Abstract
Objective
To explore the effects of Rhizoma Polygoni Cuspidati and Ramulus Cinnamomi compatibility (PR) on uric acid metabolism and the expression of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in rats with hyperuricemia.
Methods
Seventy male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into 7 groups with 10 rats per group, including the normal group, model group, allopurinol group, benzbromarone group and PR groups at 3 doses (3.5, 7, 14 g/kg). Except the normal group, rats of the other groups were intragastrically administered 100 mg/kg hypoxanthine and 250 mg/kg ethambutol, and subcutaneously injected with 200 mg/kg potassium oxonate. All rats were continuously modeled for 17 days, and gavaged with corresponding drugs. The rats of the normal and model groups were gavaged with saline, once a day, for 2 weeks. The levels of serum uric acid (SUA), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr) were determined. In addition, the contents of NGAL and KIM-1 in urine and the mRNA and protein expressions of xanthine oxidase (XOD) in liver of hyperuricemia rats were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot, respectively. Moreover, the pathological changes of kidney were analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain method.
Results
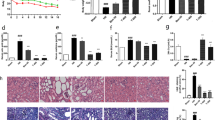
Compared with the normal group, the levels of SUA, BUN, NGAL and KIM-1 and the expressions of hepatic XOD mRNA and protein in the hyperuricemia rats were increased signifificantly (P<0.01). PR signifificantly decreased the levels of SUA, BUN, NGAL and KIM-1 and down-regulated the mRNA and protein expressions of hepatic XOD (P<0.05 or P<0.01). In addition, the pathological changes of kidney were signifificantly suppressed by oral administration of PR.
Conclusions
PR ameliorated uric acid metabolism and protected renal function, the underlying mechanism was mediated by decreasing the levels of SUA, BUN, NGAL and KIM-1, inhibiting the expression of hepatic XOD and ameliorating the pathological change of kidney.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avram Z, Krishnan E. Hyperuricaemia—where nephrology meets rheumatology. Rheumatology 2008;47:960–964.
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang X, Liu L, Wang H. The association between plasma uric acid and renal function decline in a Chinese population-based cohort. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012;27:1836–1839.
Shi YW, Wang CP, Liu L, Liu YL, Wang X, Hong Y, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of resveratrol and its analogues in hyperuricemic mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 2012;56:1433–1444.
Hwang SH, Choi YG, Jeong MY, Hong YM, Lee JH, Lim S. Microarray analysis of gene expression profile by treatment of Cinnamomi Ramulus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 cells. GENE 2009;443:83–90.
Wang YF, Han B, Jia Z, Li Z, Hu XG, Dai WQ, et al. Study of different ratio of cold-heat compatibility of Tong-Feng-Ke in rat gout model. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul (Chin) 2012;18:185–189.
Han B, Hu XG, Li Z, Wang YF. The comparative study on effect of different compatibility of Lexing Tongfengke for experimental gout. Shenzhen J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2011;21:9–11.
Farris AB, Colvin RB. Renal interstitial fibrosis: mechanisms and evaluation. Curt Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2012;21:289–300.
Liu TH, ed. Diagnostic pathology. 2nd ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House; 2006:407.
Wang J, Liu S, Ma B, Chen L, Song F, Liu ZQ, et al. Rapid screening and detection of XOD inhibitors from S. tamariscina by ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI-MS combined with HPCCC. Anal Bioanal Chem 2014;406:7379–7387.
Kamatani N, Fujimori S, Hada T, Hosoya T, Kohri K, Nakamura T, et al. An allopurinol-controlled, randomized, double-dummy, double-blind, parallel between-group, comparative study of febuxostat (TMX-67), a non-purineselective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in patients with hyperuricemia including those with gout in Japan: phase 3 clinical study. J Clin Rheumatol 2011;17:S13–S18.
Faruque LI, Ehteshami-Afshar A, Wiebe N, Tjosvold L, Homik J, Tonelli M. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the safety and efficacy of febuxostat versus allopurinol in chronic gout. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2013;43:367–375.
Li XC, Liu XH, Gao H, Fan ML, Liu K, Wang W. Study on inhibition and enzyme kinetics of different solvent extractions from Polygonum cuspidatum on xanthine oxidase. China Pharm 2015;26:494–496.
Chen L, Lan Z, Lin QX, Mi X, He YY, Wei LH, et al. Polydatin ameliorates renal injury by attenuating oxidative stressrelated inflammatory responses in fructose-induced urate nephropathic mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2013;52:28–35.
Zhao X, Zhu JX, Mo SF, Pan Y, Kong LD. Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver. J Ethnopharmacol 2006;103:357–365.
Malyszko J, Malyszko JS, Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Poniatowski B, Dobrzycki S, Mysliwiec M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a new and sensitive marker of kidney function in chronic kidney disease patients and renal allograft recipients. Transplant Proc 2009;41:158–161.
Paragas N, Qiu A, Hollmen M, Nickolas TL, Devarajan P, Barasch J. NGAL-siderocalin in kidney disease. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta 2012;1823:1451–1458.
Huo W, Zhang K, Nie Z, Li Q, Jin F. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel kidney-specific injury molecule playing potential double-edged functions in kidney injury. Transplant Rev 2010;24:143–146.
Xu PC, Zhang JJ, Chen M, Lv JC, Liu G, Zou WZ, et al. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in patients with IgA nephropathy is closely associated with disease severity. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011;26:3229–3236.
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, eds. Robbins basic pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2003:1003–1006.
Batsford S, Duermueller U, Seemayer C, Mueller C, Hopfer H, Mihatsch M. Protein level expression of toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 9 in renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011;26:1413–1416.
Hu QH, Miao MX, Lu G, Ji H. Effects of quercetin on expression of renal NLRP3 and TLRs in rats with uric acid nephtopathy. Chin Tradit Herb Drug (Chin) 2013;44:3496–3502.
Chen Y, Lu Y, Wang YN, Lin ZC, Gu W, Tan L, et al. Effect of Compound Qingqin Liquid on the expression of toll-like receptor in the renal tissue of rats with urate nephropathy. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2014;34:722–727.
Gu ZL, Huang HZ, Shi W, Hu XG, Han B. Impacts of herb pair of Rhizoma Polygoni Cuspidati and Ramula Cinnamomi on acute gouty arthritis. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol (Chin) 2015;26:315–319.
Ko GJ, Grigoryev DN, Linfert D, Jang HR, Watkins T, Cheadle C, et al. Transcriptional analysis of kidneys during repair from AKI reveals possible roles for NGAL and KIM-1 as biomarkers of AKI-to-CKD transition. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2010;298:F1472–F1483.
Shi YF, Wang L, Xu LQ, Zhuang SG, Yan HD, Liu N. Research progress of renal damage in patients with hyperuricemia. Chin J Nephrol (Chin) 2014;30:794–797.
Wu G, Wu HB, Jiang H. Anti-hyperuricemia effect and mechanism of polydatin in mice. Acta Pharm Sin (Chin) 2014;49:1739–1742.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81173194)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, B., Zhu, Cx., Shi, W. et al. Effect of Rhizoma Polygoni Cuspidati and Ramulus Cinnamomi compatibility on uric acid metabolism and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 in rats with hyperuricemia. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 535–542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2649-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2649-0