Abstract
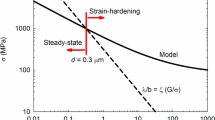
The relationship between the strain rate and the stress in power law and diffusional creep has usually been derived with the assumption that all the grains have the same size, which predicts a sharp transition from power law creep, with a stress exponent of about four to five, to diffusional creep, where the stress exponent is equal to one. We show that the use of distributed grain size can lead to a transition from power law to diffusional creep that is spread over several orders of magnitude in strain rate. The breadth of this transition depends on the standard deviation of the grain size probability density function. The experimental values for the stress exponent that are apparently greater than one, when measured over two or three orders of magnitude in strain rate, can result from a very gradual change in the stress exponent with the strain rate for a distributed grain size. Data sets from copper are compared to the model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Herring: J. Appl. Phys., 1950, vol. 21, pp. 437.
R.L. Coble: J. Appl. Phys., 1963, vol. 34, pp. 1679.
A.K. Mukherjee, J.E. Bird, and J.E. Dorn: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, p. 155.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby: Deformation-Mechanism Maps, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1982.
T.G. Langdon and F.A. Mohamed: J. Aus. Inst. Met., 1977, vol. 22, p. 189.
R. Raj and A.K. Ghosh: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, p. 283.
A.K. Ghosh and R. Raj: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, p. 607.
J.C.M. Li: Rate Processes in Plastic Deformation of Materials, Proc. J.E. Dorn Symp., No. 4 in ASM Series for Metals Materials/Metal-working Technology, J.C. Li and A.K. Mukherjee, eds., ASM, Cleveland, OH, 1975, p. 479.
B. Freeman and C.C. Ferguson: J. Geophys. Res., 1986, vol. 91, p. 3849.
J.H. Ter Heege, J.H.P. Bresser, and C.J. Spiers: J. Struct. Geol., 2004, vol. 26, p. 1693.
M. Herwegh, J.H.P. De Bresser, and J.H. Ter Heege: J. Struct. Geol., 2005, vol. 27, p. 503.
W.S. Jong, J.M. Rickman, H.M. Chan, and M.P. Harmer: J. Mater. Res., 2002, vol. 17 (2), p. 348.
R. Raj, J.S. Kong, D. Frangopol, and I.E. Raj: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, p. 1471.
C.S. Pande: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, p. 2161.
P. Feltham and J.D. Meakin: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, p. 614.
B. Wilshire and C.J. Palmer: Scripta Mater., 2002, vol. 46, p. 483.
B. Burton and G.W. Greenwood: Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, p. 1237.
M.F. Ashby: Scripta Metall., 1969, vol. 3, p. 837.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Raj, R. Influence of grain size variability on the strain rate dependence of the stress exponent in mixed-mode power law and diffusional creep. Metall Mater Trans A 36, 2913–2919 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0064-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0064-9