Abstract
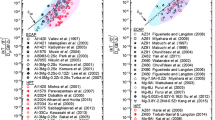
Asymmetric rolling (ASR) followed by annealing has been used to produce very fine grain sizes in the commercial Al-3 wt pct Mg alloy, AA5754. The appropriate rolling and annealing practice can produce grain sizes as small as 1 μm, and the tensile response of this fine-grained material has been compared with that of other fine-grained alloys produced by alternative methods. It is shown that the material obeys a Hall-Petch relationship, with a slope very similar to that of AA5754 produced by equal-channel angular extrusion (ECAE) and by conventional hot and cold rolling. The high yield strengths at fine grain sizes are accompanied by a low tensile elongation, which reflects the stress-strain response of very fine grain sizes. The stress-strain response can be described by the Voce equation, with the dislocation-accumulation rate decreasing with decreasing grain size and the rate of dynamic recovery being controlled by the Mg solute. Tensile elongations generally decrease with decreasing grain size, but a duplex grain structure appears to provide a good compromise between strength and elongation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ultrafine Grained Materials II, Y.T. Zhu, T.G. Langdon, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, M.J. Saran, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS Warrendale, PA, 2002.
M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2002, vol. A324, pp. 82–89.
J.S. Hayes, R. Keyte, and P.B. Prangnell: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 1259–63.
T. Hebesberger, R. Pippan, and H.P. Stuwe: Ultrafine Grained Materials II, T.G. Langdon, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, M.J. Saran, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2002, pp. 133–40.
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, and T. Sakai: Acta Mater., 1990, vol. 47, pp. 578–83.
C.-H. Choi, K.-H. Kim, and D.N. Lee: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1998, vols. 273–275, pp. 391–96.
Q. Cui and K. Ohari: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 1095–1101.
D.G. Morris and M.A. Muñoz-Morris: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 4047–60.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Amealing Phenomena, Pergamon, Oxford, UK, 1995, pp. 173–216.
G.B. Burger, A.K. Gupta, P.W. Jeffrey, and D.J. Lloyd: Mater. Characterization, 1995, vol. 35, pp. 23–39.
F.J. Humphreys: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 5031–39.
S.A. Court, K.M. Gatenby, and D.J. Lloyd: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2001, vols. A319–A321, pp. 443–47.
B.J. Brindley and P.J. Worthington: Metall. Rev., 1970, vol. 145, pp. 101–14.
W.B. Morrison and R.L. Miller: Ultrafine—Grain Metals, John J. Burke and Volker Weiss eds., Syracuse University Press, Syracuse, NY, 1970, pp. 183–211.
N. Tsuji, Y. Ito, Y. Koizumi, Y. Minamino, and Y. Saito: Ultrafine Grained Materials II, T.G. Langdon, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, M.J. Saran, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2002, pp. 389–97.
D.J. Lloyd: Met. Sci., 1980, vol. 14, pp.193–98.
R. Mahmudi: Mater. Lett., 1994, vol. 19, pp. 243–46.
D.J. Lloyd and L.R. Morris: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 25, pp. 857–61.
D.J. Lloyd, S.A. Court, and K.M. Gatenby: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 13, pp. 660–66.
H. Conrad: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, vol. A341, pp. 216–28.
R.Z. Valiev, N.A. Krasilnikov, and N.K. Tsenev: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, vol. A137, pp. 35–40.
M. Furkawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, R.Z. Valiev, and T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4619–629.
P. Lukac: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1996, vols. 217–222, pp. 71–82.
U.F. Kocks: Trans. ASME, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1976, vol. 98, pp. 76–85.
H. Mecking and U.F. Kocks: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 1865–75.
U.F. Kocks and H. Mecking: Progr. Mater. Sci., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 171–273.
J.H. Palm: Appl. Sci. Res., Sect. A, 1948, vol. 1, pp. 198–210.
E. Voce: J. Inst. Met., 1948, vol. 74, pp. 537–562.
D.J. Lloyd, H. Sang, J.D. Embury, P. Wycliffe, and G. LeRoy: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 36, pp. 35–46.
N.J. Petch: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, vol. 174, pp. 25–28.
H. Conrad: Ultrafine—Grain Metals, John J. Burke and Voker Weiss, eds., Syracuse University Press, Syracuse, NY, 1970, pp. 213–29.
M.F. Ashby: Phil. Mag., 1970, vol. 21, pp. 399–424.
A. Needleman and J. Gil Sevillano: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 109–83.
D.J. Lloyd and S.A. Court: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 19, pp. 1349–54.
Y. Estrin and H. Mecking: Elastic-Plastic Failure Modeling of Structures with Applications, D. Hui and T.J. Kozik, eds., ASME, New York, NY, 1988, vol. 141, pp. 181–91.
Y. Estrin and H. Mecking: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 57–70.
T. Narutani and J. Takamura: Acta Metall., 1991, vol. 39, pp. 2037–49.
M.H. Shankula, D.J. Lloyd, and J.D. Embury: Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, pp. 1293–99.
A.W. Thompson and M.I. Baskes: Phil. Mag., 1973, vol. 28, pp. 301–08.
D.A. Hughes, N. Hansen, and D.J. Bammann: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 147–53.
Q. Liu, X. Huang, D.J. Lloyd, and N. Hansen: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 3789–3802.
A. Considère: Ann. Ponts et Chaussées, 1885, vol. 9, pp. 574–775.
D.J. Lloyd: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 341–44.
M. Legros, B.R. Elliot, M.N. Rittner, J.R. Wertman, and K.J. Hemker: Phil. Mag. A, 2000, vol. 80, pp. 1017–26.
V.L. Tellkamp, A. Melmed, and E.J. Lavemia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2335–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Lloyd, D.J. The tensile response of a fine-grained AA5754 alloy produced by asymmetric rolling and annealing. Metall Mater Trans A 35, 997–1006 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-1003-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-1003-x