Abstract
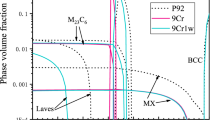
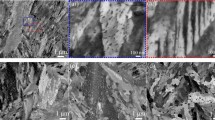
Morphology and coarsening kinetics of MC-type carbide (MC-carbide) precipitating during the tempering process have been investigated in V- and Nb-bearing Cr-Mo martensitic steels. Detailed transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations show that the addition of V and Nb stabilizes the B1-type MC-carbide instead of L’3-type M2C-carbide. The morphology of the MC-carbide is characterized as disk-like with Baker and Nutting orientation relationships with the matrix. When the specimens are fully solution treated followed by quenching, the MC-carbide precipitates as a multicomponent system with continuous solid solution of VC, NbC, and MoC. The V-, Nb-, and Mo-partitioning control the lattice parameter of MC-carbide and consequently affect the coherency between MC-carbide and the matrix. The coherent MC-carbide grows into an incoherent one with the progress of tempering. The numerical analysis on TEM observations has shown that the coarsening kinetics of MC-carbide is equated to (time)1/5 criteria, while the coarsening kinetics of the coexisting cementite is equated to (time)1/3 criteria. It is thus suggested that the Ostwald ripening of MC-carbide is controlled by pipe diffusion of V, Nb, and Mo along dislocations. It has been confirmed that the coarsening rate of the multicomponent MC-carbide is affected by V, Nb, and Mo content. Applying the thermodynamic solution database, the rate equation for MC-carbide coarsening can be expressed as a function of V, Nb, and Mo content, and the activation energy for pipe diffusion can be estimated as ΔQ v: ΔQ Nb: ΔQ Mo=1:3.9:0.6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.B. Pickering: Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers, Ltd., London, 1978, pp. 60–100.
R.W.K. Honeycombe: Steels, Microstructure and Properties, Edward Arnold, London, 1980, pp. 140–65.
R.W.K. Honeycombe: Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 915–36.
P.J. Grobner, D.L. Sponseller, and W.W. Cias: Mater. Performance, 1975, vol. 14(6), pp. 35–37.
T. Kaneko, Y. Okada, and A. Okeda: NACE Corrosion 87, NACE, Houston, TX, 1987, paper no. 291.
S.W. Ciaraldi: in Stress-Corrosion Cracking, By Russell H. Jones, ed., 1992, pp. 41–62.
W.B. Pearson: Lattice Spacings and Structures of Metals and Alloys, Pergamon Press, London, 1958, pp. 924–65.
G. Ghosh, C.E. Cambell, and G.B. Olson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 501–12.
J.W. Christian: in The Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys, G.V. Raynor, ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1965, pp. 433–70.
C. Wagner: Z. Elektrochem., 1961, vol. 65, pp. 581–91.
I.M. Lifshitz and V.V. Slyozov: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1961, vol. 19, pp. 35–50.
M.V. Speight: Acta Metall., 1969, vol. 16, pp. 133–38.
H.O.K. Kirchner: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2861–864.
M. Kreye: Z. Metallkd., 1970, vol. 61, pp. 108–19.
A.J. Ardell: Acta Metall., 1972, vol. 20, pp. 601–09.
A.J. Ardell: Acta Metall., 1972, vol. 20, pp. 61–71.
Byeong Joo Lee: Z. Metallkd., 1992, vol. 83, pp. 292–99.
W. Huang: Z. Metallkd., 1990, vol. 81, pp. 397–404.
J.O. Andersson: CALPHAD, 1988, vol. 12, pp. 9–23.
H.G. Lee and J.Y. Lee: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 131–36.
H. Oikawa: “Lattice Self-Diffusion in Solid Iron; A Critical Review,” Technical Report, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 1982, vol. 46, pp. 67–77.
A.W. Bowen and G.M. Leak: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1695–1700.
J. Kucera, B. Million, and K. Ciha: Kov. Mater., 1969, vol. 7, pp. 97–107.
T. Sato, T. Nishizawa, and H. Honda: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1954, vol. 40, pp. 1115–19.
E. Furubayashi: Trans. Nat. Res. Inst. Met., 1989, vol. 31, pp. 1–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyata, K., Kushida, T., Omura, T. et al. Coarsening kinetics of multicomponent MC-type carbides in high-strength low-alloy steels. Metall Mater Trans A 34, 1565–1573 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0303-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0303-x