Abstract
Objective
To investigate the antifibrotic effect of the Chinese herbs Modified Danggui Buxue Decoction (加味当归补血汤, MDBD) on adraimycin-induced nephropathy in rats.
Methods
Thirty-two male Sprague Dawley albino rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: the control, model, and two treatment groups, with 8 in each group. Nephropathy was induced in the latter 3 groups by intravenous injection of adriamycin. Rats in the two treatment groups received intragastric administration of benazepri (a positive control) or MDBD, which is composed of extracts of Radix Angelicae sinensis, Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge and Rhizoma chuanxiong. Serum albumin, blood lipids, 24-h urine protein and urine N-acetyl-b-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) were measured every 2 weeks. The ratio of kidney to body weight was measured. The expressions of extracellular matrix proteins in the renal cortex, including colleagen IV (Col-IV) and fibronectin (FN), were examined by immunohistochemistry, and the transcription of genes encoding transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), the tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) were analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) at the end of the 8-week treatment.
Results
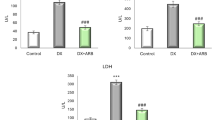
Compared with the untreated rats in the model group, MDBD significantly increased serum albumin, lowered the blood lipids and decreased the ratio of kidney to body weight. MDBD significantly reduced the excretion levels of urinary protein and NAG as well as the accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM), including Col-IV and FN, in the renal cortex. Further, MDBD decreased TIMP-1 and TGF-β1 gene expressions and increased MMP-9 gene expression in the kidney.
Conclusions
MDBD was effective in treating the rat model of nephropathy. The clinical benefit was associated with reduction of renal fibrosis. The antifibrotic effect of MDBD may be mediated through the regulation of TIMP-1, MMP and TGF-β1 gene expressions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabbiani G. The biology of the myofibroblast. Kidney Int 1992;41:530–532.
Muchaneta-Kubara EC, el Nahas AM. Myofibroblast phenotypes expression in experimental renal scarring. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997;12:905–915.
Jerums G, Panagiotopoulos S, Tsalamandris C, Allen TJ, Gilbert RE, Comper WD. Why is proteinuria such an important risk factor for progression in clinical trial? Kidney Int 1997;52:S87–S92.
Rysz J, Pedzik A, Markuszewski L, Kujawski K, Blaszczak R, Olszewski R. The role of metalloproteinases in kidney pathophysiology. Pol Merkur Lekarski (Polish) 2005;19:812–815.
Ahmed AK, Haylor JL, El Nahas AM, Johnson TS. Localization of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in experimental progressive kidney scarring. Kidney Int 2007;71:755–763.
Beaudeux JL, Giral P, Bruckert E, Foglietti MJ, Chapman MJ. Matrix metalloproteinases, inflammation and atherosclerosis: therapeutic perspectives. Clin Chem Lab Med 2004;42:121–131.
Liu S, Li Y, Zhao H, Chen D, Huang Q, Wang S, et al, Huang H. Increase in extracellular cross-linking by tissue transglutaminase and reduction in expression of MMP-9 contribute differentially to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 2006;284:9–17.
Wei MG, Xiong PH, Zhang L, Chen AP. The protective effect of Chinese medicine on IgA nephritis-induced renal tubule lesion. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;47:839–840.
Bertani T, Poggi A, Pozzoni R, Delaini F, Sacchi G, Thoua Y, et al. Adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats: sequence of pathologic events. Lab Invest 1982;46:16–23.
Saad SY, Najjar TA, Al-Rikabi AC. The preventive role of deferoxamine against acute doxorubicin-induced cardiac, renal and hepatic toxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 2001;43:211–218.
Abbate M, Zoja C, Remuzzi G. How does proteinuria cause progressive renal damage? J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:2974–2984.
Dance N, Price RG, Cattell WR, Lansdell J, Richards B. The excretion of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and betagalactosidase by patients with renal disease. Clin Chim Acta 1970;27:87–92.
Oseto S, Moriyama T, Kawada N, Nagatoya K, Takeji M, Ando A, et al. Therapeutic effect of all-transretinoic acid on rats with anti-GBM antibody glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2003;64:1241–1252.
Border WA, Noble NA. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1286–1292.
Varga J, Rosenbloom J, Jimenez SA. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem J 1987;247:597–604.
McAnulty RJ, Campa JS, Cambrey AD, Laurent GJ. The effect of transforming growth factor beta on rates of procollagen synthesis and degradation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1991;1091:231–235.
Van Obberghen-Schilling E, Roche NS, Flanders KC, Sporn MB, Roberts AB. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem 1988;263:7741–7746.
Fu XY, Park WC, Heineche JW. Activation and silencing of matrix metalloproteinases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2008;19:2–13.
Steinmann-Niggli K, Ziswiler R, Küng M, Marti HP. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases attenuates anti-Thyl.1 nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 1998;9:397–407.
McMillan JI, Riordan JW, Couser WG, Pollock AS, Lovett DH. Characterization of glomerular epithelial cell metalloproteinaseas matrix metalloproteinase-9 with chanced expression in a model of membranous nephropathy. J Clin Invest 1996;97:1094–1101.
Wagner J, Dechow C, Morath C, Lehrke I, Amann K, Waldherr R, et al. Retinoic acid reduces glomerular injury in a rat model of glomerular damage. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000;11:1479–1487.
Sun SZ, Wang Y, Li Q, Tian YJ, Liu MH, Yu YH. Effects of benazepril on renal function and kidney expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in diabetic rats. Chin Med J 2006;119:814–821.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Grant from Soochow University Natural Science Foundation of Young Teacher (No. Q3122937) and the Natural Science Foundation of Bureau of Science and Technology of Suzhou (No. SYS201016)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Mg., Sun, W., Xiong, Ph. et al. Antifibrotic effect of the Chinese herbs Modified Danggui Buxue Decoction (加味当归补血汤) on adriamycin-induced nephropathy in rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 591–598 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0816-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0816-x