5Cr-9Fe alloys formed a uniform Ni(OH)2 film at PPRs less than 0.09, and the higher chromium alloys formed chromium-rich oxide films over the entire PPR range studied. Corrosion coupon results show that grain boundary oxides extended for significant depths (>150 nm) below the sample surface for all but the highest Cr containing alloy. Constant extension rate tensile (CERT) test results showed that intergranular cracking varied with PPR and cracking was more pronounced at a PPR value where nonprotective Ni(OH)2 was able to form and a link between the nonprotective Ni(OH)2 film and the formation of grain boundary oxides is suggested. The observation of grain boundary oxides in stressed and unstressed samples as well as the influence of alloy content on IG cracking and oxidation support SIO as a mechanism for IGSCC.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments, Hillsboro, OR (now PEI).
REFERENCES
W. Bamford and J. Hall: 11th Conf. on Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems: Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, 2003, La Grange Park, IL, pp. 1071–81
K. Norring, J. Engstrom, H. Tornblom: 4th Int. Symp. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, NACE, Houston, TX, 1989, pp. 12-1–12-10
F.P. Ford: Corrosion, 1996, vol. 52, pp. 375–95
H.K. Birnbaum, P. Sofronis: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1994, vol. 176A, pp. 191–202
T. Magnin, D. Delafosse, B. Bayle, C. Bosch, D. Tanguy: Proc. Int. Conf. on Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior and Corrosion Deformation Interactions, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2003, pp. 563–76
J.R. Galvele: Corr. Sci., 1987, vol. 27, pp. 1–33
Y. Shen, P. Shewmon: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 1857–64
D.S. Morton, S.A. Attanasio, G.A. Young: 10th Int. Conf. on the Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, NACE, Houston, TX, 2002.
P.M. Scott and P. Combrade: 11th Int. Conf. on the Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 2003, pp. 29–38
P.M. Scott, M.L. Calvar: 6th Int. Symp. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 657–65
R.B. Rebak, Z. Xia, Z. Szklarska-Smialowska: Corrosion, 1995, vol. 51, pp. 689–97
G. Economy, R.J. Jacko, F.W. Pement: Corrosion, 1987, vol. 43, pp. 727–34
P. Kofstad: High Temperature Corrosion, Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1988, pp. 324–41
G.C. Wood, F.H. Stott, D.P. Whittle, Y. Shida, B.D. Bastow: Corr. Sci., 1983, vol. 23, pp. 9–25
R.W. Staehle, Z.W. Fang: 9th Int. Conf. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 69–78
J. Park, C.J. Altstetter: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 43–50
P.M. Scott: 9th Int. Symp. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 3–11
A.F. Gourgues, E. Andrieu: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, vol. 351A, pp. 39–55
T.S. Gendron, S.J. Bushby, R.D. Cleland, R.C. Newman: Corrosion—Deformation Interaction, CDI ‘96, Institute of Metals, London, 1997, pp. 485–95
L.E. Thomas, S.M. Bruemmer: Corrosion, 2000, vol. 55, pp. 572–87
Y.K. Rao: Stoichiometry and Thermodynamics of Metallurgical Processes, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 1985, pp. 883–84
P.F. Browning, M.F. Henry, K. Rajan: Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 665–78
D.D. Wagman, W.H. Evans, V.B. Parker, R.H. Schumm, I. Halow, S.M. Bailey, K.L. Churney, and R.L. Nuttall: The NBS Tables of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties: Selected Values for Inorganic and C 1 and C2 Organic Substances in SI Units, National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, 1982, pp. 2–166
M. Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, R. Oesten, P. Wilde, R.A. Huggins: Solid State Ionics, 1996, vols. 86–88, pp. 841–47
R.A. Rapp: Corrosion, 1965, vol. 21, pp. 382–401
C. Soustelle, M. Foucault, P. Combrade: 9th Int. Symp. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 105–14
J.H. Kim and I.S. Hwang: 11th Int. Symp. on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, American Nuclear Society, La Grange Park, IL, 2003, pp. 51–62
S. Yamaura, Y. Igarashi, S. Tsurekawa, T. Watanabe: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 1163–74
T.M. Angeliu, D.J. Paraventi, G.S. Was: Corrosion, 1995, vol. 51, pp. 837–48
B.A. Alexandreanu, B.M. Capell, G.S. Was: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, vol. 300, pp. 94–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 14, 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capell, B., Was, G. Selective Internal Oxidation as a Mechanism for Intergranular Stress Corrosion Cracking of Ni-Cr-Fe Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 38, 1244–1259 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9124-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9124-7