Abstract
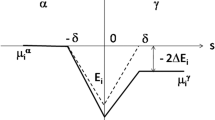
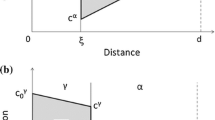
The growth of a planar ferrite (α): austenite (γ) boundary in low-carbon iron and Fe-Mn alloys continuously cooled from austenite through the (α+γ) two-phase field and the α single-phase field was simulated by incorporating carbon diffusion in austenite, intrinsic boundary mobility, and the drag of an alloying element. At a very high cooling rate (≥ 103 °C/s), the width of the carbon diffusion spike in austenite approaches the limit at which spikes are viable, so that the growth of ferrite in which carbon is not partitioned can occur even above the α solvus. In this context, the upper limiting temperature of partitionless growth of ferrite is the T 0 temperature. In the presence of drag of an alloying element, e.g., Mn, both carbon-partitioned and partitionless growth of ferrite begins to occur at finite undercoolings from the Ae 3, T 0, or α-solvus temperature, at which the driving force for transformation exceeds the drag force. The intrinsic mobility of the α:γ boundary may play a significant role at an extremely high cooling rate (≥105 °C/s).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.D. Swanson and J.G. Parr: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1964, vol. 202, pp. 104–07.
F.W. Jones and W.I. Pumphrey: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1949, vol. 163, pp. 121–31.
T.B. Massalski, A.J. Perkins, and J. Jaklovsky: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 687–94.
T.B. Massalski, J.H. Perepezko, and J. Jaklovsky: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1975, vol. 18, pp. 193–98.
E.S.K. Menon, M.R. Plichta, and H.I. Aaronson: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 321–32.
M. Hillert: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 411–19.
E.A. Wilson: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 615–30.
G.P. Krielaart, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. A238, pp. 104–16.
T.A. Kop, Y. van Leeuwen, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 713–18.
M. Suehiro, Z.-K. Liu, and J. Ågren: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4241–51.
M. Enomoto: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 3533–40.
G.R. Purdy, W.T. Reynolds, Jr., and H.I. Aaronson: Proc. Int. Conf. on Solid → Solid Phase Transformations (PTM ’99), M. Koiwa, K. Ohtsuka, and T. Miyazaki, eds., Japan Institute of Metals, Kyoto, 1999, pp. 1461–64.
M. Hillert: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 4481–505.
M. Hillert and M. Schalin: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 461–68.
K. Oi, C. Lux, and G.R. Purdy: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48 pp. 2147–55.
E.S.K. Menon, M.R. Plichta, and H.I. Aaronson: Scripta Metall., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 1455–57.
M. Enomoto and N. Nojiri: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 36, pp. 625–32.
I.I. Kolodner: Comm. Pure Appl. Math., 1956, vol. 6, pp. 1–31.
M. Enomoto and C. Atkinson: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 3237–44.
M. Hillert: Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 5–19.
M. Enomoto, T. Sonoyama, and H. Yada: Mater. Trans., JIM, 1998, vol. 39, pp. 189–95.
M. Enomoto, M. Kagayama, N. Maruyama, and T. Tarui: Proc. Int. Conf. on Solid → Solid Phase Transformations (PTM ’99), Kyoto, 1999, M. Koiwa, K. Ohtsuka, and T. Miyazaki eds., Japan Institute of Metals, Kyoto, 1989, pp. 1453–60.
J.W. Cahn: Acta Metall., 1962, vol. 10, pp. 789–98.
M. Hillert, J. Odqvist, and J. Ågren: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 221–27.
L. Kaufman, S.V. Radcliffe, and M. Cohen: in Decomposition of Austenite by Diffusional Processes, V.F. Zackay and H.I. Aaronson, eds., Interscience Publishers, New York, NY, 1962, pp. 313–52.
M. Enomoto and H.I. Aaronson: CALPHAD, 1985, vol. 9, pp. 43–58.
B. Uhrenius: in Hardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel, D.V. Doane and J.S. Kirkaldy, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1978, pp. 28–81.
G.P. Krielaart, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, vol. A237, pp. 216–23.
A. Borgenstam and M. Hillert: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 1499–510.
J. Friedberg, L.-E. Torndahl, and M. Hillert: Jernkont. Ann., 1969, vol. 153, pp. 263–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made at the symposium entitled “The Mechanisms of the Massive Transformation,” a part of the Fall 2000 TMS Meeting held October 16–19, 2000, in St. Louis, Missouri, under the auspices of the ASM Phase Transformations Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enomoto, M. Simulation of ferrite growth in continuously cooled low-carbon iron alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 33, 2309–2316 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0354-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0354-4