Abstract
The Neo-Archean Sonakhan Greenstone Belt (SGB) located in the north-eastern fringes of Bastar craton, Central India, is dominated by Basalts, Andesites, Dacites and Rhyolites association. Partial melting modeling on the SGB metabasalts indicates that these rocks were derived by 20% melting of spinel peridotite. Fractional crystallisation modeling with REE reveal that the most evolved samples represent the product of fractional crystallization of least evolved magma with 35% plagioclase, 35% clinopyroxene, 20% olivine, 5% magnetite and 5% ilmenite as fractionating minerals with 40% remaining magma. Depletion of HFSE with reference to the LILE and LREE/HFSE ratios and Nb, Zr anomalies in the multi-element diagram of the mafic rocks of SGB indicate Island arc magmatic setting. The enriched Th/Yb values further substantiate that the mantle arrays were modified by subduction-related fluids or melts. The general conclusions drawn indicate that the metabasalts from the SGB were formed as a result of subduction of an intraoceanic lithosphere in a fore-arc suprasubduction zone environment.

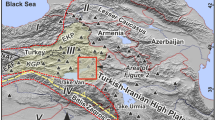
(after Das et al. 1990)


(Pearce 2008)

(Normalizing factors are from Boynton 1984)

(Normalizing factors are from McDonough and Sun 1995)


(Jung et al. 2006)







(Condie 1989)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allegre CJ, Minster JF (1978) Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38(1):1–25
Anderson RN, Stephen ED, Schwarz WM (1980) Dehydration, asthenospheric convection and seismicity in subduction zones. J Geol 88:445–451
Arndt NT (1994) Archean komatiites. Dev Precambrian Geol 11:11–44
Arndt NT, Goldstein SL (1989) An open boundary between lower continental crust and mantle: its role in crust formation and crustal recycling. Tectonophysics 161(3):201–212
Arth JG, Hanson GN (1975) Geochemistry and origin of the early Precambrian crust of northeastern Minnesota. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 39(3):325–362
Baker JA, Menzies MA, Thirlwall MF, MacPherso CG (1997) Petrogenesis of Quaternary intraplate volcanism, Sana’a, Yemen: implications for plume–lithosphere interaction and polybaric melt hybridization. J Petrol 38(10):1359–1390
Balasubramanyan MN (2006) Geology and tectonics of India: an overview. International Association of Gondwana Research, Kochi, Japan, p 206
Boynton WV (1984) Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements; meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed) Rare earth element geochemistry. Elsevier Sci. Publ. Co., Amsterdam, pp 63–114
Condie KC (1989) Geochemical changes in basalts and andesites across the Archean Proterozoic boundary: identification and significance. Lithos 23:1–18
Condie KC, Harrison NM (1976) Geochemistry of the archean Bulawayan group, Midlands Greenstone Belt, Rhodesia. Precambrian Res 3(3):253–271
Das N, Royburman K, Vatsa US, Mahurkar VY (1990) Sonakhan Schist Belt, a Precambrian granite—greenstone complex. Geol Surv India Spec Publ 28:118–132
Deshmukh SD, Hari KR, Diwan P (2006) Pillow Lavas of Baghmara Formation (Sonakhan Greenstone Belt), Central India: geochemical constraints from major elements. Gond Geol Mag 21(1):37–42
Deshmukh SD, Hari KR, Diwan P, Basavarajappa HT (2008) Spinifex textured metabasalt from Sonakhan Greenstone Belt, Central India. Indian Miner 42:71–83
Deshmukh SD, Hari KR, Diwan P, Manu Prasanth MP (2017) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of felsic meta-volcanic rocks of Baghmara Formation, Sonakhan Greenstone Belt, Central India. J Geosci Res 2(1):69–74
Floyd PA, Winchester JA (1975) Magma type and tectonic setting discrimination using immobile elements. Earth Planet Sci Lett 27:211–218
Foley S, Tiepolo M, Vannucci R (2002) Growth and early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones. Nature 417:837–840
Furnes H, De Wit M, Dilek Y (2014) Four billion years of ophiolites reveal secular trends in oceanic crust formation. Geosci Front 5(4):571–603
Furnes H, Dilek Y, De Wit M (2015) Precambrian greenstone sequences represent different ophiolite types. Gondwana Res 27(2):649–685
Ghosh S, Rajajaiya V, Ashiya ID (1995) Rb-Sr dating of components from the Sonakhan Granite-Greenstonebelt, Raipur District. MP Rec Geolo Surv India 128:11–13
Hawkesworth CJ, Gallagher K, Hergt JM (1993) Mantle and slab contributions in arc magmas. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 21:175–204
Hawkesworth CJ, Dhuime B, Pietranik AB, Cawood PA, Kemp AI, Storey CD (2010) The generation and evolution of the continental crust. J Geol Soc 167:229–248
Jung C, Jung S, Hoffer E, Berndt J (2006) Petrogenesis of Tertiary mafic alkaline magmas in the Hocheifel, Germany. J Petrol 47(8):1637–1671
Keleman PB, Hanghoj K, Greene AR (2004) One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust. In: Holland HD, Turekian KK (eds) Treatise on geochemistry 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 593–659
Kerrich R, Wyman DA, Fan J, Bleeker W (1998) Boninite series: low Ti-tholeiite associations from the 2.7 Ga Abitibi Greenstone Belt. Earth Planet Sci Lett 164:303–316
Kröner A, Hoffmann JE, Xie H, Wu F, Münker C, Hegner E, Wong J, Wan Y, Liu D (2013) Generation of early Archaean felsic greenstone volcanic rocks through crustal melting in the Kaapvaal craton, southern Africa. Earth Planet Sci Lett 381:188–197
Lafleche MR, Dupuy C, Dostal J (1992) Tholeiitic volcanic rocks of the late Archaean Blake River group, southern Abitibi Greenstone Belt: origin and geodynamic implications. Can J Earth Sci 29:1448–1458
Le Bas MJ, Streckeisen AL (1991) The IUGS systematics of igneous rocks. J Geol Soc Lond 148:825–833
Le Bas MJ, Lemaitre RW, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B (1986) A chemical classification of volcanic-rocks based on the total alkali silica diagram. J Petrol 27(3):745–750
Ludden J, Gélinas L, Trudel P (1982) Archean metavolcanics from the Rouyn-Noranda district, Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Quebec. 2. Mobility of trace elements and petrogenetic constraints. Can J Earth Sci 19(12):2276–2287
MacGeehan PJ, MacLean WH (1980) An Archaean sub-seafloor geothermal system, calc-alkali’trends, and massive sulphide genesis. Nature 286:767–771
Manning CE (2004) The chemistry of subduction-zone fluids. Earth Planet Sci Lett 223:1–16
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) Composition of the earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
Metcalf RV, Shervais JW (2008) Suprasubduction-zone ophiolites: Is there really an ophiolite conundrum? Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 438:191–222
Mibe K, Kawamoto T, Matsugake KN, Fei Y, Ono S (2011) Slab melting versus slab dehydration in subduction-zone magmatism. PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010968108/-/DCSupplemental
Morris JD, Leeman WP, Tera F (1990) The subducted component in island arc lavas: constraints from Be isotopes and B-Be systematics. Nature 344:31–36
Mottl MJ (1983) Metabasalts, axial hot springs, and the structure of hydrothermal systems at mid-ocean ridges. Geol Soc Am Bull 94(2):161–180
Naqvi SM (2005) Geology and evolution of the Indian plate. Capital Publishing, New Delhi, p 450
Naqvi SM, Rogers JJW (1987) Precambrian geology of India. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 223
Pearce JA (1982) Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries. In: Thorpe RS (ed) Andesites. Wiley, Chidester, pp 525–548
Pearce JA (2008) Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos 100:14–48
Pearce JA (2014) Immobile element fingerprinting of ophiolites. Elements 10(2):101–108
Pearce JA, Peate DW (1995) Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas. Annu Revi Earth Planet Sci 23:251–285
Pearce JA, Stern RJ (2006) Origin of back-arc basin magmas: trace element and isotope perspectives. Back-arc spreading systems: geological, biological, chemical and physical interactions. Geophys Monogr Ser 166:66–86
Perfit MR, Gust DA, Bence AE, Arculus RJ, Taylor SR (1980) Chemical characteristics of island-arc basalts: implications for mantle sources. Chem Geol 30(3):227–256
Polat A (2013) Geochemical variations in Archean volcanic rocks, southwestern Greenland: traces of diverse tectonic settings in the early Earth. Geology 41(3):379–380
Polat A, Hofmann AW, Rosing Minik Thorleif (2002) Boninite-like volcanic rocks in the 3.7–3.8 Ga Isua Greenstone Belt, West Greenland: geochemical evidence for intra-oceanic subduction zone processes in the early Earth. Chem Geol 184(3):231–254
Radhakrishna BP (1976) Two greenstone groups in Dharwar Craton. Ind Miner 16:12–15
Radhakrishna BP, Ramakrishnan M (1988) Archaean-Proterozoic boundary in India. J Geol Soc Ind 32:263–278
Radhakrishna BP, Ramakrishnan M (eds) (1990) Archaean Greenstone Belts of South India. Geological Society of India, Mem. 19:497
Rajamani V, Shivkumar K, Hanson GN, Shirey AS (1985) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of amphibolites, Kolar Schist Belt, South India: evidence for komatiitic magma derived by low percentages of melting of the mantle. J Petrol 26(1):92–123
Ramakrishnan M, Vaidyanadhan R (2008) Geology of India, vol 1. Geological Society of India, p 994
Ramchandra HM, Roy A, Mishra VP, Dutta NK (2001) A critical review of the tectonothermal evolution of the Bastar Craton. MS Krishnan Cent Comm Nat Sem Geol Surv Ind Spec Publ 55:161–180
Rapp R, Shimizu N, Norman MD (2003) Growth of early continental crust by partial melting of eclogite. Nature 425:605–609
Ray RK, Rai KL (2004) Geological setting and petrogenesis of the auriferous metavolcanic complex of Sonakhan, Raipur district, Chhattisgarh. SAAEG J Ecol Geol 1:45–60
Ray RK, Pandey HK, Rai KL (2000) Geochemistry of Mafic volcanics associated with sulphide mineralization in Sonakhan, Raipur district, Madhya Pradesh. In: Gyani KC, Kataria P (eds) Proc nat Sem on ‘Tectonomagmatism, Geochemistry and Metamorphism of Precambrian terrain.’ Univ Dept of Geology Udaipur, pp 381–393
Rogers JJW, Santosh M (2003) Supercontinents in earth history. Gondwana Res 6:357–368
Rollinson HR (1993) A terrane interpretation of the Archaean Limpopo Belt. Geol Mag 130(06):755–765
Rollinson H (1999) Petrology and geochemistry of metamorphosed komatiites and basalts from the Sula Mountains Greenstone Belt, Sierra Leone. Contrib Miner Petrol 134(1):86–101
Sajona FG, Maury RC, Bellon H, Cotten J, Defant M (1996) High field strength element enrichment of Pliocene—Pleistocene Island Arc Basalts, Zamboanga Peninsula, Western Mindanao (Philippines). J Petrol 37(3):693–726
Shervais JW (1982) Ti–V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 32:114–120
Tatsumi Y, Hamilton DL, Nesbitt RW (1986) Chemical characteristics of fluid phase from the subducted lithosphere: evidence from high-pressure experiments and natural rocks. J Volcanol Geother Res 29:293–309
Venkatesh AS (2001) Geochemical signatures and auriferous implications in Sonakhan Greenstone Belt, Chhattisgarh. Geol Surv India Spec Publ 55:219–228
Wilson M (1989) Igneous petrogenesis: a global tectonic approach. Unwyn Hyman, London
Wilson M, Davidson JP (1984) The relative roles of crust and upper mantle in the generation of oceanic island-arc magmas. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 310:661–674
Wyman DA (2003) Upper mantle processes beneath the 2.7 Ga Abitibi belt, Canada: a trace element perspective. Precambrian Res 127:143–165
Wyman DA, Kerrich R (2009) Plume and arc magmatism in the Abitibi subprovince: implications for the origin of Archean continental lithospheric mantle. Precambrian Res 168:4–22
Xiao WJ, Santosh M (2014) The western Central Asian Orogenic Belt: a window to accretionary orogenesis and continental growth. Gond Res 25:1429–1444. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.01.008
Xie Q, Kerrich R, Fan J (1993) HFSE/REE fractionations recorded in three komatiite-basalt sequences, Archean Abitibi Greenstone Belt: implications for multiple plume sources and depths. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57(16):4111–4118
Yedekar DB, Jain SC, Nair KKK, Dutta KK (1990) Central Indian collision suture. Geol Surv Ind Spec Publ 29:1–43
Yedekar DB, Karmalkar N, Pawar NJ, Jain SC (2003) Tectonomagmatic evolution of central Indian terrain. Gond Geol Mag Spec 7:67–68
Zhai MG (2014) Multi-stage crustal growth and cratonization of the North China Craton. Geosci Front. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2014.01.003
Acknowledgements
SDD expresses his sincere thanks to Dr. S. K. Rajput, Principal, Govt. V.Y.T.PG Autonomous College, Durg. The authors are also thankful to Dr. Sandeep Vansutre and Dr. Shailesh Agrawal for their help in the preparation of the manuscript. Financial support from UGC to S.D. Deshmukh is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshmukh, S.D., Hari, K.R., Diwan, P. et al. Geochemical constraints on the tectonic setting of the Sonakhan Greenstone Belt, Bastar Craton, Central India. Acta Geochim 37, 489–499 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0213-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-017-0213-z