Abstract
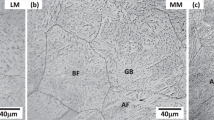
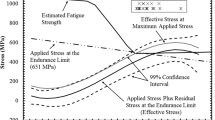
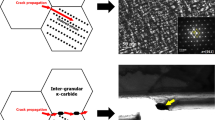
This study is concerned with the effects of alloying elements on fracture toughness in the transition temperature region of base metals and heat-affected zones (HAZs) of Mn-Mo-Ni low-alloy steels. Three kinds of steels whose compositions were varied from the composition specification of SA 508 steel (grade 3) were fabricated by vacuum-induction melting and heat treatment, and their fracture toughness was examined using an ASTM E1921 standard test method. In the steels that have decreased C and increased Mo and Ni content, the number of fine M2C carbides was greatly increased and the number of coarse M3C carbides was decreased, thereby leading to the simultaneous improvement of tensile properties and fracture toughness. Brittle martensite-austenite (M-A) constituents were also formed in these steels during cooling, but did not deteriorate fracture toughness because they were decomposed to ferrite and fine carbides after tempering. Their simulated HAZs also had sufficient impact toughness after postweld heat treatment. These findings indicated that the reduction in C content to inhibit the formation of coarse cementite and to improve toughness and the increase in Mo and Ni to prevent the reduction in hardenability and to precipitate fine M2C carbides were useful ways to improve simultaneously the tensile and fracture properties of the HAZs as well as the base metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.G. Druce and B.C. Edwards: Nucl. Energy, 1980, vol. 19, pp. 347–60.
K. Suzuki: J. Nucl. Mater., 1982, vols. 108–109, pp. 443–50.
J.R. Hawthorne: Nucl. Eng. Design, 1985, vol. 89, pp. 223–32.
P. Brown, S.G. Druce, and J.F. Knott: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 1121–31.
K.D. Haverkamp, K. Forch, K.-H. Piehl, and W. Witte: Nucl. Eng. Design, 1984, vol. 81, pp. 207–17.
R. Havel, M. Vacek, and M. Brumovsky: ASTM STP 1170, Philadelphia, PA, 1993, pp. 163–71.
D.P.G. Lidbury and E. Morland: Int. J. Pressure Vessel Piping, 1987, vol. 29, pp. 343–428.
S.G. Druce: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 219–32.
R.L. Bodnar, R.F. Cappellini, and R.I. Jaffee: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1987, vol. 14, pp. 185–94.
J.P. Naylor: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 861–73.
T. Enami, S. Sato, T. Tanaka, and T. Funakoshi: Kawasaki Steel Tech. Rep., 1974, vol. 6, pp. 145–61.
N. Ohashi, M. Tanaka, T. Enami, H. Oi, and T. Sekine: Kawasaki Steel Tech. Rep., 1979, vol. 11, pp. 56–66.
B.C. Kim, S. Lee, N.J. Kim, and D.Y. Lee: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 139–49.
J.H. Yoon, B.S. Lee, and J.H. Hong: Met. Mater. Int., 2001, vol. 7, pp. 505–12.
K. Suzuki, I. Sato, and H. Tsukada: Nucl. Eng. Design, 1994, vol. 151, pp. 513–22.
P. Bocquet, A. Cheviet, and R. Dumont: Nucl. Eng. Design, 1994, vol. 151, pp. 503–11.
H.G. Pisarski and J. Kudoh: in Welding Metallurgy of Structural Steels, J.Y. Koo, ed., TMS, Denver, CO, 1987, pp. 263–75.
K. Uchino and Y. Ohno: Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 1988, Houston, TX, ASME, Golden, CO, pp. 159–65.
J. Jang, Y. Yang, W. Kim, and D. Kwon: Met. Mater., 1997, vol. 3, pp. 230–38.
ASTM Standard E399-90, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1990.
ASTM Standard E1737-96, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1996.
T.L. Anderson and R.H. Dodds: J. Testing Evaluation, 1991, vol. 19, pp. 123–34.
British Standards Institution Document BS 5762, British Standards Institution, London, U.K., 1979.
ASTM Standard E1921-97, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1997.
R.L. Miller: Trans. ASM, 1964, vol. 57, pp. 892–99.
R.L. Miller: Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 592–97.
S. Kim, S.Y. Kang, S.J. Oh, S.-J. Kwon, S. Lee, J.H. Kim, and J.H. Hong: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 1107–19.
D. Rosenthal: Trans. ASME, 1946, Nov., pp. 849–66.
Atlas for Bainitic Microstructures, ISIJ, Tokyo, 1992, vol. 1.
Document Number IX-1533-88, IXJ-123-87 Revision 2, IIW, Paris, France, 1988.
S. Kim, Y.R. Im, S. Lee, H.C. Lee, Y.J. Oh, and J.H. Hong: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 903–11.
K. Sato and M. Toyoda: Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 1988, Houston, TX, ASME, Golden, CO, pp. 495–502.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, McGraw-Hill, London, 1988, ch. 6.
K. Wallin: Eng. Fract. Mech., 1984, vol. 19, pp. 1085–93.
T.L. Anderson and D. Stienstra: J. Testing Evaluation, 1989, vol. 17, pp. 46–53.
A.R. Marder: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1569–79.
X.P. Shen and R. Priestner: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 2547–53.
J.H. Chen, Y. Kikuta, T. Araki, M. Yoneda, and Y. Matsuda: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 1779–88.
C.A.N. Lanzillotto and F.B. Pickering: Met. Sci., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 371–82.
R.W. Hertzberg: Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1996, ch. 10.
O.M. Akselsen, J.K. Solberg, and Ø. Grong: Scand. J. Metall., 1998, vol. 17, pp. 194–200.
O.M. Akselsen, Ø. Grong, and J.K. Solberg: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 3, pp. 649–65.
H.P. Shen, T.C. Lei, and J.Z. Liu: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2, pp. 28–33.
N.J. Kim and G. Thomas: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 483–89.
A.F. Szewezyk and J. Garland: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1821–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Im, YR., Lee, S. et al. Effects of alloying elements on fracture toughness in the transition temperature region of base metals and simulated heat-affected zones of Mn-Mo-Ni low-alloy steels. Metall Mater Trans A 35, 2027–2037 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0151-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0151-3