Abstract
Objective
This study observed attenuating effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA), an effective ingredient of aqueous extract of Carthamus tinctorius L, on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endothelium inflammatory injury.
Methods
Eahy926 human endothelium cell (EC) line was used; thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) test was assayed to observe the viability of EC; Luciferase reporter gene assay was applied to measure nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 subunit nuclear binding activity in EC; Western blot technology was used to monitor mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and NF-κB activation. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method was applied to observe intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and E-selectin mRNA level; EC surface ICAM-1 expression was measured with flow cytometry and leukocyte adhesion to EC was assayed with Rose Bengal spectrophotometry technology.
Results
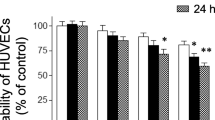
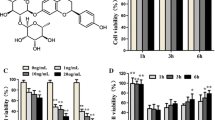
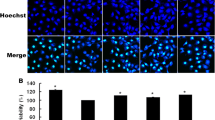
HSYA protected EC viability against LPS-induced injury (P <0.05). LPS-induced NF-κB p65 subunit DNA binding (P <0.01) and nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor α (IκBα) phosphorylation was inhibited by HSYA. HSYA attenuated LPS triggered ICAM-1 and E-selectin mRNA levels elevation and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK or c-Jun N-terminal kinase MAPK. HSYA also inhibited LPS-induced cell surface ICAM-1 protein expression P <0.01) and leukocyte adhesion to EC (P <0.05).
Conclusion
HSYA is effective to protect LPS-induced high expression of endothelium adhesive molecule and inflammatory signal transduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun CY, Pei CQ, Zang BX, Wang L, Jin M. The ability of hydroxysafflor yellow A to attenuate lipopolysaccharideinduced pulmonary inflammatory injury in mice. Phytother Res 2010;24:1788–1795.
Zang BX, Jin M, Li JR. Large scale preparation of pure hydroxysafflor yellow A by macroporus resin-gel column chromatography. J Cardiovasc Pulm Dis (Chin) 2008;27:363–365.
Feng ZM, He J, Jiang JS, Chen Z, Yang YN, Zhang PC. NMR solution structure study of the representative component hydroxysafflor yellow A and other quinochalcone C-glycosides from Carthamus tinctorius. J Nat Prod 2013;76:270–274.
Gamble JR, Vadas MA. A new assay for the measurement of the attachment of neutrophils and other cell types to endothelial cells. J Immunol Methods 1988;109:175.
Gye YP, John WC. Nuclear factor Kappa B is a promising therapeutic target in inflammatory lung disease. Current Drug Targets 2006;7:661–668.
Fitzgerald KA, Rowe DC, Barnes BJ, Caffrey DR, Visintin A, Latz E, et al. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-κB involves the Toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J Exp Med 2003;198:1043–1055.
Schwartz MD, Moore EE, Moore FA, Shenkar R, Moine P, Haenel JB, et al. Nuclear factor-κB is activated in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 1996;24:1285–1292.
Zang BX, Jin M, Si N, Zhang Y, Wu W, Piao YZ. Antagonistic effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on the platelet activating factor receptor. Acta Pharm Sin (Chin) 2002;37:696–699.
Zang BX, Jin M, Li JR. Study on β receptor antagonistic effect of safflor yellow and hydroxysafflor yellow A. J Cardiovasc Pulm Dis (Chin) 2008;27:301–303.
Jin M, Sun CY, Pei CQ, Wang L, Zhang PC. Study of the effect of safflor yellow injection on inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammatory injury in mice. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:836–843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270103) and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No. 7102025)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, M., Sun, Cy. & Zang, Bx. Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelium inflammatory injury. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 36–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-1976-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-1976-x