Abstract
Objective
To explore the molecular mechanism of realgar-induced apoptosis of cervical cancer cells.
Methods
The cervical cancer cell line Siha was used to determine the cell viability and apoptosis after treatment with realgar using MTT assay and flow cytometry. The activities of caspase-3, -8, and -9 were detected by fluorescence resonance energy transfer technology and colorimetric assay, while the levels of Bcl-2, cytochrome c, and Bax were detected by Western blot method.
Results
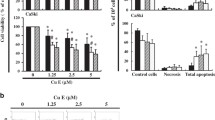
Induction of apoptosis by realgar was detected in Siha cell line in a dose-dependent manner. The apoptosis was accompanied by a significant increase in cytochrome c release and activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 but not caspase-8. Further, the realgar-induced apoptosis was inhibited by a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor, a caspase-3 inhibitor, and a caspase-9 inhibitor but not by a caspase-8 inhibitor. Bcl-2 and Bax protein expressions were not changed by realgar.
Conclusion
The induction of apoptosis by realgar is mediated through a cytochrome c-dependent pathway, which sequentially activates caspase-9 and caspase-3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye HQ, Gan L, Yang XL, Xu HB. Membrane toxicity accounts for apoptosis induced by realgar nanoparticles in promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 2005;103:117–132.
Leu L, Mohassel L. Arsenic trioxide as first-line treatment for acute promyelocytic leukemia. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2009;66:1913–1918.
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y, Yan XJ, et al. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:4826–4831.
Roboz GJ. Arsenic and old lace: novel approaches in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol 2008;45:S22–S24.
Moghimi S M, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. J FASEB J 2005;19:311–330.
Luo KQ, Yu VC, Pu Y, Chang DC. Application of the fluorescence resonance energy transfer method for studying thedynamics of caspase-3 activation during UVinduced apoptosis in living HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001;283:1054–1060.
Lin J, Zhang Z, Yang J, Zeng S, Liu B F, Luo Q. Real-time detection of caspase-2 activation in a single living HeLa cell during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biomed Opt 2006;11:024011.
Dörrie J, Gerauer H, Wachter Y, Zunino SJ. Resveratrol induces extensive apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membranes and activating caspase-9 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Res 2001;61:4731–4739.
Liu XS, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang XD. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cyt c. Cell 1996;86:147–157.
Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998;281:1309–1312.
Miller WH. Molecular target of arsenic trioxide in malignant cells. Oncologist 2002;7:14–19.
Siu KP, Chan JY, Fung KP. Effect of arsenic trioxide on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells: inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Life Sci 2002;71:275–285.
Chou RH, Huang H. Restoration of p53 tumor suppressor pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells by sodium arsenite. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;293:298–306.
Helen MP, Alexander P, Matilda MP, Jenny K, Leif J, Maria C, et al. Arsenic trioxide is highly cytotoxic to small cell lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8:160–170.
Zhu J, Okumura H, Ohtake S, Nakamura S, Nakao S. Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in leukemia/lymphoma cell lines via the CD95/CD95L system. Oncol Rep 2003;10:705–709.
Zhu J, Okumura H, Ohtake S, Nakamura S, Nakao S. The molecular mechanism of arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and oncosis in leukemia/lymphoma cell lines. Acta Haematol 2003;110:1–10.
Nakagawa Y, Akao Y, Morikawa H, Hirata I, Katsu K, Naoe T, et al. Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis through oxidative stress in cells of colon cancer cell lines. Life Sci 2002;70:2253–2269.
Lu M, Levin J, Sulpice E, Sequeira-Le GA, Alemany M, Caen JP, et al. Effect of arsenic trioxide on viability, proliferation and apoptosis in human megakaryocytic leukemia cell lines. Exp Hematol 1999;27:845–852.
Du YH, Ho PC. Arsenic compounds induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in cisplatin-sensitive and-resistant gynecological cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2001;47:481–490.
Cai X, Yu Y, Huang Y, Zhang L, Jia P M, Zhao Q, et al. Arsenic trioxide-induced mitotic arrest and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2003;17:1333–1337.
Hyun PW, Hee CY, Won J C, Oh PJ, Kim K, Hyuck IY, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of A498 renal cell carcinoma cells via cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003;300:230–235.
Larochette N, Decaudin D, Jacotot E, Brenner C, Marzo I, Susin S A, et al. Arsenite induces apoptosis via a direct effect on the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Exp Cell Res 1999;249:413–421.
Porter AG, Jänicke RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 1999;6:99–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Yx., Liu, R., Wang, Q. et al. Realgar-induced apoptosis of cervical cancer cell line Siha via cytochrome c release and caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 359–365 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0697-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0697-z