Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of Ganfukang (肝复康, GFK) on connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/protein kinase B (PKB or Akt) signal pathway in a hepatic fibrosis rat model and to explore the underlying therapeutic molecular mechanisms of GFK.
Methods
Fifty SD rats were randomly divided into five groups as follows: the control group, the model group (repeated subcutaneous injection of CCl4), and the three GFK treatment groups (31.25, 312.5, and 3125 mg/kg, intragastric administration). Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry were used to examine the expression of CTGF, integrin α5, integrin β1, FAK/Akt signal pathway, cyclinD1, and collagen in the different-treated rats.
Results
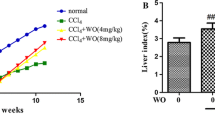
GFK attenuated the up-regulation of CTGF, integrin α5, and integrin β1 in hepatic fibrosis rats and suppressed both the phosphorylation of FAK and the phosphorylation of Akt simultaneously (P<0.01). At the same time, the expression of cyclinD1, collagen I, and collagen III was decreased by GFK significantly (P<0.01).
Conclusions
CTGF and FAK/Akt signal pathway were activated in the CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis rats, which contribute to increased expression of cyclinD1 and collagen genes. The mechanisms of the anti-fibrosis activity of GFK may be due to its effects against CTGF and FAk/Akt signal pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 2011;6:425–456.
Jiao J, Friedman SL, Aloman C. Hepatic fibrosis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2009;25:223–229.
Ahmad A, Ahmad R. Understanding the mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and potential therapeutic approaches. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2012;18:155–167.
Jian YC, Li W, He Y, Jiang M, Liu YB, Xiong WJ. Effect of oxymatrine on hepatic gene expression profile in experimental liver fibrosis of rats. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:445–450.
Bradham DM, Igarashi A, Potter RL, Grotendorst GR. Connective tissue growth factor: a cysteine-rich mitogen secreted by human vascular endothelial cells is related to the SRC-induced immediate early gene product CEF-10. J Cell Biol 1991;114:1285–1294.
Chaqour B, Goppelt-Struebe M. Mechanical regulation of the Cyr61/CCN1 and CTGF/CCN2 proteins. Febs J 2006;273:3639–3649.
Gressner OA, Gressner AM. Connective tissue growth factor: a fibrogenic master switch in fibrotic liver diseases. Liver Int 2008;28:1065–1079.
Gressner OA, Lahme B, Demirci I, Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R. Differential effects of TGF-beta on connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) expression in hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes. J Hepatol 2007;47:699–710.
George J, Tsutsumi M. siRNA-mediated knockdown of connective tissue growth factor prevents N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gene Ther 2007;14:790–803.
Morikawa H, Tamori A, Nishiguchi S, Enomoto M, Habu D, Kawada N, et al. Expression of connective tissue growth factor in the human liver with idiopathic portal hypertension. Mol Med 2007;13:240–245.
Phanish MK, Winn SK, Dockrell ME. Connective tissue growth factor-(CTGF, CCN2)-a marker, mediator and therapeutic target for renal fibrosis. Nephron Exp Nephrol 2010;114(3):e83–e92.
Bogatkevich GS, Ludwicka-Bradley A, Singleton CB, Bethard JR, Silver RM. Proteomic analysis of CTGFactivated lung fibroblasts: identification of IQGAP1 as a key player in lung fibroblast migration. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2008;295:L603–L611.
Huang G, Brigstock DR. Integrin expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2). J Cell Mol Med 2011;15:1087–1095.
An J, Zheng L, Xie S, Dun Z, Hao L, Yao D, et al. Downregulation of focal adhesion kinase by short hairpin RNA increased apoptosis of rat hepatic stellate cells. APMS 2011;119:319–329.
Xu TT, Jiang MN, Li C, Che Y, Jia YJ. Effect of Chinese traditional compound, Gan-fu-kang, on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats and its probable molecular mechanisms. Hepatol Res 2007;37:221–229.
Gao Y, Song LX, Jiang MN, Ge GY, Jia YJ. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine on endotoxin and its receptors in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Inflammation 2008;31:121–132.
Lou JL, Jiang MN, Li C, Zhou Q, He X, Lei HY, et al. Herb medicine Gan-fu-kang attenuates liver injury in a rat fibrotic model. J Ethnopharmacol 2010;128:131–138.
Li G, Li D, Xie Q, Shi Y, Jiang S, Jin Y. RNA interfering connective tissue growth factor prevents rat hepatic stellate cell activation and extracellular matrix production. J Gene Med 2008;10:1039–1047.
Yuhua Z, Wanhua R, Chenggang S, Jun S, Yanjun W, Chunqing Z. Disruption of connective tissue growth factor by short hairpin RNA inhibits collagen synthesis and extracellular matrix secretion in hepatic stellate cells. Liver Int 2008;28:632–639.
Tong Z, Chen R, Alt DS, Kemper S, Perbal B, Brigstock DR. Susceptibility to liver fibrosis in mice expressing a connective tissue growth factor transgene in hepatocytes. Hepatology 2009;50:939–947.
Zhao X, Guan JL. Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Advan Drug Delivery Revi 2011;63:610–615.
Zhou Q, Lui VW, Yeo W. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol 2011;7:1149–1167.
Wang Y, Gao J, Zhang D, Zhang J, Ma J, Jiang H. New insights into the antifibrotic effects of sorafenib on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 2010;53:132–144.
Jiang Q, Zhang H, Zhang P. ShRNA-mediated gene silencing of MTA1 influenced on protein expression of ER alpha, MMP-9, CyclinD1 and invasiveness, proliferation in breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2011;30(1):60.
Mao XR, Yue W, Yuan H, Chen H, Xue M. Inhibition effect of small interfering RNA targeting connective tissue growth factor on liver fibrosis in rats. J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci) 2011;40:603–608.
Kodama T, Takehara T, Hikita H, Shimizu S, Shigekawa M, Tsunematsu H, et al. Increases in p53 expression induce CTGF synthesis by mouse and human hepatocytes and result in liver fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 2011;121:3343–3356.
Paik YH, Kim JK, Lee JI, Kang SH, Kim DY, An SH, et al. Celecoxib induces hepatic stellate cell apoptosis through inhibition of Akt activation and suppresses hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut 2009;58:1517–1527.
Wang Y, Jiang XY, Liu L, Jiang HQ. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates hepatic stellate cell apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:5186–5191.
Gentilini A, Lottini B, Brogi M, Caligiuri A, Cosmi L, Marra F, et al. Evaluation of intracellular signalling pathways in response to insulin-like growth factor I in apoptotic-resistant activated human hepatic stellate cells. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2009;2:1–11.
Biernacka A, Dobaczewski M, Frangogiannis NG. TGF-β signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors 2011;29:196–202.
Martin IV, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Zok S, van Roeyen CR, Eriksson U, Boor P, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-C neutralization reveals differential roles of PDGF receptors in liver and kidney fibrosis. Am J Pathol 2013;182:107–117.
Liu Y, Wang Z, Kwong SQ, Lui EL, Friedman SL, Li FR, et al. Inhibition of PDGF, TGF-β, and Abl signaling and reduction of liver fibrosis by the small molecule Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase antagonist Nilotinib. J Hepatol 2011;55:612–625.
Li GS, Jiang WL, Tian JW, Qu GW, Zhu HB, Fu FH. In vitro and in vivo antifibrotic effects of rosmarinic acid on experimental liver fibrosis. Phytomedicine 2010;17:282–288.
Hou J, Tian J, Jiang W, Gao Y, Fu F. Therapeutic effects of SMND-309, a new metabolite of salvianolic acid B, on experimental liver fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol 2011;650:390–395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Natural Science Fund of Liaoning Province, China (No. 201102055)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Jiang, Mn., Zhang, Ch. et al. Effects of Ganfukang (肝复康) on expression of connective tissue growth factor and focal adhesion kinase/protein kinase B signal pathway in hepatic fibrosis rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 20, 438–444 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1597-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1597-1